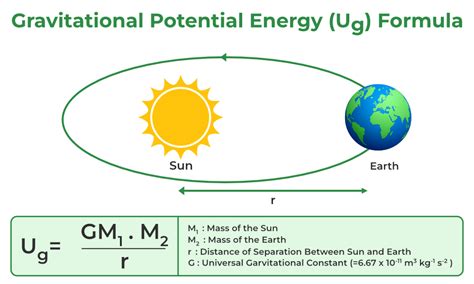
Gravitational potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the energy an object possesses due to its position within a gravitational field. This form of potential energy is directly related to the gravitational force, which is a universal force that attracts two objects with mass towards each other. The concept of gravitational potential energy is crucial in understanding various phenomena, ranging from the motion of objects on Earth's surface to the orbits of celestial bodies in the universe.
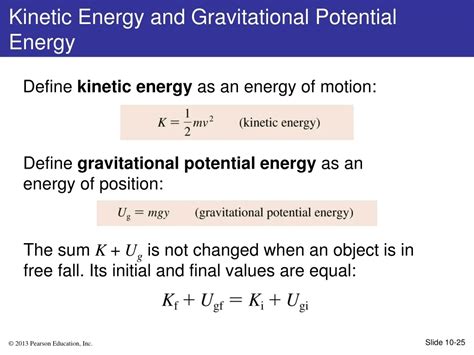
The gravitational potential energy of an object depends on its mass, the mass of the Earth (or any other celestial body it is near), and the distance between the object and the center of the Earth. It is calculated using the formula U = mgh, where U is the gravitational potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 meters per second squared on Earth's surface), and h is the height of the object above a reference point, typically the Earth's surface. This formula indicates that the gravitational potential energy of an object increases as its mass and height above the reference point increase.
Key Points
- Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field.
- The formula for gravitational potential energy is U = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above a reference point.
- Gravitational potential energy is a form of potential energy, which can be converted into kinetic energy as the object moves.
- The concept is essential for understanding the behavior of objects under the influence of gravity, from the falling of objects on Earth to the orbits of planets and stars.
- Gravitational potential energy plays a critical role in various applications, including the design of roller coasters, the calculation of the escape velocity from a planet, and the understanding of tides and ocean currents.
Understanding Gravitational Potential Energy

Gravitational potential energy is a result of the gravitational interaction between two masses. On Earth, the most common reference frame for calculating gravitational potential energy is the Earth’s surface. As an object is lifted or moved to a greater height above the Earth’s surface, its gravitational potential energy increases because it is positioned farther away from the center of the Earth, thus increasing the distance over which the gravitational force acts.
Conversely, when an object falls towards the Earth, its gravitational potential energy decreases as it moves closer to the Earth's center. This decrease in potential energy is accompanied by an increase in kinetic energy, illustrating the principle of conservation of energy. The total energy of an isolated system remains constant, but it can be converted from one form to another. In the case of gravitational potential energy, it is converted into kinetic energy as the object falls.
Applications of Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy has numerous practical applications across various fields. In engineering, the concept is crucial for designing structures that withstand gravitational forces, such as buildings and bridges. In the context of transportation, understanding gravitational potential energy is essential for the design of roller coasters and ski lifts, where the conversion between potential and kinetic energy is exploited to achieve desired speeds and heights.
In astronomy, gravitational potential energy plays a pivotal role in understanding the orbits of planets, moons, and stars. The gravitational potential energy between celestial bodies influences their orbits and the stability of planetary systems. Furthermore, the concept of gravitational potential energy is used to calculate the escape velocity from a planet or moon, which is the minimum speed an object must have to escape the gravitational pull of the celestial body.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Structural Engineering | Designing buildings and bridges to withstand gravitational forces. |
| Transportation | Design of roller coasters and ski lifts, exploiting the conversion between potential and kinetic energy. |
| Astronomy | Understanding orbits of planets and stars, and calculating escape velocities from celestial bodies. |
| Energy Generation | Hydroelectric power plants, where water's gravitational potential energy is converted into electricity. |
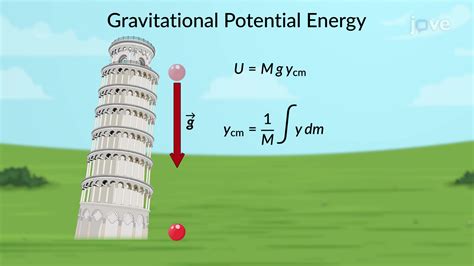
Calculation and Conversion of Gravitational Potential Energy
The calculation of gravitational potential energy is straightforward using the formula U = mgh. However, understanding the conversion of this energy into other forms, particularly kinetic energy, is crucial for predicting the motion of objects under the influence of gravity. As an object falls, its potential energy decreases, and its kinetic energy increases, with the total energy remaining constant in the absence of external forces like friction.
The conversion between gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy is a fundamental principle in physics and is observed in various natural phenomena, from the falling of raindrops to the motion of comets in the solar system. This principle is also harnessed in human-made systems, such as hydroelectric power plants, where the gravitational potential energy of water stored behind a dam is converted into kinetic energy as the water flows down, and then into electrical energy through turbines.
Implications and Future Directions
The concept of gravitational potential energy has significant implications for our understanding of the universe, from the smallest scales of everyday objects to the vast scales of cosmic structures. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of gravitational interactions, the importance of gravitational potential energy in understanding these phenomena will only continue to grow.
Furthermore, advancements in technology and engineering will likely lead to more efficient ways to harness and convert gravitational potential energy, potentially opening up new avenues for energy production and storage. The study of gravitational potential energy, therefore, not only deepens our understanding of fundamental physics but also contributes to the development of innovative solutions for global energy challenges.
What is the formula for calculating gravitational potential energy?
+The formula for gravitational potential energy is U = mgh, where U is the gravitational potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above a reference point.
How is gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy?
+Gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as an object moves under the influence of gravity. For example, as an object falls, its potential energy decreases, and its kinetic energy increases, with the total energy remaining constant in the absence of external forces like friction.
What are some practical applications of gravitational potential energy?
+Gravitational potential energy has numerous practical applications, including the design of structures that withstand gravitational forces, the operation of roller coasters and ski lifts, the understanding of orbits in astronomy, and the generation of electricity in hydroelectric power plants.