Toxic stress is a state of chronic stress that can have devastating effects on an individual's physical and mental health. It occurs when an individual experiences prolonged exposure to stressful situations, such as poverty, abuse, or neglect, without adequate support or resources to cope. This type of stress can alter the body's stress response system, leading to changes in the brain, nervous system, and other bodily functions. As a result, toxic stress can increase the risk of developing various health problems, including anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and even chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
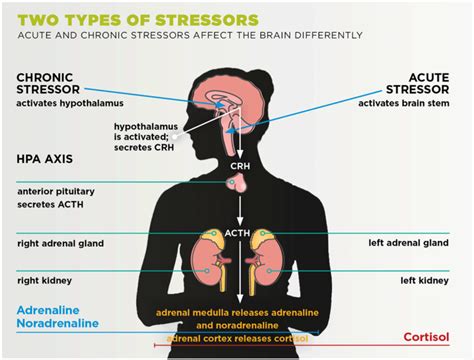
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, toxic stress can have a profound impact on a child's developing brain and body. When a child experiences toxic stress, their brain's stress response system is activated, releasing stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. While these hormones can help the child respond to the immediate threat, chronic exposure can lead to changes in the brain's structure and function, affecting areas responsible for learning, memory, and emotional regulation. Furthermore, toxic stress can also affect the development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which plays a critical role in regulating the body's stress response.
Key Points
- Toxic stress is a state of chronic stress that can have devastating effects on physical and mental health.
- It occurs when an individual experiences prolonged exposure to stressful situations without adequate support or resources to cope.
- Toxic stress can alter the body's stress response system, leading to changes in the brain, nervous system, and other bodily functions.
- It can increase the risk of developing various health problems, including anxiety, depression, PTSD, and chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
- Early intervention and support can help mitigate the effects of toxic stress and promote healthy development.
Causes and Consequences of Toxic Stress

The causes of toxic stress are varied and can include experiences like physical or emotional abuse, neglect, poverty, and exposure to violence. Additionally, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) can also contribute to the development of toxic stress. ACEs refer to traumatic events that occur during childhood, such as parental substance abuse, divorce, or incarceration. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 61% of adults in the United States have experienced at least one ACE, and 16% have experienced four or more.
The consequences of toxic stress can be severe and long-lasting. Chronic exposure to stress can lead to changes in the brain's structure and function, affecting areas responsible for learning, memory, and emotional regulation. This can result in difficulties with academic and professional achievement, as well as increased risk of mental health problems like anxiety and depression. Furthermore, toxic stress can also increase the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease, as the body's stress response system is designed to respond to immediate threats, rather than chronic stress.
The Impact of Toxic Stress on Physical Health
Toxic stress can have a profound impact on physical health, increasing the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. When the body’s stress response system is activated, it releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can help the body respond to immediate threats. However, chronic exposure to these hormones can lead to changes in the body’s physiological response, affecting areas like the immune system and metabolic function. For example, chronic stress can lead to increased inflammation, which can contribute to the development of chronic diseases like arthritis and cardiovascular disease.
| Category | Effect of Toxic Stress |
|---|---|
| Immune System | Increased inflammation, impaired immune function |
| Metabolic Function | Changes in glucose regulation, increased risk of diabetes |
| Cardiovascular Health | Increased blood pressure, cardiovascular disease risk |
| Mental Health | Increased risk of anxiety, depression, PTSD |
Mitigating the Effects of Toxic Stress

Mitigating the effects of toxic stress requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the individual’s physical, emotional, and social needs. This can include interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which can help individuals develop coping skills and strategies to manage stress. Additionally, mindfulness-based interventions like meditation and yoga can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. It is also essential to address the underlying causes of toxic stress, providing support and resources to individuals and families affected by poverty, abuse, or neglect.
In conclusion, toxic stress is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive approach to mitigation and prevention. By understanding the causes and consequences of toxic stress, we can develop effective interventions and support systems to promote healthy development and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. As a society, it is essential that we prioritize the well-being of individuals and families, providing resources and support to those affected by toxic stress.
What is toxic stress, and how does it affect physical and mental health?
+Toxic stress is a state of chronic stress that can have devastating effects on physical and mental health. It occurs when an individual experiences prolonged exposure to stressful situations without adequate support or resources to cope, leading to changes in the brain, nervous system, and other bodily functions.
What are the causes of toxic stress, and how can they be prevented?
+The causes of toxic stress include experiences like physical or emotional abuse, neglect, poverty, and exposure to violence. Prevention requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes of toxic stress, providing support and resources to individuals and families affected by these experiences.
What are the consequences of toxic stress, and how can they be mitigated?
+The consequences of toxic stress can be severe and long-lasting, increasing the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease, as well as mental health problems like anxiety and depression. Mitigation requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the individual’s physical, emotional, and social needs, including interventions like CBT and mindfulness-based interventions.



