The Milky Way, our home galaxy, has long been a subject of fascination for astronomers and scientists. At its center lies a supermassive black hole, known as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), with a mass of approximately 4 million times that of our sun. This black hole is surrounded by a dense cluster of stars, gas, and dust, making it a challenging region to study. However, recent advances in observational and computational techniques have allowed researchers to uncover some of the secrets hidden at the center of the Milky Way.
One of the most significant discoveries in recent years is the presence of a large, spherical structure at the heart of the Milky Way. This structure, known as the Central Molecular Zone (CMZ), is a region of high-density gas and dust that surrounds the supermassive black hole. The CMZ is thought to be the result of a combination of gravitational and magnetic forces that have shaped the gas and dust in the region over millions of years. Studies have shown that the CMZ is approximately 200 parsecs in diameter and contains a significant fraction of the galaxy's total molecular gas mass.
Key Points
- The Milky Way's center is home to a supermassive black hole, Sgr A*, with a mass of approximately 4 million times that of our sun.
- The Central Molecular Zone (CMZ) is a large, spherical structure surrounding the black hole, composed of high-density gas and dust.
- The CMZ is approximately 200 parsecs in diameter and contains a significant fraction of the galaxy's total molecular gas mass.
- Star formation is thought to occur in the CMZ, with young stars and star clusters observed in the region.
- The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is thought to play a key role in regulating star formation and galaxy evolution.
The Supermassive Black Hole at the Heart of the Milky Way
The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, Sgr A*, is one of the most well-studied black holes in the universe. With a mass of approximately 4 million times that of our sun, it is a significant object of study for astronomers. The black hole is thought to have formed through the merger of smaller black holes and the accretion of gas and dust over billions of years. Its event horizon, the point of no return around a black hole, is approximately 12 million kilometers in diameter, making it a relatively small but extremely dense object.
Recent studies have shown that the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is not just a passive object, but an active participant in the evolution of the galaxy. The black hole's gravitational influence can regulate the flow of gas and dust in the CMZ, affecting the formation of new stars and the growth of the galaxy. Additionally, the black hole's activity can also impact the surrounding environment, with outflows of energy and matter observed in the form of jets and winds.
Star Formation in the Central Molecular Zone
Despite the harsh conditions at the center of the Milky Way, star formation is thought to occur in the CMZ. Young stars and star clusters have been observed in the region, and studies have shown that the CMZ is a significant site of star formation in the galaxy. The formation of stars in this region is thought to be triggered by the collapse of dense gas and dust clouds, which can be triggered by the gravitational influence of the supermassive black hole or other external factors.
However, star formation in the CMZ is not without its challenges. The region is subject to strong tidal forces, which can disrupt the formation of stars and planetary systems. Additionally, the high levels of radiation and intense magnetic fields in the region can also impact the formation and evolution of stars and planets. Despite these challenges, the CMZ remains an important region for studying star formation and galaxy evolution.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass of Sgr A* | 4 million M⊙ |
| Diameter of the CMZ | 200 parsecs |
| Gas mass in the CMZ | 10^7 M⊙ |
| Star formation rate in the CMZ | 0.1-1 M⊙/yr |
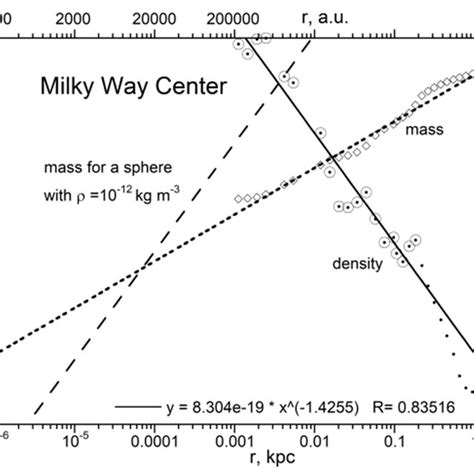
Implications for Galaxy Evolution
The study of the Milky Way’s center has significant implications for our understanding of galaxy evolution. The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is thought to have played a key role in the evolution of the galaxy, regulating the flow of gas and dust and influencing the formation of stars. Similarly, the CMZ is thought to be a significant site of star formation, with young stars and star clusters forming in the region.
However, the Milky Way is not unique in having a supermassive black hole at its center. Many galaxies are thought to have similar objects, and the study of these black holes can provide insights into the evolution and growth of galaxies. By understanding the complex interplay between the supermassive black hole, the CMZ, and star formation, we can gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental processes that shape the universe.
Future Research Directions
Despite the significant progress made in recent years, there is still much to be learned about the center of the Milky Way. Future research directions include the study of the supermassive black hole’s activity and its impact on the surrounding environment, as well as the formation and evolution of stars and planetary systems in the CMZ. Additionally, the development of new observational and computational techniques will be crucial for advancing our understanding of this complex region.
One of the most exciting areas of research is the study of the Milky Way's center in the context of galaxy evolution. By comparing the Milky Way to other galaxies, we can gain insights into the universal processes that shape the evolution of galaxies. This research has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe, and will likely remain an active area of research for years to come.
What is the mass of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way?
+The mass of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is approximately 4 million times that of our sun.
What is the Central Molecular Zone (CMZ)?
+The Central Molecular Zone (CMZ) is a large, spherical structure at the heart of the Milky Way, composed of high-density gas and dust.
What is the significance of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way?
+The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is thought to play a key role in regulating star formation and galaxy evolution, and its study can provide insights into the fundamental processes that shape the universe.