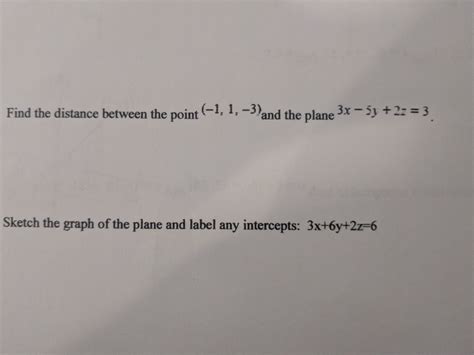The concept of distance between two points, in this case, 1.3 and 14, can be understood in various contexts, including mathematical, physical, and even abstract interpretations. Mathematically, the distance between two points on a number line is determined by the absolute difference between their values. This principle applies when calculating the distance between 1.3 and 14.
Mathematical Interpretation

In mathematics, the distance formula between two points on a one-dimensional number line is given by the absolute value of the difference between the two numbers. For the points 1.3 and 14, the calculation would be |14 - 1.3| = |12.7| = 12.7. This means that the distance between 1.3 and 14 on the number line is 12.7 units.
Physical Interpretation
From a physical perspective, if we were to consider 1.3 and 14 as distances or positions along a straight line (such as a ruler or a road), the distance between these two points would still be 12.7 units, assuming the units are consistent (e.g., both in meters, feet, etc.). This interpretation is directly applicable to real-world measurements and movements.
Key Points
- The mathematical distance between two points on a number line is calculated using the absolute difference between their values.
- The distance between 1.3 and 14 is 12.7 units, based on the formula |14 - 1.3|.
- This principle applies to both mathematical and physical interpretations, given consistent units of measurement.
- Understanding distance calculations is fundamental in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering.
- Applying the distance formula requires attention to the absolute value, ensuring the result is always positive or zero.
Abstract Interpretation
In more abstract contexts, such as data analysis or statistical studies, the concept of distance can be extended to represent differences or similarities between data points. While the numerical distance between 1.3 and 14 remains 12.7, in data analysis, this difference might be interpreted in terms of variability, dispersion, or the spread of data points within a dataset. The interpretation of distance in these contexts depends on the specific application and the nature of the data being analyzed.
| Calculation Type | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mathematical Distance | Absolute difference between two numbers | 12.7 |
| Physical Distance | Distance between two points in space | 12.7 units |
| Abstract Distance | Difference or similarity in data analysis | Context-dependent |
In conclusion, the distance between 1.3 and 14, calculated as 12.7, represents a fundamental concept that transcends mere numerical calculation, touching upon mathematical precision, physical measurement, and abstract data interpretation. Understanding and applying this concept are crucial for navigating various fields of study and real-world applications.
What is the formula for calculating distance between two points on a number line?
+The distance between two points on a number line is given by the absolute value of the difference between the two numbers, or |x2 - x1|, where x1 and x2 are the two points.
Is the concept of distance limited to mathematical and physical contexts?
+No, the concept of distance can also be applied in abstract contexts, such as data analysis, to represent differences or similarities between data points.
What is the importance of understanding distance calculations in real-world applications?
+Understanding distance calculations is crucial for problem-solving in mathematics, physics, engineering, and data analysis, as it provides a basis for measuring, comparing, and interpreting spatial and numerical relationships.