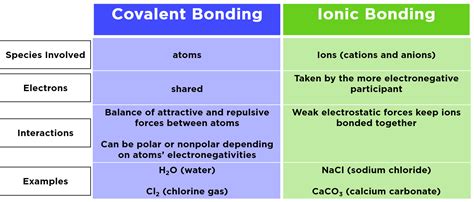
The fundamental building blocks of chemistry, bonds, are the glue that holds atoms together in molecules. Among these, covalent and ionic bonds are two primary types that differ significantly in their formation, characteristics, and the types of compounds they form. Understanding the distinction between covalent and ionic bonds is crucial for grasping the basics of chemistry and the properties of various substances.
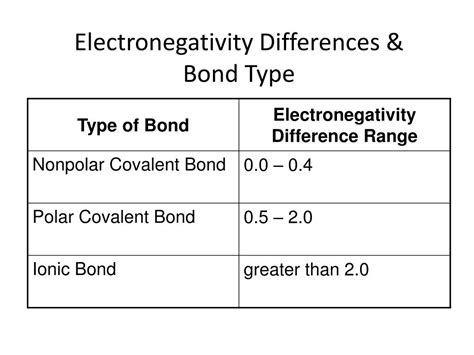
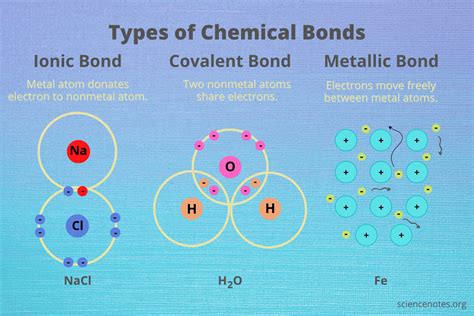
Covalent bonds are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration, typically resulting in a full outer shell. This sharing can occur between atoms of the same element, such as in oxygen (O2) or hydrogen (H2) molecules, or between different elements, as seen in water (H2O) or methane (CH4). The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, holding them together. Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved. Polar covalent bonds occur when there is a significant difference in electronegativity, leading to a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other, as in the case of water molecules.
On the other hand, ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion (cation), while the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion (anion). The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together, forming an ionic compound. Sodium chloride (NaCl), or common table salt, is a classic example of an ionic compound, where sodium (Na) loses an electron to become a positive ion, and chlorine (Cl) gains an electron to become a negative ion.
Key Points
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions.
- The nature of the bond (covalent or ionic) influences the physical and chemical properties of the compound.
- Covalent compounds typically have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds.
- Ionic compounds are usually soluble in water due to their ability to dissociate into ions.
Differences in Formation and Characteristics
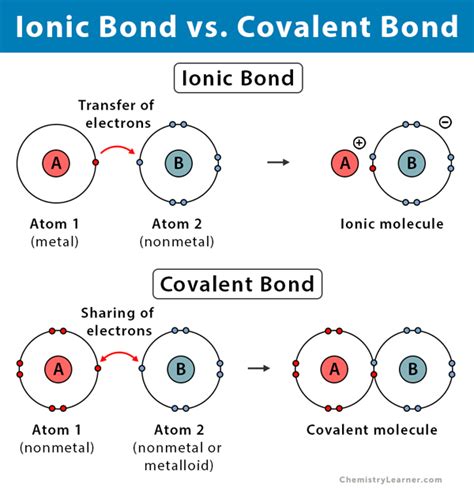
The formation of covalent and ionic bonds differs fundamentally. Covalent bonds require the sharing of electrons, which can occur between similar or dissimilar atoms, whereas ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, typically between metals and nonmetals. This difference in formation leads to distinct characteristics in the resulting compounds. Covalent compounds, for instance, tend to be more flexible and have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds, which are often rigid and have higher melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between the ions.
Physical Properties of Covalent and Ionic Compounds
One of the notable differences between covalent and ionic compounds is their solubility in water. Ionic compounds are generally soluble in water because they can dissociate into their constituent ions, which are then stabilized by water molecules. Covalent compounds, especially those that are nonpolar, tend to be less soluble in water. Another significant difference lies in their conductivity; ionic compounds can conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, due to the movement of ions, whereas covalent compounds typically do not conduct electricity unless they are polar and can dissociate into ions under certain conditions.
| Type of Bond | Formation | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Covalent | Sharing of electrons | Flexible, lower melting/boiling points, less soluble in water | O2, H2O, CH4 |
| Ionic | Transfer of electrons | Rigid, higher melting/boiling points, soluble in water | NaCl, CaCO3, MgO |
Applications and Implications
The differences between covalent and ionic bonds have significant implications for the properties and applications of various materials. In biology, the structures of molecules like DNA and proteins are largely determined by the types of bonds they contain. In materials science, the choice between covalent and ionic compounds can affect the strength, durability, and conductivity of materials. Furthermore, understanding these bonds is crucial for the development of new materials and technologies, such as nanomaterials and semiconductors, where the precise control of bond types can lead to tailored properties.
In conclusion, the distinction between covalent and ionic bonds is a foundational concept in chemistry, with far-reaching implications for the properties and applications of substances. By grasping the differences in their formation, characteristics, and implications, one can better understand the complex world of chemistry and its numerous applications across various fields.
What is the primary difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
+The primary difference lies in how the bonds are formed: covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, leading to the formation of oppositely charged ions.
Which type of bond is typically found in metals and nonmetals?
+Metal-nonmetal interactions typically form ionic bonds, while metal-metal and nonmetal-nonmetal interactions can form covalent bonds or metallic bonds, respectively.
How do the physical properties of covalent and ionic compounds differ?
+Covalent compounds tend to have lower melting and boiling points and are less soluble in water compared to ionic compounds, which have higher melting and boiling points and are generally soluble in water.