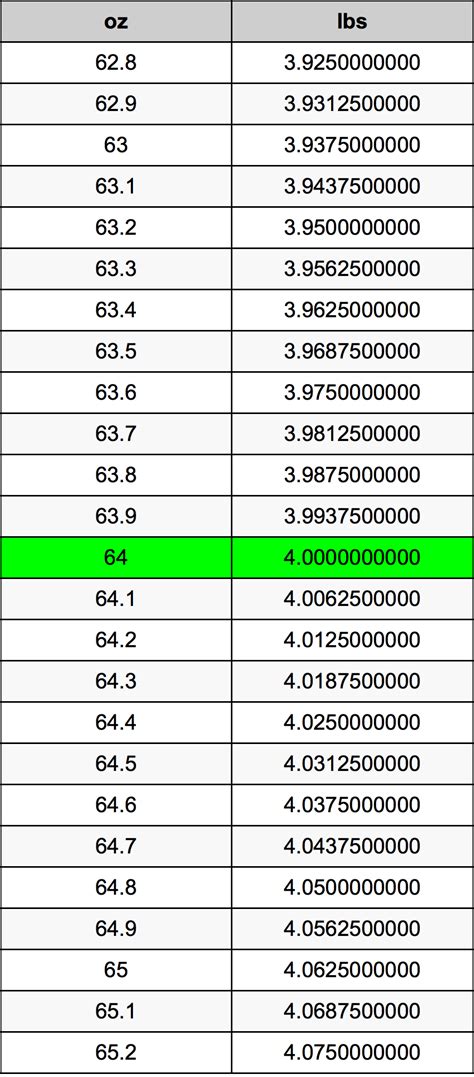
Dust, a ubiquitous substance found in every corner of our lives, is often overlooked despite its omnipresence. However, understanding what dust is made of can provide valuable insights into its impact on our health, environment, and daily activities. Dust is a complex mixture of various particles, and its composition can vary significantly depending on the location, climate, and human activities in the surrounding area.
Research has shown that dust is primarily composed of inorganic particles, such as soil, minerals, and metals, which can originate from natural sources like erosion, weathering of rocks, and volcanic eruptions. These particles can be further broken down into smaller fragments, such as silica, calcium carbonate, and iron oxide, which are commonly found in dust samples. Additionally, organic particles like pollen, mold spores, and insect fragments can also be present, contributing to the complexity of dust composition.
Key Points
- Dust is a complex mixture of inorganic and organic particles
- Inorganic particles, such as soil and minerals, are the primary components of dust
- Organic particles, like pollen and mold spores, can also be present in dust
- Dust composition can vary significantly depending on location and climate
- Understanding dust composition is crucial for mitigating its impact on human health and the environment
Natural Sources of Dust
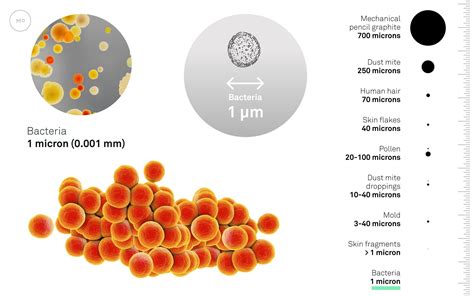
Natural sources of dust are numerous and diverse, including soil erosion, rock weathering, and volcanic eruptions. These processes can release massive amounts of particles into the air, which can then settle and become part of the dust that surrounds us. For example, a study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research found that soil erosion alone can contribute up to 20% of the total dust particles in the atmosphere.
Human Activities and Dust Generation
Human activities, such as construction, mining, and agriculture, can also generate significant amounts of dust. The use of heavy machinery, vehicles, and other equipment can stir up particles, releasing them into the air and contributing to the dust that accumulates in our surroundings. Furthermore, indoor activities, like cleaning and renovation, can also generate dust, which can then become airborne and pose health risks.
| Source | Contribution to Dust (%) |
|---|---|
| Soil erosion | 20% |
| Rock weathering | 15% |
| Volcanic eruptions | 10% |
| Human activities (construction, mining, agriculture) | 30% |
| Indoor activities (cleaning, renovation) | 25% |
Health Impacts of Dust
The health impacts of dust can be substantial, particularly for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Exposure to dust can exacerbate symptoms, reduce lung function, and even trigger acute respiratory episodes. Moreover, long-term exposure to dust has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Environmental Impacts of Dust
The environmental impacts of dust are equally significant, with dust particles contributing to climate change, soil degradation, and water pollution. Dust can also affect ecosystems, altering the balance of nutrients and habitats for various plant and animal species. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Environmental Science found that dust particles can reduce photosynthesis in plants, leading to decreased crop yields and altered ecosystem dynamics.
What are the main components of dust?
+Dust is primarily composed of inorganic particles, such as soil and minerals, as well as organic particles like pollen and mold spores.
How does dust affect human health?
+Exposure to dust can exacerbate respiratory conditions, reduce lung function, and increase the risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease.
What are the environmental impacts of dust?
+Dust can contribute to climate change, soil degradation, and water pollution, as well as affect ecosystems and alter the balance of nutrients and habitats for various plant and animal species.
In conclusion, dust is a complex and multifaceted substance that can have significant impacts on human health and the environment. By understanding the composition and sources of dust, we can develop effective strategies for mitigating its negative effects and promoting a healthier and more sustainable future.