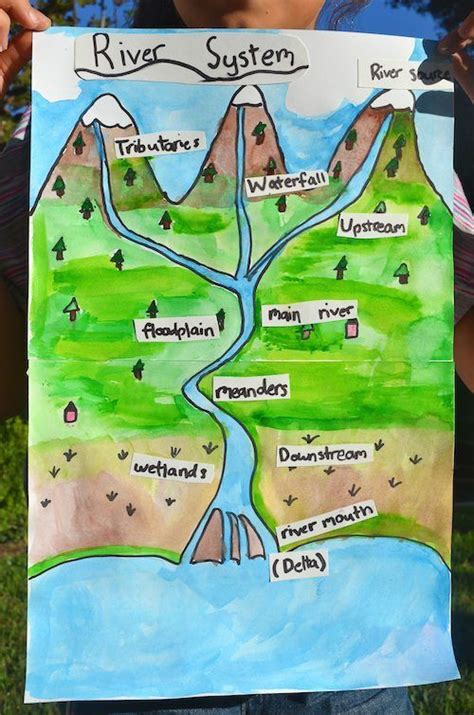
The term "delta" in geography refers to a landform that forms at the mouth of a river, where the river deposits sediment as it flows into a slower-moving body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. Deltas are characterized by a network of distributaries, which are smaller channels that branch off from the main river and carry sediment and water into the surrounding area. Over time, the sediment deposited by the river can build up and create a unique landscape of sandy or muddy islands, marshes, and wetlands.
Deltas are important ecosystems that provide habitat for a wide variety of plants and animals, and they also play a critical role in filtering and purifying water. However, deltas are also vulnerable to environmental changes, such as sea level rise, storms, and human activities like deforestation and pollution. As a result, many deltas around the world are facing significant challenges and are in need of conservation and management efforts to protect these valuable ecosystems.
Key Points
- A delta is a landform that forms at the mouth of a river, where sediment is deposited as the river flows into a slower-moving body of water.
- Deltas are characterized by a network of distributaries, which carry sediment and water into the surrounding area.
- Deltas are important ecosystems that provide habitat for a wide variety of plants and animals.
- Deltas are vulnerable to environmental changes, such as sea level rise, storms, and human activities like deforestation and pollution.
- Conservation and management efforts are needed to protect deltas and the valuable ecosystems they support.
Formation of Deltas
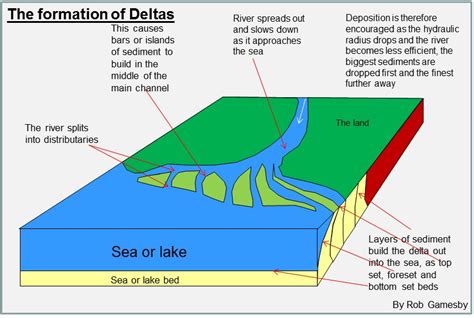
The formation of a delta is a complex process that involves the interaction of several geological and hydrological factors. When a river flows into a slower-moving body of water, it slows down and loses energy, causing it to deposit the sediment it is carrying. Over time, this sediment can build up and create a deltaic landscape. The shape and size of a delta can vary depending on factors such as the amount of sediment carried by the river, the velocity of the river, and the slope of the surrounding land.
Types of Deltas
There are several types of deltas, each with its own unique characteristics. Some common types of deltas include:
- Arcuate deltas: These deltas have a curved or arc-shaped shape, and are often found in areas where the river flows into a body of water with a strong current.
- Bird’s foot deltas: These deltas have a distinctive shape, with a main channel that splits into several smaller distributaries that resemble a bird’s foot.
- Cuspate deltas: These deltas have a pointed or cusp-shaped shape, and are often found in areas where the river flows into a body of water with a gentle slope.
| Type of Delta | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Arcuate delta | Curved or arc-shaped, often found in areas with strong currents |
| Bird's foot delta | Main channel splits into smaller distributaries, resembling a bird's foot |
| Cuspate delta | Pointed or cusp-shaped, often found in areas with gentle slopes |
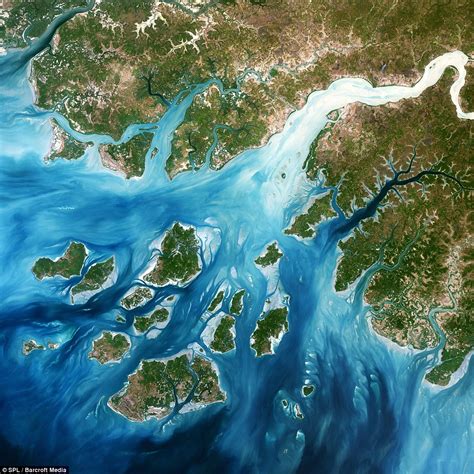

Importance of Deltas
Deltas are important ecosystems that provide a wide range of benefits to both humans and the environment. Some of the key benefits of deltas include:
- Habitat for wildlife: Deltas provide habitat for a wide variety of plants and animals, including many species that are found nowhere else.
- Water filtration: Deltas help to filter and purify water, which is important for both human consumption and ecosystem health.
- Shoreline protection: Deltas can help to protect shorelines from erosion and storm damage, which is important for both human safety and economic development.
Challenges Facing Deltas
Despite their importance, deltas are facing a range of challenges that threaten their health and sustainability. Some of the key challenges facing deltas include:
- Sea level rise: Rising sea levels are causing erosion and flooding in many deltas, which can lead to loss of habitat and displacement of human communities.
- Storms and extreme weather: Deltas are often vulnerable to storms and extreme weather events, which can cause damage to infrastructure and ecosystems.
- Human activities: Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing can harm delta ecosystems and reduce their ability to provide benefits to humans and the environment.
What is a delta in geography?
+A delta is a landform that forms at the mouth of a river, where sediment is deposited as the river flows into a slower-moving body of water.
What are the different types of deltas?
+There are several types of deltas, including arcuate, bird’s foot, and cuspate deltas, each with its own unique characteristics.
Why are deltas important ecosystems?
+Deltas provide habitat for a wide variety of plants and animals, help to filter and purify water, and protect shorelines from erosion and storm damage.