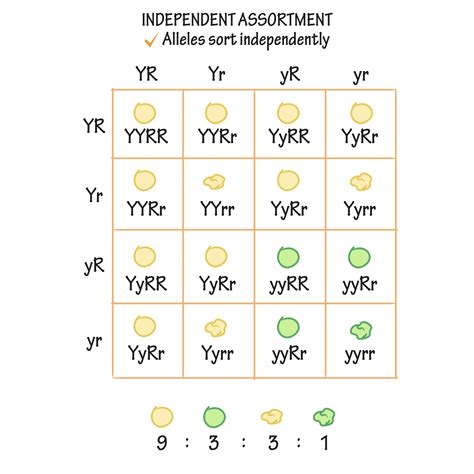
Independent assortment is a fundamental concept in genetics, referring to the random distribution of alleles during gamete formation. This process ensures genetic diversity by creating unique combinations of genes in offspring. The concept of independent assortment was first introduced by Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk who is considered the father of genetics. Mendel's laws of inheritance, including the law of independent assortment, laid the foundation for modern genetics. In this article, we will explore five ways independent assortment works, highlighting its significance in genetics and evolution.
Key Points
- Independent assortment occurs during meiosis, specifically in meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes separate.
- This process increases genetic diversity by creating new combinations of alleles in offspring.
- Independent assortment applies to all genes located on different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosome.
- It is a key factor in the creation of genetic variation, which is essential for evolution and adaptation.
- Understanding independent assortment is crucial for predicting the probability of certain traits being passed down to offspring.
Understanding Independent Assortment
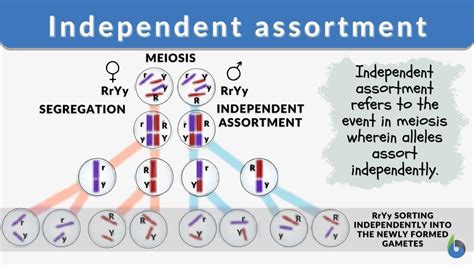
Independent assortment is the process by which different genes are sorted independently of each other during gamete formation. This means that the combination of alleles for one gene does not influence the combination of alleles for another gene. For example, if we consider two genes, one for flower color (red or white) and the other for plant height (tall or short), the alleles for these genes will be sorted independently during meiosis. This results in a random combination of alleles in the gametes, leading to increased genetic diversity in the offspring.
Meiosis and Genetic Diversity
Meiosis is the type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, resulting in the production of gametes (sperm or eggs). During meiosis, homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that carry the same genes but may have different alleles) pair up and then separate. This separation is where independent assortment occurs. Because the alleles for different genes are sorted independently, each gamete receives a unique combination of alleles. This increases genetic diversity by ensuring that offspring are not identical to their parents or siblings.
| Genetic Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | The total number of different alleles in a population or species. |
| Independent Assortment | The random distribution of alleles during gamete formation. |
| Meiosis | A type of cell division that results in the production of gametes. |
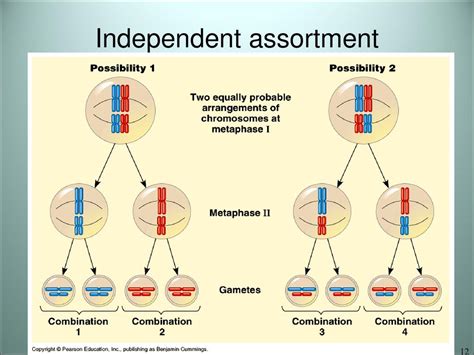
Applications of Independent Assortment
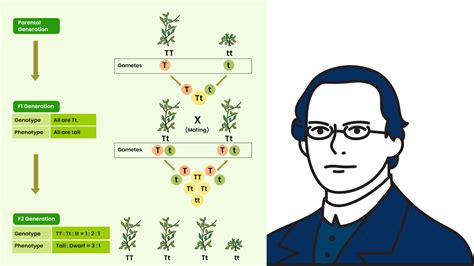
Understanding independent assortment has numerous applications in genetics, breeding, and evolutionary biology. For instance, in plant and animal breeding, knowledge of independent assortment is used to predict the likelihood of certain traits being passed down to offspring. This allows breeders to make informed decisions about which individuals to breed together to achieve desired traits. In evolutionary biology, independent assortment plays a key role in the creation of genetic variation, which is a driving force behind evolution and adaptation.
Predicting Trait Inheritance
Predicting the inheritance of traits is a fundamental aspect of genetics. Independent assortment is crucial for making these predictions because it determines how alleles for different genes are combined in offspring. By understanding how independent assortment works, geneticists can use Punnett squares and other tools to predict the probability of certain traits being expressed in offspring. This is not only important for breeding programs but also for understanding the genetic basis of diseases in humans and other organisms.
What is the main outcome of independent assortment?
+The main outcome of independent assortment is increased genetic diversity due to the random combination of alleles for different genes in offspring.
How does independent assortment occur?
+Independent assortment occurs during meiosis I when homologous chromosomes separate, resulting in a random distribution of alleles to the gametes.
What is the significance of independent assortment in evolution?
+Independent assortment is significant in evolution because it creates genetic variation, which is essential for adaptation and survival in changing environments.
In conclusion, independent assortment is a critical process in genetics that ensures genetic diversity by randomly distributing alleles during gamete formation. Understanding how independent assortment works is essential for predicting the inheritance of traits, understanding genetic diversity, and appreciating the mechanisms behind evolution and adaptation. As research in genetics and evolutionary biology continues to advance, the principles of independent assortment will remain foundational, guiding our understanding of the complex interactions between genes, environments, and the evolution of life on Earth.