The terms megabyte (MB) and kilobyte (KB) are fundamental units of measurement in the digital world, used to express the size of digital files, storage capacity, and data transfer rates. Understanding the difference between these units is crucial for navigating the vast landscape of digital technology, from managing personal files to designing complex data storage solutions. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, comparisons, and practical applications of MB and KB, providing a comprehensive overview for both novice and advanced users.
Defining MB and KB
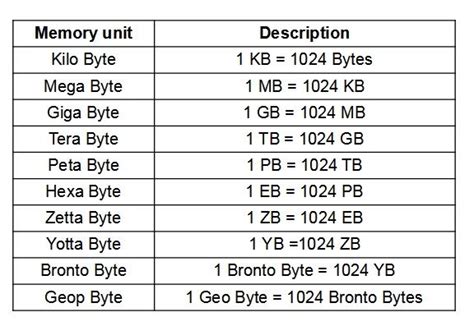
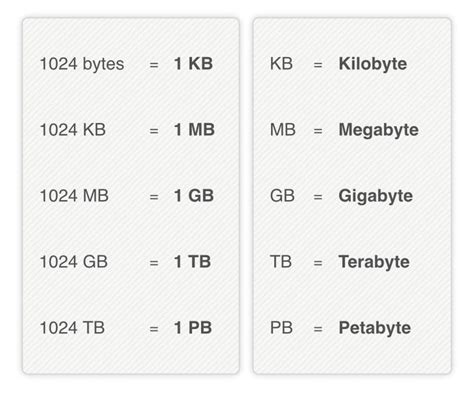
To begin, it’s essential to define what MB and KB represent. A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information that equals 1,024 bytes. Each byte, in turn, can represent a single character, such as a letter or a number, in a digital context. A megabyte (MB), on the other hand, is a larger unit that equals 1,024 kilobytes or 1,048,576 bytes. This distinction in size reflects the hierarchical nature of digital measurement units, with each step up representing a significant increase in capacity.
Size Comparison: MB vs. KB
When comparing MB and KB, the primary difference lies in their size. Since 1 MB equals 1,024 KB, it’s clear that MB is the larger unit. To put this into perspective, consider that a typical short text document might be around 10-20 KB in size, while a high-resolution image could range from a few hundred KB to several MB. Video files, which require significantly more data to store motion and sound, can easily exceed 100 MB or even several GB (gigabytes) for longer, higher-quality content.
| Unit | Size in Bytes | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Kilobyte (KB) | 1,024 bytes | Short text document or small image |
| Megabyte (MB) | 1,048,576 bytes | High-resolution image or short video clip |
Practical Applications and Considerations
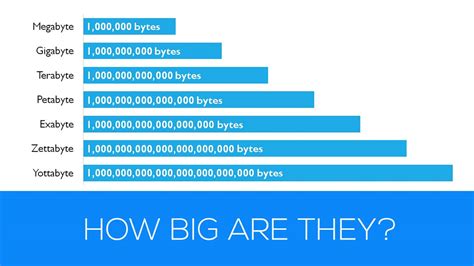
In practical terms, the difference between MB and KB affects how we interact with digital content and technologies. For instance, when purchasing storage devices like hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs), understanding that 1 TB (terabyte) equals 1,024 GB, and each GB equals 1,024 MB, is crucial for making informed decisions about storage capacity needs. Similarly, when downloading files or streaming content, recognizing the file size in MB or GB can help manage expectations regarding download times or required internet bandwidth.
Storage and Transfer Implications
The implications of MB and KB sizes extend to data transfer rates and storage capacities. For example, a file transfer speed of 100 MB/s is significantly faster than one of 100 KB/s, highlighting the importance of unit awareness in digital transactions. Furthermore, the capacity of storage devices, often measured in GB or TB, dictates how many files of various sizes (in MB or KB) can be stored, underscoring the need for a clear understanding of these units in managing digital assets.
Key Points
- The megabyte (MB) is a larger unit of digital information than the kilobyte (KB), with 1 MB equaling 1,024 KB.
- Understanding the difference between MB and KB is crucial for managing digital files, selecting appropriate storage solutions, and optimizing data transfer.
- Practical applications of MB and KB include purchasing storage devices, downloading files, and streaming content, where recognizing file sizes and transfer rates is essential.
- The hierarchical nature of digital measurement units (from bytes to kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes) reflects the vast range of digital data sizes and the need for a comprehensive understanding of these units.
- Expertise in distinguishing between MB and KB sizes is vital for both personal and professional digital management, influencing decisions on storage, transfer, and the overall efficiency of digital workflows.
In conclusion, the comparison between MB and KB highlights the fundamental importance of understanding digital measurement units in the modern world. As technology continues to evolve, with files growing in size and complexity, the ability to navigate and manage digital content efficiently will increasingly depend on a clear grasp of these concepts. Whether for personal file management or professional data analysis, recognizing the differences and applications of MB and KB will remain a cornerstone of digital literacy.
What is the primary difference between MB and KB?
+The primary difference is in their size, with 1 MB being equal to 1,024 KB, making MB the larger unit of digital measurement.
How does understanding MB and KB impact digital storage and transfer decisions?
+Understanding MB and KB sizes is crucial for selecting appropriate storage devices, managing file downloads, and optimizing data transfer rates, ensuring that digital workflows are efficient and effective.
What are some practical examples where distinguishing between MB and KB is important?
+Practical examples include purchasing storage devices, downloading files, streaming content, and managing digital assets, where recognizing file sizes in MB or KB and transfer speeds can significantly impact user experience and productivity.



