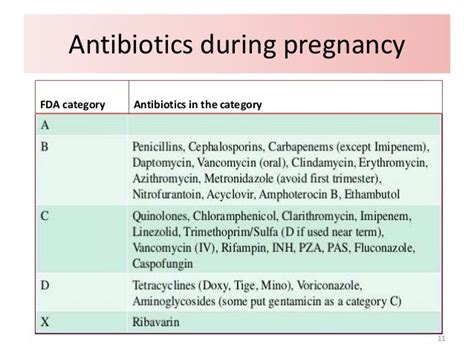
Brazil, the largest country in both South America and the Latin American region, is a nation with a rich cultural heritage and a unique linguistic identity. The official language of Brazil is Portuguese, which distinguishes it from its Spanish-speaking neighbors. This distinction is rooted in the country's history, having been a Portuguese colony from the early 16th century until its independence in 1822. The impact of Portuguese colonization on the language spoken in Brazil is profound, with Portuguese being the only language of government, education, media, and daily life.
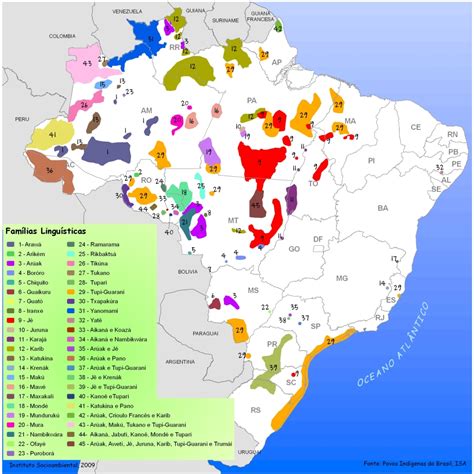
The use of Portuguese in Brazil has evolved over time, influenced by the country's indigenous peoples, African slaves, and European immigrants. This blend of influences has resulted in a variety of Portuguese that is distinct from the European version, with differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. For example, Brazilian Portuguese often uses more open vowels and diphthongs compared to European Portuguese, and there are numerous words and expressions that are unique to Brazil or have different meanings than their European counterparts.
Language Characteristics and History
Brazilian Portuguese has a history that spans nearly five centuries, with the first Portuguese settlers arriving in the early 16th century. Over time, the language has been shaped by various factors, including the indigenous languages of the native populations, the languages of African slaves brought to the country, and the languages of European immigrants who arrived in Brazil, particularly from Italy and Spain, during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. This melting pot of languages has contributed to the unique characteristics of Brazilian Portuguese, making it a vital part of Brazilian culture and identity.
Language and Culture Integration
The integration of language and culture in Brazil is complex and multifaceted. Language plays a crucial role in shaping cultural identity, and in Brazil, this is evident in the country’s literature, music, and art. The use of Portuguese has facilitated the exchange of ideas and cultural practices between Brazil and other Portuguese-speaking countries, such as Portugal, Angola, and Mozambique. Furthermore, the distinctive features of Brazilian Portuguese, such as its vocabulary and pronunciation, reflect the country’s history of immigration and cultural exchange, making it a unique element of Brazilian cultural heritage.
| Language Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Brazilian Portuguese is known for its open vowels and diphthongs, which differentiate it from European Portuguese. |
| Vocabulary | Includes words and expressions influenced by indigenous languages, African languages, and other European languages. |
| Grammar | Similar to European Portuguese, with some differences in verb conjugation and sentence structure. |
Key Points

Key Facts About the Brazilian Language
- Brazil is the only country in South America where Portuguese is the official language.
- Brazilian Portuguese has distinct differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar compared to European Portuguese.
- The language has been influenced by indigenous languages, African languages, and other European languages, reflecting the country’s history of immigration and cultural exchange.
- Portuguese is the language of government, education, media, and daily life in Brazil.
- Understanding Brazilian Portuguese is essential for communicating effectively in Brazil and for appreciating the country’s unique cultural identity.
In conclusion, the Brazilian language is a vital component of the country's cultural identity, reflecting its history, cultural exchange, and unique characteristics. The distinct features of Brazilian Portuguese, such as its pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar, make it an essential aspect of Brazilian heritage and a key factor in the country's cultural and linguistic diversity.
What is the official language of Brazil?
+The official language of Brazil is Portuguese.
How does Brazilian Portuguese differ from European Portuguese?
+Brazilian Portuguese differs from European Portuguese in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar, due to influences from indigenous languages, African languages, and other European languages.
What role does language play in Brazilian culture?
+Language plays a crucial role in Brazilian culture, shaping cultural identity, facilitating cross-cultural communication, and reflecting the country’s history and cultural exchange.