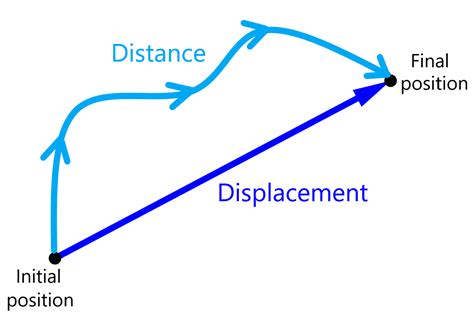
The concept of displacement is a fundamental principle in physics and engineering, describing the process by which an object moves from one position to another, often resulting in the replacement of a surrounding fluid, such as air or water. Displacement can occur in various forms and is crucial in understanding numerous natural and man-made phenomena. In this article, we will delve into the workings of displacement, exploring five distinct ways it manifests and its implications in different fields.
Key Points
- Displacement in fluids, such as water and air, is a critical concept in understanding buoyancy and floating objects.
- The principle of displacement is essential in the design and operation of ships and submarines.
- Soil displacement is a key consideration in construction and geotechnical engineering.
- Displacement in solids, like metals, is relevant to materials science and mechanical engineering.
- Psychological displacement refers to the redirection of emotions or behaviors and is a concept within psychology.
Fluid Displacement
One of the most intuitive forms of displacement is observed in fluids. When an object is partially or fully submerged in a fluid (like water or air), it displaces a volume of fluid equal to the volume of the object that is submerged. This principle, known as Archimedes’ Principle, states that the buoyancy force (or upward force) exerted on a body immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid the body displaces. For example, a ship displaces a large volume of water, which results in an upward buoyant force that keeps the ship afloat. Understanding fluid displacement is crucial for designing and operating vessels, as well as predicting the behavior of objects in various fluid environments.
Applications of Fluid Displacement
The application of fluid displacement is not limited to naval architecture. It is also critical in the design of offshore platforms, where the stability and buoyancy of the structure must be carefully calculated to withstand harsh marine conditions. Furthermore, fluid displacement plays a significant role in the field of aerospace engineering, particularly in the design of aircraft and spacecraft, where the interaction between the vehicle and the surrounding air or vacuum is of paramount importance.
| Type of Fluid | Example of Displacement |
|---|---|
| Water | Ship floating on the ocean |
| Air | Airplane flying through the atmosphere |
| Liquid Metals | Molten metal flowing through a pipe |

Soil Displacement
Soil displacement refers to the movement or removal of soil from one location to another, often as a result of construction, excavation, or natural processes like erosion. Understanding soil displacement is crucial in geotechnical engineering, as it affects the stability and structural integrity of buildings, tunnels, and other underground constructions. The properties of the soil, such as its density, cohesion, and friction angle, play a significant role in determining the extent and impact of soil displacement.
Factors Influencing Soil Displacement
Several factors influence soil displacement, including the type of soil, the presence of groundwater, and the method of excavation or construction. For instance, soils with high clay content are more susceptible to displacement due to their lower permeability and higher cohesion, which can lead to significant changes in soil volume during excavation or loading. On the other hand, sandy soils are more prone to erosion due to their higher permeability and lower cohesion.
Displacement in Solids
Displacement in solids, particularly in metals, is an important concept in materials science and mechanical engineering. When a solid object is subjected to an external force, it can undergo deformation, which involves a change in shape or volume. The displacement of atoms or molecules within the solid can lead to the formation of defects, such as dislocations or vacancies, which can significantly affect the material’s properties, including its strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity.
Implications of Displacement in Solids
The understanding of displacement in solids has numerous implications in the development of new materials and technologies. For example, the study of plastic deformation in metals is crucial for understanding the forming and shaping processes in manufacturing. Moreover, the knowledge of displacement in solids is essential for predicting the behavior of materials under various loading conditions, such as tension, compression, and shear, which is critical in the design of structural components and mechanical systems.
Psychological Displacement
Psychological displacement refers to the process by which an individual redirects their emotions, feelings, or behaviors from an original source to a more acceptable or less threatening target. This concept is rooted in psychoanalytic theory and is often observed in situations where an individual is unable to express their true feelings directly, leading to a displacement of these emotions onto another person, object, or activity. Understanding psychological displacement is important in clinical psychology and psychotherapy, as it can help in diagnosing and treating various mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and personality disorders.
Cases of Psychological Displacement
Psychological displacement can manifest in various ways, including the redirection of anger, fear, or love towards a substitute object or person. For instance, an individual who is angry with their boss may displace this anger onto a family member or a pet, leading to inappropriate or harmful behavior. Recognizing and addressing psychological displacement is essential for promoting mental health and well-being, as well as improving interpersonal relationships and social functioning.
What is the principle of displacement in physics?
+The principle of displacement states that the volume of fluid displaced by an object is equal to the volume of the object that is submerged in the fluid.
How does soil displacement affect construction projects?
+Soil displacement can affect the stability and structural integrity of buildings and underground constructions, requiring careful consideration in geotechnical engineering and construction planning.
What are the implications of displacement in solids for materials science?
+Understanding displacement in solids is crucial for predicting the behavior of materials under various loading conditions and for developing new materials with specific properties, such as strength, ductility, and electrical conductivity.
In conclusion, displacement is a multifaceted concept that manifests in various forms and fields, from the physical displacement of objects in fluids and solids to the psychological displacement of emotions and behaviors. Understanding these different aspects of displacement is essential for advancing knowledge in physics, engineering, materials science, and psychology, and for addressing the complex challenges and opportunities that arise in these fields.