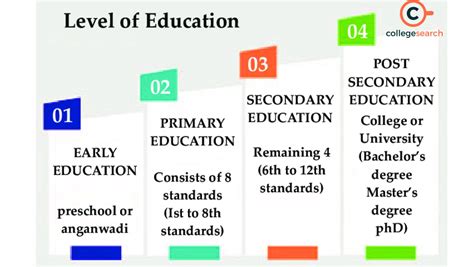
Secondary education is a critical phase in a student's academic journey, serving as a bridge between primary education and higher learning or vocational training. It is during this stage that students begin to explore their interests, develop essential skills, and lay the groundwork for their future careers. The way secondary education works can vary significantly from one country to another, influenced by factors such as cultural norms, educational policies, and economic conditions. However, there are several key aspects that underpin the secondary education system worldwide.
Key Points
- Secondary education typically encompasses a broad curriculum that includes core subjects like mathematics, languages, and sciences, alongside elective courses.
- The structure of secondary education can vary, with some countries adopting a more generalized approach and others opting for specialization from an early stage.
- Assessment and evaluation methods play a crucial role in secondary education, with a mix of internal and external assessments used to measure student performance.
- Extracurricular activities and vocational training are integral components of secondary education, providing students with a well-rounded experience and practical skills.
- Transitioning from secondary education to further education or the workforce is a significant step, with many institutions offering guidance and support to help students make informed decisions about their future.
The Curriculum and Its Components

The curriculum in secondary education is designed to be comprehensive, aiming to equip students with a wide range of skills and knowledge. Core subjects such as mathematics, languages (including the native language and often one or more foreign languages), and sciences (including biology, chemistry, and physics) form the backbone of the curriculum. In addition to these, students are usually required to study social sciences, such as history and geography, and may have the opportunity to explore arts and humanities subjects like music, art, and literature.
Elective Courses and Specialization
Beyond the core subjects, secondary education often offers elective courses or pathways that allow students to explore their interests and talents in greater depth. This can include vocational training, where students learn specific skills related to a trade or profession, or more academically oriented courses that prepare students for higher education. The degree of specialization can vary, with some systems encouraging students to choose a specific stream (e.g., sciences, humanities, or arts) from an early stage, while others maintain a more generalized approach until the final years of secondary education.
| Country | Structure of Secondary Education |
|---|---|
| United States | Typically a comprehensive high school with a broad curriculum, followed by the option to pursue vocational training or attend college. |
| Germany | A more specialized approach, with students divided into different types of secondary schools (Gymnasium, Realschule, Hauptschule) based on their academic ability and career aspirations. |
| Australia | A mix of comprehensive and specialized education, with students able to pursue both academic and vocational pathways within the same institution. |

Assessment and Evaluation
Assessment and evaluation are critical components of secondary education, serving to measure student learning, understand knowledge gaps, and guide teaching practices. The methods of assessment can vary, including internal evaluations conducted by teachers, external examinations set by national or international bodies, and project-based assessments that require students to apply what they have learned to real-world scenarios. The balance between these methods can influence the educational experience, with some systems placing a heavy emphasis on external exams and others focusing more on continuous, formative assessment.
Extracurricular Activities and Vocational Training
Beyond the academic curriculum, secondary education institutions often provide a range of extracurricular activities and vocational training programs. These can include sports teams, clubs focused on specific interests (such as music, drama, or environmental issues), and community service projects. Vocational training, which may be integrated into the curriculum or offered as an alternative pathway, equips students with practical skills related to a specific trade or profession, preparing them for direct entry into the workforce.
These aspects of secondary education are vital for providing students with a well-rounded experience, helping them develop social skills, build confidence, and explore their passions and interests outside the traditional classroom setting.
Transitioning to Further Education or the Workforce
The transition from secondary education to further education or the workforce is a significant milestone for students. Many secondary education institutions offer guidance and support to help students make informed decisions about their future. This can include career counseling, information sessions about higher education options, and workshops on skills such as resume writing and job interviewing. For students pursuing vocational training, apprenticeships or internships may be available, providing them with hands-on experience in their chosen field.
What is the typical age range for secondary education?
+The typical age range for secondary education varies globally but generally spans from approximately 11 to 18 years old.
How does vocational training fit into secondary education?
+Vocational training is integrated into secondary education to provide students with practical skills related to a specific trade or profession, preparing them for direct entry into the workforce.
What role do extracurricular activities play in secondary education?
+Extracurricular activities are crucial for providing students with a well-rounded experience, helping them develop social skills, build confidence, and explore their passions and interests outside the traditional classroom setting.
In conclusion, secondary education is a complex and multifaceted phase of a student’s educational journey, influenced by a wide array of factors including curriculum design, assessment methods, extracurricular opportunities, and transitions to further education or the workforce. Understanding these components is essential for educators, policymakers, and families seeking to support students in achieving their full potential.