Priming, a concept deeply rooted in psychology, refers to the process by which our thoughts, feelings, or actions are influenced by external stimuli. This influence can manifest in various forms, from visual cues to auditory suggestions, and even olfactory triggers. At its core, priming operates on the premise that our brain's neural networks are highly interconnected, allowing for a wide range of stimuli to affect our behavior, often in subtle yet significant ways.
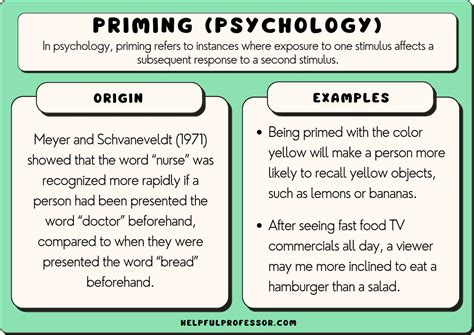
The study of priming has a rich history, dating back to the early days of psychology. Researchers have long been fascinated by how certain words, images, or even environmental conditions can alter an individual's perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors. For instance, a seminal study might expose participants to words related to elderly stereotypes (e.g., "gray," "wrinkled," "retired") and then measure how quickly they walk down a hallway, often finding that those primed with such words walk more slowly than their counterparts. This effect, while seemingly minor, underscores the profound impact that external stimuli can have on our internal states and subsequent actions.
Key Points
- Priming is a psychological phenomenon where external stimuli influence thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
- It operates through the brain's interconnected neural networks, allowing various stimuli to affect behavior.
- Priming can be observed through changes in perception, attitude, and action after exposure to specific stimuli.
- Studies have demonstrated the effect of priming on physical behavior, such as walking speed after exposure to certain words.
- Understanding priming is crucial for recognizing how our environment and the information we consume can shape our actions and decisions.
Types of Priming
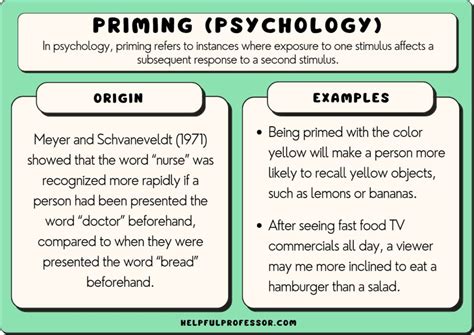
Priming is not a uniform concept; it comes in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and effects. One of the most commonly discussed types is semantic priming, where the meaning of a word or phrase influences the interpretation of subsequent words or phrases. For example, if someone is shown the word “dog” and then asked to categorize the word “bone,” they are likely to respond more quickly than if they had been shown an unrelated word, due to the associative link between dogs and bones.
Another form of priming is affective priming, which involves the influence of emotional stimuli on judgments or behaviors. This can be observed in how a positive or negative mood induced by a stimulus can affect one's perception of neutral stimuli. For instance, someone who has just watched a funny video might rate a neutral face as more attractive than someone who has watched a sad video, illustrating how emotional states can prime certain responses.
Priming in Everyday Life
Priming is not just a laboratory phenomenon; it is an integral part of our daily experiences. From the advertisements we see to the music we listen to, our environment is filled with primes that can influence our mood, our preferences, and even our decisions. Understanding priming can help us navigate these influences more effectively, making us more aware of the subtle forces that shape our behaviors and attitudes.
| Type of Priming | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Semantic Priming | Influence of word meanings | Faster response to "bone" after seeing "dog" |
| Affective Priming | Influence of emotional states | Rating a face as more attractive after watching a funny video |
| Environmental Priming | Influence of physical environment | Feeling more relaxed in a nature setting |
Implications of Priming
The implications of priming are vast and varied, touching upon fields such as marketing, education, and social policy. In marketing, for example, understanding priming can help businesses design more effective advertisements and store layouts, influencing consumer behavior in subtle yet powerful ways. In education, recognizing how priming can affect learning outcomes can lead to the development of more supportive and conducive learning environments.
On a broader societal level, priming can inform policies aimed at promoting positive behaviors and attitudes. For instance, public health campaigns can use priming principles to encourage healthier lifestyles or to reduce prejudice by exposing people to positive, counter-stereotypical images and stories.
In conclusion, priming is a fundamental aspect of human psychology, influencing our perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors in profound ways. By understanding and acknowledging the role of priming in our lives, we can harness its power to create positive change, both at an individual and a societal level.
What is priming in psychology?
+Priming refers to the process where external stimuli influence our thoughts, feelings, or actions, often in subtle yet significant ways.
What are the different types of priming?
+There are several types of priming, including semantic priming, affective priming, and environmental priming, each influencing our behaviors and attitudes in unique ways.
How does priming affect our daily lives?
+Priming influences our mood, preferences, and decisions, making it a crucial factor in how we experience and interact with the world around us.