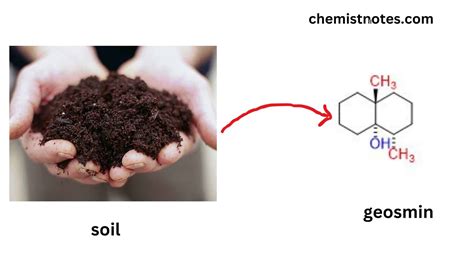
Geosmin, which translates to "earth smell" in Greek, is a naturally occurring compound that is responsible for the distinct earthy odor that many people associate with soil and aquatic environments. This compound is produced by certain types of bacteria, including Actinomycetes, which are found in soil and water. Geosmin is a significant component of the earthy smell that people often notice after a rainstorm or when they are near a body of water. In addition to its role in producing the earthy smell, geosmin also plays a crucial role in the ecosystem, serving as a source of food and shelter for various organisms.
One of the most interesting facts about geosmin is its ability to be detected by humans at extremely low concentrations. In fact, the human nose can detect geosmin at concentrations as low as 0.01 parts per billion, making it one of the most potent odor-causing compounds known. This sensitivity is thought to be an evolutionary adaptation that allows humans to detect the presence of water, which is essential for survival. Geosmin is also used as a indicator of the presence of certain types of bacteria, including those that can cause disease in humans. As a result, geosmin is often used as a tool in water quality monitoring and public health surveillance.
Key Points
- Geosmin is a naturally occurring compound that is responsible for the earthy smell of soil and water.
- It is produced by certain types of bacteria, including Actinomycetes, which are found in soil and water.
- Geosmin can be detected by humans at extremely low concentrations, making it one of the most potent odor-causing compounds known.
- It plays a crucial role in the ecosystem, serving as a source of food and shelter for various organisms.
- Geosmin is used as a tool in water quality monitoring and public health surveillance due to its ability to indicate the presence of certain types of bacteria.
The Science Behind Geosmin

Geosmin is a type of sesquiterpene, a class of compounds that are found in plants and microorganisms. It is produced through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that involve the conversion of simpler compounds into more complex ones. The exact mechanism of geosmin production is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve the action of multiple enzymes and the presence of specific nutrients and environmental factors. Geosmin is also known to be produced by other types of microorganisms, including fungi and algae, although the exact role of these organisms in geosmin production is not well understood.
Geosmin and Water Quality
Geosmin is often used as an indicator of water quality due to its ability to detect the presence of certain types of bacteria. These bacteria, including Actinomycetes, can produce geosmin as a byproduct of their metabolism, and the presence of geosmin in water can indicate the presence of these bacteria. Geosmin is also used to monitor the presence of other types of microorganisms, including those that can cause disease in humans. For example, geosmin has been used to detect the presence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia, two types of parasites that can cause waterborne illness.
| Type of Bacteria | Geosmin Production |
|---|---|
| Actinomycetes | High |
| Fungi | Low |
| Algae | Variable |

Practical Applications of Geosmin
Geosmin has a number of practical applications, including its use in water quality monitoring and public health surveillance. It is also used in the production of certain types of food and beverages, including wine and beer, where it can impart a distinct earthy flavor. Geosmin is also used in the production of certain types of perfumes and fragrances, where it can add a unique and distinctive scent. In addition to these uses, geosmin is also being researched for its potential medicinal properties, including its ability to act as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent.
Geosmin and Human Health
Geosmin has been shown to have a number of potential health benefits, including its ability to act as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. It has also been shown to have antimicrobial properties, making it effective against certain types of bacteria and other microorganisms. However, geosmin can also have negative effects on human health, particularly at high concentrations. For example, exposure to high levels of geosmin has been linked to respiratory problems and other health issues. As a result, it is essential to monitor geosmin levels in water and other environments to ensure public health and safety.
What is geosmin and where is it found?
+Geosmin is a naturally occurring compound that is responsible for the earthy smell of soil and water. It is produced by certain types of bacteria, including Actinomycetes, which are found in soil and water.
What are the practical applications of geosmin?
+Geosmin has a number of practical applications, including its use in water quality monitoring and public health surveillance. It is also used in the production of certain types of food and beverages, including wine and beer, where it can impart a distinct earthy flavor.
What are the potential health benefits of geosmin?
+Geosmin has been shown to have a number of potential health benefits, including its ability to act as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. It has also been shown to have antimicrobial properties, making it effective against certain types of bacteria and other microorganisms.
In conclusion, geosmin is a complex and multifaceted compound that plays a crucial role in the ecosystem and has a number of practical applications. Its ability to be detected by humans at extremely low concentrations makes it a valuable tool in water quality monitoring and public health surveillance. As research continues to uncover the potential health benefits and risks of geosmin, it is clear that this compound will remain an important area of study in the fields of environmental science and public health.