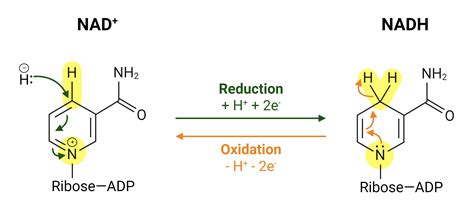
NADPH, or Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, is a crucial electron carrier molecule found in all living cells. It plays a pivotal role in various cellular processes, including energy metabolism, detoxification, and the synthesis of essential biomolecules. The definition of NADPH revolves around its ability to donate electrons and thereby reduce other molecules, which is fundamental to its function in maintaining cellular redox balance and supporting anabolic reactions.
One of the primary functions of NADPH is its involvement in the pentose phosphate pathway, where it serves as a reducing agent. This pathway is essential for generating NADPH and pentoses from glucose-6-phosphate. The electrons carried by NADPH are used in reductive biosynthetic reactions, such as fatty acid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis, and the synthesis of steroids and other isoprenoids. Additionally, NADPH is critical in the reduction of oxidized glutathione, which protects the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). This protective mechanism is vital for maintaining cellular integrity and function.
Key Points
- NADPH is a reducing agent that donates electrons in various cellular reactions.
- It plays a crucial role in the pentose phosphate pathway for generating NADPH and pentoses.
- NADPH is involved in reductive biosynthetic reactions, including fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis.
- It helps protect cells from oxidative damage by reducing oxidized glutathione.
- NADPH is essential for maintaining cellular redox balance and supporting anabolic reactions.
NADPH and Energy Metabolism
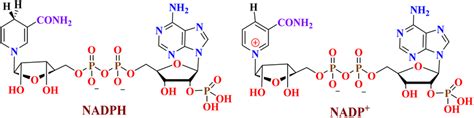
NADPH is closely linked with energy metabolism, primarily through its role in the pentose phosphate pathway. This pathway not only generates NADPH but also produces ribose-5-phosphate, a precursor for nucleotide synthesis. The balance between NADPH production and consumption is critical for the proper functioning of cellular metabolism. An imbalance can lead to metabolic disorders, highlighting the importance of NADPH in maintaining energy homeostasis within the cell.
NADPH in Detoxification Processes
Beyond its metabolic roles, NADPH is also crucial in detoxification processes. It is a cofactor for several enzymes involved in the reduction of oxidized compounds, thereby protecting the cell from oxidative stress. The cytochrome P450 family of enzymes, for example, relies on NADPH to reduce molecular oxygen, facilitating the metabolism and clearance of drugs and xenobiotics. This process underscores the versatile function of NADPH in maintaining cellular health and resilience against environmental stressors.
| Metabolic Process | Role of NADPH |
|---|---|
| Fatty Acid Synthesis | Reducing agent for the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA |
| Cholesterol Synthesis | Provides reducing equivalents for the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate |
| Pentose Phosphate Pathway | Generated through the oxidative phase of the pathway and used in the reductive phase |
| Detoxification | Cofactor for enzymes involved in the reduction of oxidized compounds and metabolism of xenobiotics |

NADPH and Disease
Dysregulation of NADPH metabolism has been implicated in various diseases. For instance, alterations in NADPH levels can affect the activity of enzymes involved in antioxidant defense, leading to increased susceptibility to oxidative stress and related disorders. Furthermore, impaired NADPH production can impact the synthesis of essential biomolecules, contributing to metabolic and developmental abnormalities. Understanding the role of NADPH in disease pathogenesis can provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies aimed at modulating NADPH levels or activity.
Future Perspectives
Given the critical roles of NADPH in cellular metabolism and detoxification, further research is warranted to explore its potential as a therapeutic target. Elucidating the mechanisms by which NADPH levels are regulated and how these levels impact cellular function will be essential for developing strategies to manipulate NADPH metabolism for therapeutic benefit. Additionally, investigating the interplay between NADPH and other metabolic pathways will provide a more comprehensive understanding of its function in health and disease.
What is the primary function of NADPH in cells?
+NADPH primarily serves as a reducing agent, donating electrons in various cellular reactions, including reductive biosynthetic reactions and the protection against oxidative damage.
How is NADPH involved in energy metabolism?
+NADPH is involved in energy metabolism through its generation in the pentose phosphate pathway and its role in reductive biosynthetic reactions, contributing to the synthesis of essential biomolecules and maintaining cellular redox balance.
What are the implications of NADPH dysregulation in disease?
+Dysregulation of NADPH metabolism can lead to increased susceptibility to oxidative stress, impaired synthesis of essential biomolecules, and contribute to the pathogenesis of various diseases, including metabolic and developmental disorders.
Meta Description: NADPH plays a critical role in cellular metabolism, serving as a reducing agent in reductive biosynthetic reactions and protecting against oxidative stress. Its dysregulation is implicated in various diseases, highlighting its importance as a potential therapeutic target.