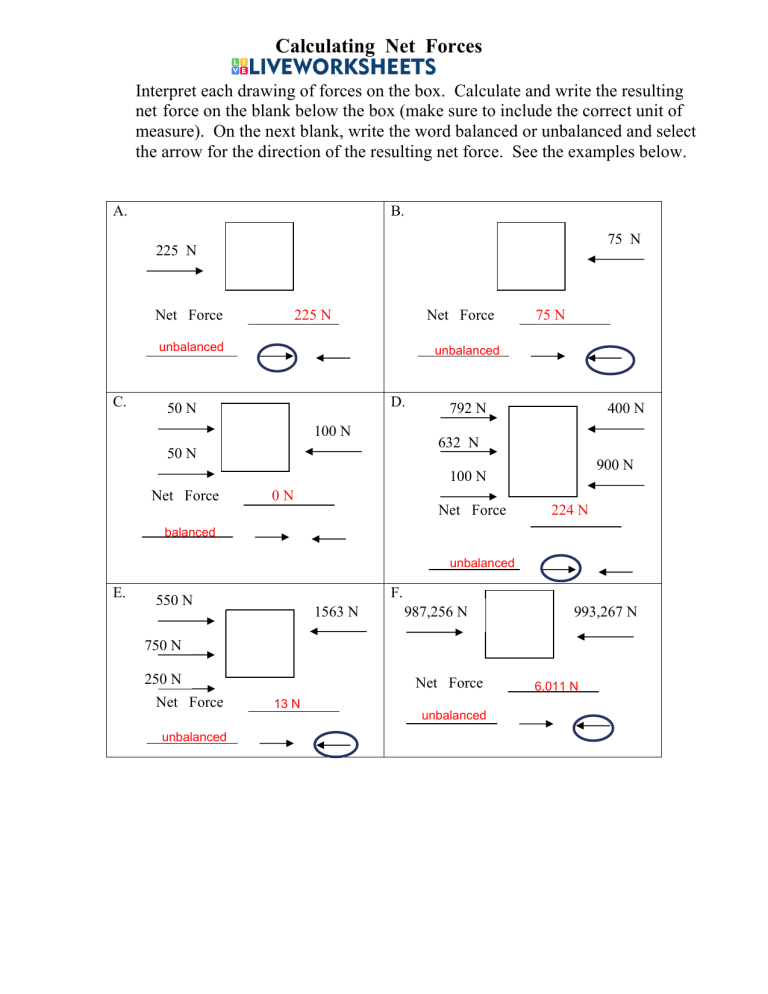
The concept of net force is a fundamental principle in physics, describing the overall force acting on an object when multiple forces are applied. Understanding how net force works is crucial for predicting the motion of objects in various scenarios, from the trajectory of projectiles to the stability of structures. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of net force, exploring its definition, calculation, and applications through five distinct perspectives.
Key Points
- Net force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object, determining its acceleration.
- The calculation of net force involves adding forces in the same direction and subtracting forces in opposite directions.
- Net force is essential for understanding Newton's laws of motion, particularly the second law, which relates force, mass, and acceleration.
- Real-world applications of net force include designing safety features in vehicles, calculating the thrust of rockets, and understanding the mechanics of athletic performance.
- Net force analysis is also critical in engineering, where it is used to ensure the structural integrity of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure.
Definition and Calculation of Net Force
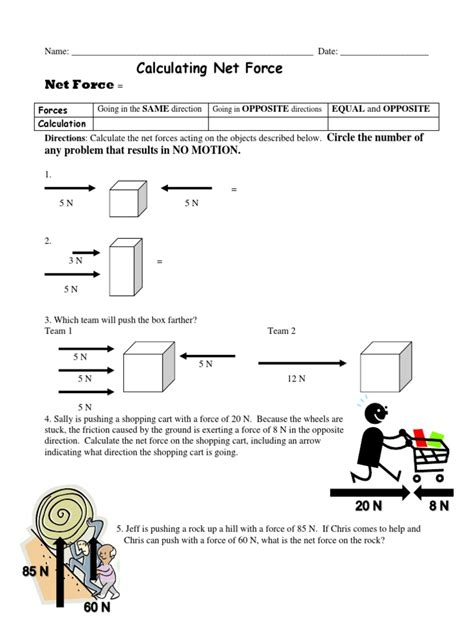
Net force, denoted by the symbol F_net, is the resultant force acting on an object when all the forces acting on it are combined. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. The calculation of net force involves vector addition, where forces acting in the same direction are added together, and forces acting in opposite directions are subtracted. This can be represented mathematically as F_net = F1 + F2 +… + Fn, where F1, F2,…, Fn are the individual forces acting on the object.
Newton’s Laws of Motion and Net Force
Newton’s second law of motion, F = ma, where F is the net force acting on an object, m is its mass, and a is its acceleration, underscores the importance of net force in understanding how objects move. According to this law, the net force acting on an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and inversely proportional to its mass. This principle is foundational in physics and engineering, guiding the design of everything from machinery to transportation systems.
| Force Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frictional Force | A force opposing the relative motion of two surfaces in contact. |
| Normal Force | A force exerted by a surface on an object in contact with it, perpendicular to the surface. |
| Applied Force | An external force applied to an object, which can cause it to accelerate. |

Applications of Net Force in Real-World Scenarios

The principle of net force has numerous practical applications across various fields. In vehicle safety, understanding net force is crucial for designing features like airbags and seatbelts, which must effectively counteract the forces acting on occupants during a crash. Similarly, in aerospace engineering, the net force acting on a rocket determines its thrust and trajectory. Athletes and coaches also utilize principles related to net force to optimize performance, whether it’s perfecting the jump technique in basketball or the sprint start in track and field.
Engineering and Structural Integrity
In the field of civil engineering, net force analysis is essential for ensuring the structural integrity of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure. Engineers must calculate the net force acting on these structures under various conditions, including wind, earthquakes, and the weight of the structure itself, to design them to withstand such forces without collapsing. This involves a deep understanding of the forces at play and how they interact to produce a net force that the structure can safely withstand.
How is net force related to Newton's laws of motion?
+Net force is directly related to Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to its mass. This law, F = ma, is foundational in understanding how forces affect motion.
What are some common forces considered in net force calculations?
+Common forces include frictional forces, normal forces, applied forces, and gravitational forces. The specific forces considered depend on the scenario, such as the motion of an object on a surface, where friction and normal force are significant, or the motion of an object in the air, where air resistance and gravitational force are key.
How does net force impact the design of safety features in vehicles?
+Understanding net force is crucial for designing effective safety features. For instance, airbags and seatbelts are designed to counteract the forces acting on occupants during a crash, thereby reducing the risk of injury. The net force experienced by the occupants determines the necessary counterforce that these safety features must provide.
In conclusion, the concept of net force is a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the motion of objects under the influence of multiple forces. Its applications span a wide range of fields, from physics and engineering to sports and safety design. By grasping the principles of net force and how it relates to Newton’s laws of motion, individuals can better understand the complex interactions at play in the physical world and make informed decisions in various professional and personal contexts.