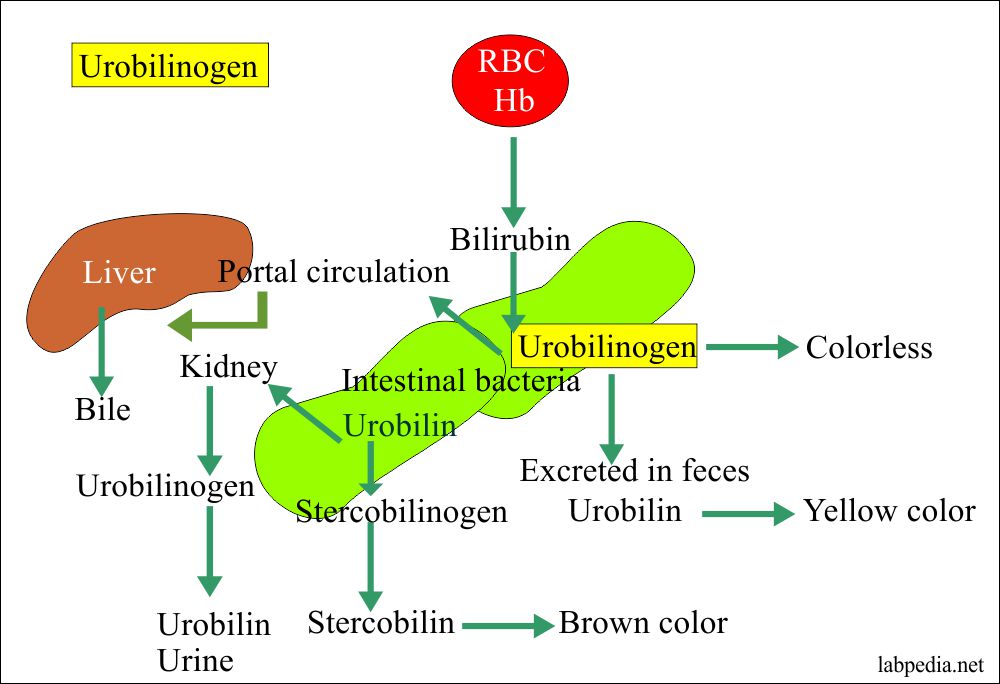
Urobilinogen is a colorless byproduct of the breakdown of hemoglobin, which is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. When red blood cells die, they are broken down, and the hemoglobin is converted into bilirubin, which is then processed by the liver and excreted into the bile. In the intestines, bilirubin is further broken down by bacteria into urobilinogen, which is then absorbed back into the bloodstream and either excreted in the urine or feces.
The presence of urobilinogen in urine is a normal finding, as small amounts are always present due to the breakdown of red blood cells. However, elevated levels of urobilinogen in urine can indicate certain medical conditions, such as liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or infections. In these cases, the body's ability to process and eliminate urobilinogen is impaired, leading to increased levels in the urine.
Key Points
- Urobilinogen is a byproduct of hemoglobin breakdown and is normally present in small amounts in urine.
- Elevated levels of urobilinogen in urine can indicate liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or infections.
- The liver plays a crucial role in processing and eliminating urobilinogen from the body.
- Urobilinogen is also excreted in the feces, where it gives stool its characteristic brown color.
- Abnormal levels of urobilinogen in urine can be detected through a urinalysis, which is a common diagnostic test.
Causes of Elevated Urobilinogen in Urine

There are several medical conditions that can cause elevated levels of urobilinogen in urine. These include liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, which can impair the liver’s ability to process and eliminate urobilinogen. Hemolytic anemia, which is a condition where red blood cells are broken down faster than they can be replaced, can also lead to increased levels of urobilinogen in urine.
Infections, such as those caused by bacteria or viruses, can also cause elevated levels of urobilinogen in urine. For example, a bacterial infection in the intestines can increase the production of urobilinogen, leading to higher levels in the urine. In some cases, elevated urobilinogen levels can also be caused by medications, such as certain antibiotics or antihistamines, which can affect the liver's ability to process and eliminate urobilinogen.
Diagnostic Tests for Urobilinogen in Urine
A urinalysis is a common diagnostic test used to detect abnormal levels of urobilinogen in urine. This test involves collecting a urine sample and analyzing it for various substances, including urobilinogen. The test can detect both the presence and concentration of urobilinogen in the urine, which can help diagnose and monitor certain medical conditions.
| Urobilinogen Level | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Normal | 0.2-1.0 mg/dL |
| Elevated | 1.1-2.0 mg/dL |
| Highly Elevated | >2.0 mg/dL |

Treatment and Management of Elevated Urobilinogen in Urine

The treatment and management of elevated urobilinogen in urine depend on the underlying cause of the condition. For example, if the elevated levels are caused by liver disease, treatment may involve medications to manage the underlying condition, such as antiviral medications or corticosteroids. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding alcohol or maintaining a healthy diet, may also be recommended.
In cases where elevated urobilinogen levels are caused by hemolytic anemia, treatment may involve medications to manage the underlying condition, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. In some cases, blood transfusions may also be necessary to replace red blood cells that have been broken down.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While some medical conditions that cause elevated urobilinogen levels in urine cannot be prevented, there are certain lifestyle modifications that can help reduce the risk of developing these conditions. For example, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress can help reduce the risk of liver disease.
In addition, getting regular check-ups and screenings can help detect medical conditions early on, when they are more easily treatable. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, can also help prevent infections that can cause elevated urobilinogen levels in urine.
What is the normal range for urobilinogen in urine?
+The normal range for urobilinogen in urine is typically considered to be 0.2-1.0 mg/dL. However, this range can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used.
What are the symptoms of elevated urobilinogen in urine?
+The symptoms of elevated urobilinogen in urine can vary depending on the underlying cause of the condition. However, common symptoms include dark or tea-colored urine, pale stools, and fatigue.
How is elevated urobilinogen in urine treated?
+The treatment for elevated urobilinogen in urine depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Treatment may involve medications, lifestyle modifications, or a combination of both.
Meta Description: Learn about urobilinogen in urine, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Discover how elevated urobilinogen levels can indicate underlying medical conditions and what you can do to manage and prevent them. (147 characters)