Postsecondary education refers to the educational programs and institutions that students attend after completing their secondary education, typically after high school. This level of education is designed to provide students with advanced knowledge, skills, and training in a specific field or discipline, preparing them for careers, further education, or personal enrichment. Postsecondary education encompasses a wide range of programs, including academic, vocational, and professional training, offered by various institutions such as universities, colleges, community colleges, and technical schools.
The postsecondary education landscape is diverse and complex, with different types of institutions and programs catering to different student needs and goals. For instance, universities and colleges offer academic programs leading to degrees such as associate's, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees, while community colleges and technical schools provide vocational training and certificates in fields like healthcare, technology, and skilled trades. Additionally, online and distance education programs have become increasingly popular, offering flexibility and accessibility to students who may not be able to attend traditional on-campus programs.
Postsecondary education is critical for individuals, societies, and economies, as it provides the foundation for personal and professional growth, innovation, and economic development. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, in 2020, approximately 67% of high school graduates in the United States enrolled in postsecondary education programs, highlighting the importance of this level of education in preparing students for the workforce and beyond. Moreover, research has shown that postsecondary education can have a significant impact on individuals' earning potential, with studies indicating that workers with a bachelor's degree typically earn about 50% more than those with only a high school diploma.
Key Points
- Postsecondary education refers to educational programs and institutions attended after secondary education.
- These programs provide advanced knowledge, skills, and training in specific fields or disciplines.
- Postsecondary education includes academic, vocational, and professional training offered by various institutions.
- Online and distance education programs offer flexibility and accessibility to students.
- Postsecondary education is critical for personal and professional growth, innovation, and economic development.
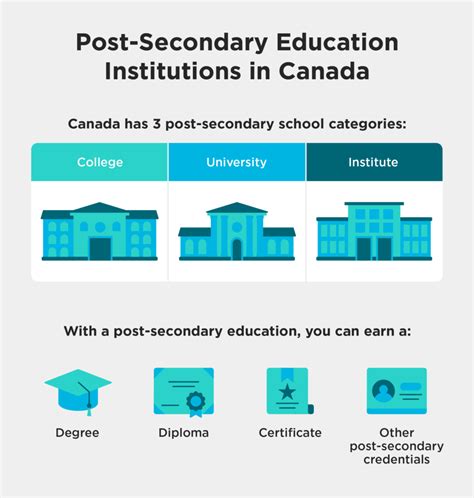
Types of Postsecondary Education Institutions
Postsecondary education institutions can be categorized into several types, each with its unique characteristics, programs, and focus areas. Universities are typically large, comprehensive institutions that offer a wide range of academic programs, including undergraduate and graduate degrees, as well as research opportunities. Colleges, on the other hand, are often smaller and may focus on undergraduate education, offering associate’s and bachelor’s degrees in various fields. Community colleges provide vocational training, certificates, and associate’s degrees, often with a focus on local workforce development and community needs.
Technical schools and vocational schools specialize in providing training in specific trades or industries, such as technology, healthcare, or culinary arts. These institutions often have strong ties with local employers and industries, ensuring that students gain relevant skills and knowledge for the workforce. Online and distance education programs have become increasingly popular, offering flexibility and accessibility to students who may not be able to attend traditional on-campus programs. These programs can range from fully online degree programs to hybrid models that combine online and on-campus instruction.
Programs and Credentials
Postsecondary education programs and credentials vary widely, depending on the institution and field of study. Academic programs typically lead to degrees such as associate’s, bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees, while vocational programs result in certificates, diplomas, or associate’s degrees. Certification programs are designed to provide specialized training and credentials in specific industries or professions, such as healthcare, technology, or finance.
The credentialing process is critical in postsecondary education, as it ensures that students have acquired the necessary knowledge, skills, and competencies to enter the workforce or pursue further education. Credentials can include degrees, diplomas, certificates, and certifications, each with its own set of requirements and standards. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, in 2020, the most common postsecondary credentials held by workers in the United States were bachelor's degrees (34%), followed by associate's degrees (12%), and certificates (10%).
| Postsecondary Credential | Percentage of Workers |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree | 34% |
| Associate's degree | 12% |
| Certificate | 10% |
| Master's degree | 8% |
| Doctoral degree | 3% |
Challenges and Opportunities
Postsecondary education faces numerous challenges, including access and affordability, student debt, and workforce readiness. Many students struggle to access postsecondary education due to financial constraints, and those who do enroll often graduate with significant debt. Moreover, the rapidly changing workforce requires postsecondary education institutions to adapt and innovate, providing students with relevant and in-demand skills and knowledge.
Despite these challenges, postsecondary education also presents numerous opportunities for individuals, societies, and economies. Lifelong learning and professional development are essential in today's fast-paced and rapidly changing workforce, and postsecondary education institutions can play a critical role in providing workers with the skills and knowledge they need to adapt and thrive. Moreover, postsecondary education can have a significant impact on social mobility and economic growth, as it provides individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to access better-paying jobs and contribute to their communities and economies.
What is the purpose of postsecondary education?
+The purpose of postsecondary education is to provide students with advanced knowledge, skills, and training in specific fields or disciplines, preparing them for careers, further education, or personal enrichment.
What types of postsecondary education institutions are available?
+Postsecondary education institutions include universities, colleges, community colleges, technical schools, and online and distance education programs, each with its unique characteristics, programs, and focus areas.
What are the benefits of postsecondary education?
+The benefits of postsecondary education include increased earning potential, improved job prospects, and enhanced social mobility and economic growth, as well as personal growth and development.