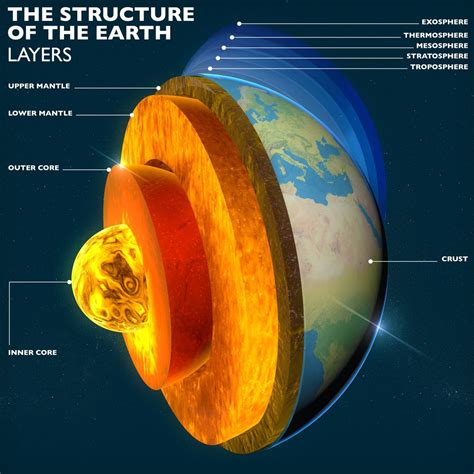
The Earth's outer core is a complex and fascinating region, composed of a variety of elements and compounds. While the exact composition of the outer core is still a subject of ongoing research and debate, scientists have made several key discoveries that shed light on its makeup. The outer core is a liquid layer, approximately 2,250 kilometers thick, and is located between the inner core and the mantle. It is this region that is responsible for generating the Earth's magnetic field, a crucial component of our planet's defense against harmful solar and cosmic radiation.
Key Points
- The Earth's outer core is primarily composed of iron (~85%) and nickel (~10%) alloys.
- Sulfur and oxygen are also present in smaller quantities, with estimates suggesting ~5% and ~1% respectively.
- Other elements, such as silicon, carbon, and hydrogen, may be present in trace amounts.
- The outer core's liquid state is due to the high temperatures (~4,000-6,000°C) and pressures (~3.5 million times atmospheric pressure) at these depths.
- The dynamic movement of the outer core's liquid iron is responsible for generating the Earth's magnetic field through a process known as the geodynamo effect.
Composition of the Outer Core
Research suggests that the outer core is primarily composed of iron (~85%) and nickel (~10%) alloys. These elements are thought to be present in the form of a liquid iron-nickel alloy, with the exact proportions of each element still a subject of ongoing research. The presence of these elements is inferred through a combination of seismic data, laboratory experiments, and theoretical modeling. Seismic data, for example, provides valuable insights into the outer core’s composition and temperature, as seismic waves travel at different speeds through different materials.
Sulfur and Oxygen in the Outer Core
In addition to iron and nickel, scientists believe that sulfur and oxygen are also present in the outer core, albeit in smaller quantities. Estimates suggest that sulfur may comprise up to ~5% of the outer core’s composition, while oxygen may make up ~1%. These elements are thought to be present in the form of iron sulfide (FeS) and iron oxide (FeO) compounds, which are stable at the high temperatures and pressures found in the outer core. The presence of these compounds can have significant effects on the outer core’s physical properties, such as its viscosity and density.
| Element | Estimated Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Iron | 85 |
| Nickel | 10 |
| Sulfur | 5 |
| Oxygen | 1 |
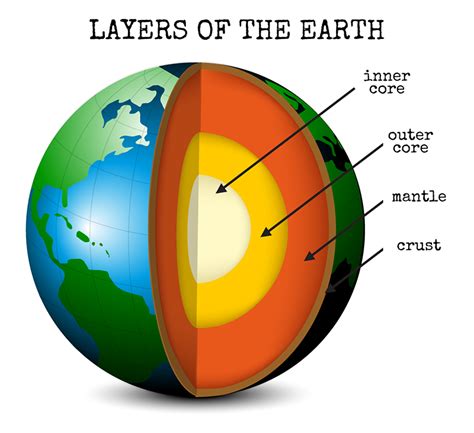
Dynamics of the Outer Core

The outer core’s liquid state is due to the high temperatures (~4,000-6,000°C) and pressures (~3.5 million times atmospheric pressure) at these depths. This liquid iron-nickel alloy is in constant motion, with convective currents driven by heat from the inner core and the mantle. The dynamic movement of the outer core’s liquid iron is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field through a process known as the geodynamo effect. This process involves the interaction between the moving liquid iron and the Earth’s rotation, resulting in the generation of electric currents and the subsequent creation of the magnetic field.
Geodynamo Effect and Magnetic Field Generation
The geodynamo effect is a complex process that involves the interaction between the outer core’s liquid iron, the Earth’s rotation, and the magnetic field itself. The movement of the liquid iron generates electric currents, which in turn produce the magnetic field. This process is self-sustaining, meaning that the magnetic field is generated and maintained by the movement of the outer core’s liquid iron. The geodynamo effect is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field, which plays a crucial role in protecting our planet from harmful solar and cosmic radiation.
What is the primary composition of the Earth’s outer core?
+The Earth’s outer core is primarily composed of iron (~85%) and nickel (~10%) alloys, with smaller quantities of sulfur and oxygen.
What is the geodynamo effect, and how does it generate the Earth’s magnetic field?
+The geodynamo effect is the process by which the movement of the outer core’s liquid iron generates electric currents, producing the Earth’s magnetic field. This process involves the interaction between the moving liquid iron, the Earth’s rotation, and the magnetic field itself.
Why is the Earth’s magnetic field important, and what would happen if it were to disappear?
+The Earth’s magnetic field is crucial for protecting our planet from harmful solar and cosmic radiation. If the magnetic field were to disappear, the Earth’s surface would be exposed to increased levels of radiation, potentially leading to significant changes in the planet’s climate and ecosystems.