Nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a state, characterized by the individual's allegiance to the state and the state's protection of the individual. It is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses various aspects, including citizenship, ethnicity, culture, and identity. Nationality is often associated with a person's country of birth, residence, or ancestry, but it can also be acquired through naturalization, marriage, or other means.
Definition and Types of Nationality
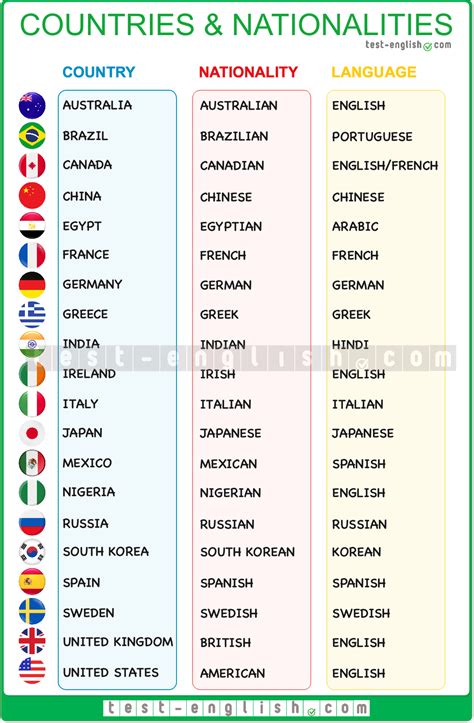
Nationality can be defined in different ways, depending on the context and perspective. From a legal standpoint, nationality is a person’s membership in a nation-state, which confers certain rights and responsibilities. There are several types of nationality, including:
- Citizenship by birth: This type of nationality is acquired through birth within a country’s territory or to parents who are citizens of that country.
- Citizenship by descent: This type of nationality is acquired through ancestry, where an individual’s parents or grandparents are citizens of a particular country.
- Naturalization: This type of nationality is acquired through the process of naturalization, where an individual meets certain requirements and is granted citizenship by a country.
- Dual nationality: This type of nationality occurs when an individual holds citizenship in two or more countries simultaneously.
Factors Influencing Nationality
Nationality is influenced by various factors, including:
- Birthplace: The country where an individual is born can determine their nationality.
- Parentage: The nationality of an individual’s parents can also determine their nationality.
- Residence: The country where an individual resides can influence their nationality, particularly if they apply for naturalization.
- Marriage: Marriage to a citizen of a particular country can confer nationality on the spouse.
| Country | Nationality Acquisition Methods |
|---|---|
| United States | Citizenship by birth, naturalization, and citizenship by descent |
| Canada | Citizenship by birth, naturalization, and citizenship by descent |
| United Kingdom | Citizenship by birth, naturalization, and citizenship by descent |

Key Points

Key Points
- Nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a state.
- There are several types of nationality, including citizenship by birth, citizenship by descent, naturalization, and dual nationality.
- Nationality is influenced by factors such as birthplace, parentage, residence, and marriage.
- Understanding nationality is essential for navigating the complexities of international law and individual rights.
- Nationality can have significant implications for an individual’s identity, rights, and responsibilities.
Implications of Nationality
Nationality has significant implications for an individual’s rights, responsibilities, and identity. It can affect their ability to travel, work, and reside in certain countries, as well as their access to social services, education, and healthcare. Nationality can also influence an individual’s sense of belonging and identity, particularly in cases where they hold dual nationality or have a complex nationality situation.
Nationality and International Law
Nationality is also an important concept in international law, as it can determine an individual’s rights and responsibilities under international treaties and agreements. The concept of nationality is closely tied to the principles of sovereignty and jurisdiction, and it can have significant implications for international relations and diplomacy.
What is the difference between citizenship and nationality?
+Citizenship and nationality are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Citizenship refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a state, while nationality refers to the individual's allegiance to the state and the state's protection of the individual.
Can an individual hold dual nationality?
+Yes, an individual can hold dual nationality, which means they are a citizen of two or more countries simultaneously. However, this can have significant implications for their rights, responsibilities, and identity.
How is nationality acquired?
+Nationality can be acquired through various means, including citizenship by birth, citizenship by descent, naturalization, and marriage to a citizen of a particular country.
In conclusion, nationality is a complex and multifaceted concept that has significant implications for an individual’s rights, responsibilities, and identity. Understanding the different types of nationality and the factors that influence it can help individuals navigate the complexities of nationality and make informed decisions about their own nationality. By recognizing the importance of nationality in international law and individual rights, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and equitable world for all individuals, regardless of their nationality.



