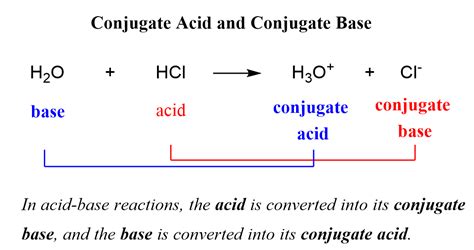
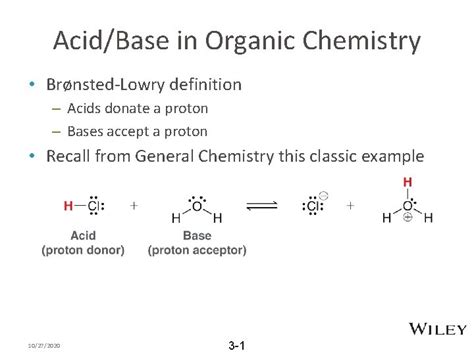
The concept of a conjugate base is fundamental in chemistry, particularly in the realm of acid-base chemistry. A conjugate base, by definition, is the species that results when an acid donates a proton (H+ ion). This process is a crucial aspect of Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory, which describes acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. Understanding conjugate bases is essential for grasping various chemical reactions and processes, including those in biochemistry, environmental science, and industrial chemistry.
Key Points
- The conjugate base of an acid is formed by the removal of a proton (H+ ion) from the acid.
- Conjugate bases are typically weaker bases than the original base from which the acid was derived.
- The strength of a conjugate base is inversely related to the strength of its corresponding acid; the stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base.
- Conjugate bases play a critical role in acid-base reactions, influencing the pH of solutions and the chemical properties of substances.
- Understanding conjugate bases is vital for predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions and for designing processes in various industrial and biological applications.
Understanding Conjugate Bases in Acid-Base Chemistry
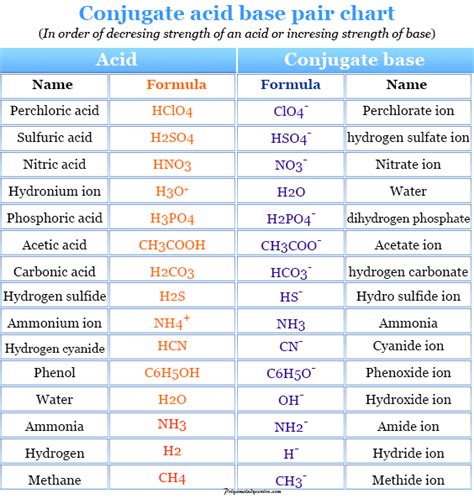
In the context of acid-base chemistry, every acid has a corresponding conjugate base, and every base has a corresponding conjugate acid. This relationship is central to the concept of acid-base equilibria, where the equilibrium constant (Ka for acids and Kb for bases) reflects the relative strengths of the acid and its conjugate base or the base and its conjugate acid. For instance, when hydrochloric acid (HCl), a strong acid, donates a proton, it forms chloride ion (Cl-), which is its conjugate base.
Conjugate Base Strength and Acid Strength Relationship
The strength of an acid and the strength of its conjugate base are inversely related. Strong acids, which completely dissociate in water, have weak conjugate bases. Conversely, weak acids have stronger conjugate bases because the equilibrium between the acid and its conjugate base lies further to the left, indicating that the acid does not readily donate its proton, and thus its conjugate base is more likely to accept a proton. This principle is crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of acids and bases in various chemical environments.
| Acid | Conjugate Base | Acid Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | Chloride Ion (Cl-) | Strong |
| Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) | Aceate Ion (CH3COO-) | Weak |
| Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) | Hydrogen Sulfate Ion (HSO4-) | Strong |
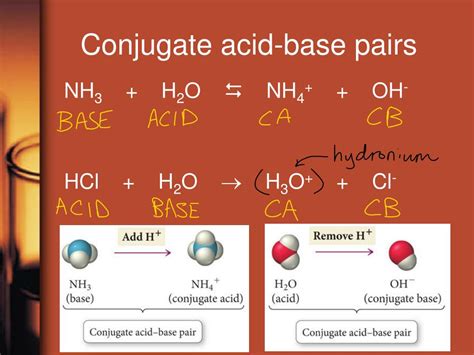
Applications of Conjugate Bases in Chemistry and Biology
Conjugate bases play significant roles in various biological and chemical processes. In biochemistry, the protonation state of molecules can affect their activity and interaction with other biomolecules. For example, enzymes often rely on the protonation state of their active site residues to facilitate catalysis. In environmental science, the acid-base properties of substances, including their conjugate bases, influence their mobility, bioavailability, and toxicity in ecosystems.
Practical Considerations and Chemical Reactions
In practical terms, understanding conjugate bases is essential for designing and optimizing chemical reactions. The choice of solvent, reaction conditions, and reagents can significantly impact the outcome of a reaction, partly due to the influence of conjugate bases. For instance, in organic synthesis, the selection of a base (and thus its conjugate acid) can determine the feasibility and yield of a reaction.
In conclusion, conjugate bases are a fundamental aspect of acid-base chemistry, with their properties and behaviors influencing a wide range of chemical and biological processes. By understanding the concept of conjugate bases and their relationship to acids, chemists and biologists can better predict and manipulate the outcomes of reactions, contributing to advancements in fields from pharmaceuticals to environmental remediation.
What is the relationship between an acid and its conjugate base?
+An acid and its conjugate base are related in that the conjugate base is what remains after the acid donates a proton (H+ ion). The strength of the acid is inversely related to the strength of its conjugate base.
How do conjugate bases influence chemical reactions?
+Conjugate bases can influence chemical reactions by acting as bases themselves, accepting protons and thereby affecting the pH and the course of the reaction. Their strength and concentration can determine the feasibility and yield of a reaction.
What role do conjugate bases play in biological systems?
+In biological systems, conjugate bases can play critical roles in enzyme catalysis, protein function, and the transport of substances across cell membranes. The protonation state of biomolecules, influenced by their conjugate bases, can affect their activity and interactions.