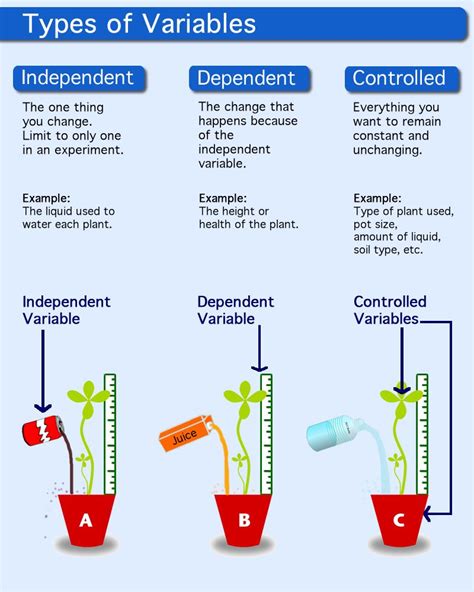
The concept of an independent variable is a cornerstone in research, experiments, and data analysis. It refers to the variable that is being manipulated or changed by the researcher to observe its effect on the dependent variable. Understanding and defining the independent variable is crucial for the validity and reliability of any study. In this article, we will delve into the definition and examples of independent variables, exploring how they are used in different fields and their significance in research methodology.
Key Points
- The independent variable is the factor that the researcher manipulates or changes in an experiment to observe its effect.
- It is a crucial component of the scientific method, allowing researchers to test hypotheses and draw conclusions.
- Independent variables can be quantitative or qualitative, depending on the nature of the study.
- Examples of independent variables include the amount of fertilizer used in a plant growth experiment, the dosage of a medication in a clinical trial, and the level of noise in a study on its effects on cognitive performance.
- Defining the independent variable correctly is essential for the internal validity of a study, ensuring that the observed effects are due to the manipulation of the independent variable and not other factors.
Definition and Role of Independent Variable
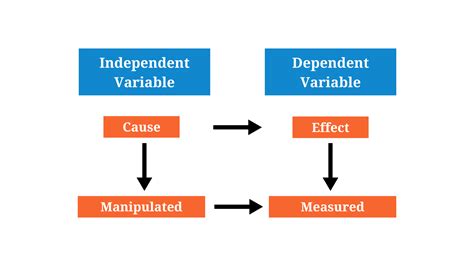
An independent variable, also known as a predictor variable, is a variable that is changed or controlled in a scientific experiment to test the effects on the dependent variable. It is the cause or the input in a cause-and-effect relationship, where the dependent variable is the effect or the output. The independent variable is crucial because it allows researchers to establish causality between variables, which is a fundamental principle of the scientific method.
Types of Independent Variables
Independent variables can be categorized based on their nature and the type of study being conducted. They can be quantitative, involving numerical data, or qualitative, involving non-numerical data such as categories or descriptions. In experiments, independent variables are often manipulated at different levels to observe their impact on the dependent variable. For example, in a study examining the effect of exercise on weight loss, the independent variable could be the intensity of the exercise (low, medium, high), and the dependent variable could be the amount of weight lost over a certain period.
| Type of Independent Variable | Example |
|---|---|
| Quantitative | Dosage of medication, amount of fertilizer |
| Qualitative | Type of music, level of education |
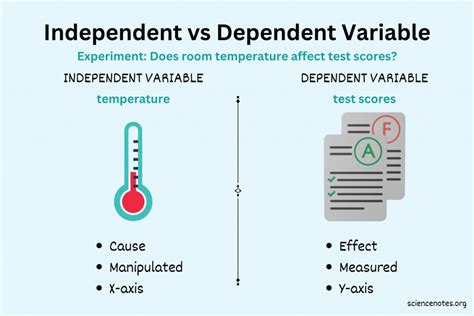
Examples and Applications

Independent variables are applied across various disciplines, including psychology, biology, economics, and sociology. In psychology, an independent variable might be the type of therapy used to treat a disorder, with the dependent variable being the reduction in symptoms. In economics, the independent variable could be the interest rate, and the dependent variable could be the level of investment. Understanding and manipulating the independent variable is key to drawing meaningful conclusions and making informed decisions in these fields.
Challenges and Considerations
One of the challenges in defining and working with independent variables is ensuring that they are isolated from confounding variables, which are factors other than the independent variable that could affect the dependent variable. Controlling for these variables is essential to establish a clear cause-and-effect relationship. Additionally, the ethical implications of manipulating independent variables, especially in experiments involving human subjects, must be carefully considered to ensure that the research is conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
In conclusion, the independent variable is a fundamental concept in research and experimentation, allowing scientists to explore relationships between variables and draw conclusions about causality. By understanding how to define, manipulate, and analyze independent variables, researchers can contribute valuable insights to their fields, ultimately advancing knowledge and informing practice.
What is the primary role of an independent variable in a research study?
+The primary role of an independent variable is to be manipulated by the researcher to observe its effect on the dependent variable, allowing for the testing of hypotheses and the establishment of causality.
How do researchers ensure the validity of their findings when working with independent variables?
+Researchers ensure the validity of their findings by controlling for confounding variables, using appropriate sampling methods, and ensuring that the manipulation of the independent variable is the sole cause of the observed effects on the dependent variable.
What are some common challenges faced by researchers when defining and working with independent variables?
+Common challenges include isolating the independent variable from confounding variables, ensuring ethical considerations are met, especially in experiments involving human subjects, and accurately measuring the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable.