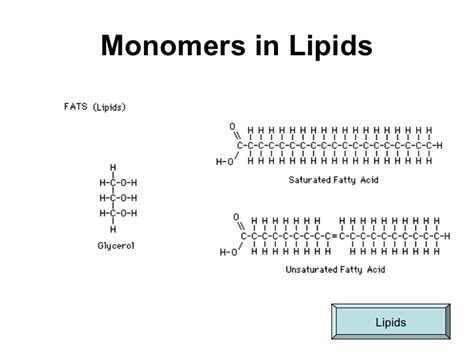
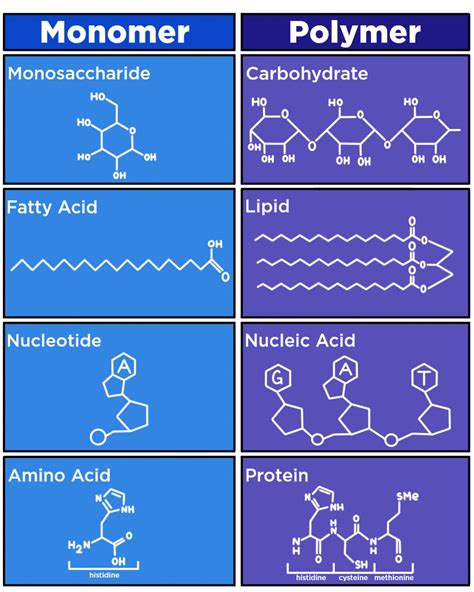
Lipid monomers are the fundamental building blocks of lipids, a diverse group of biomolecules that play critical roles in various biological processes. The composition of lipid monomers is characterized by their unique structural features, which determine their functional properties and interactions within biological systems. Understanding the composition of lipid monomers is essential for elucidating their roles in maintaining cellular integrity, regulating metabolic pathways, and influencing disease pathogenesis.
The primary lipid monomers are glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphoric acid, which combine to form various types of lipids, including triglycerides, phospholipids, and sphingolipids. Glycerol, a three-carbon molecule, serves as the backbone for triglycerides and phospholipids, while fatty acids, which are hydrophobic chains of varying lengths, contribute to the hydrophobic core of lipids. Phosphoric acid, a polar molecule, is a key component of phospholipids, enabling them to interact with aqueous environments and form lipid bilayers.
Key Points
- Lipid monomers are the basic building blocks of lipids, consisting of glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphoric acid.
- The composition of lipid monomers determines their functional properties and interactions within biological systems.
- Glycerol serves as the backbone for triglycerides and phospholipids, while fatty acids contribute to the hydrophobic core of lipids.
- Phosphoric acid is a key component of phospholipids, enabling them to interact with aqueous environments and form lipid bilayers.
- Understanding the composition of lipid monomers is essential for elucidating their roles in maintaining cellular integrity, regulating metabolic pathways, and influencing disease pathogenesis.
Types of Lipid Monomers

Lipid monomers can be categorized into several types based on their chemical structure and functional properties. Fatty acids, for example, can be classified as saturated or unsaturated, depending on the presence of double bonds in their hydrophobic chains. Saturated fatty acids, such as palmitic acid and stearic acid, have no double bonds and are typically solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic acid and linoleic acid, contain one or more double bonds and are generally liquid at room temperature.
Phospholipids, another type of lipid monomer, consist of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphoric acid group. The phosphoric acid group is linked to a variety of head groups, such as choline, ethanolamine, and serine, which determine the phospholipid's functional properties and interactions with other biomolecules. Phosphatidylcholine, for instance, is a type of phospholipid that contains a choline head group and is a major component of cellular membranes.
Fatty Acid Composition
The fatty acid composition of lipid monomers is a critical determinant of their functional properties and interactions within biological systems. Fatty acids can vary in chain length, degree of unsaturation, and branching, which influence their melting points, fluidity, and interactions with other lipids and proteins. For example, the fatty acid composition of phospholipids can affect the fluidity of cellular membranes, with unsaturated fatty acids contributing to increased fluidity and saturated fatty acids promoting rigidity.
| Fatty Acid Type | Chain Length | Degree of Unsaturation |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fatty Acids | 12-24 carbons | 0 double bonds |
| Monounsaturated Fatty Acids | 12-24 carbons | 1 double bond |
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids | 12-24 carbons | 2 or more double bonds |
Lipid Monomer Interactions

Lipid monomers interact with each other and with other biomolecules to form complex structures and regulate various biological processes. The interactions between lipid monomers are influenced by their chemical structure, functional properties, and environmental conditions. For example, the interactions between phospholipids and cholesterol can modulate the fluidity of cellular membranes, while the interactions between fatty acids and proteins can regulate metabolic pathways and influence disease pathogenesis.
The interactions between lipid monomers and other biomolecules are also critical for maintaining cellular integrity and regulating biological processes. For instance, the interactions between lipid monomers and proteins can influence protein function, localization, and degradation, while the interactions between lipid monomers and carbohydrates can regulate cellular signaling and metabolism.
Biological Functions of Lipid Monomers
Lipid monomers play critical roles in various biological processes, including energy storage, membrane structure, and cellular signaling. Triglycerides, for example, are a type of lipid monomer that serves as a primary energy storage molecule in adipocytes, while phospholipids are essential components of cellular membranes and play a critical role in maintaining membrane structure and function.
Sphingolipids, another type of lipid monomer, are involved in cellular signaling and play a critical role in regulating various biological processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival. The biological functions of lipid monomers are influenced by their chemical structure, functional properties, and interactions with other biomolecules, highlighting the importance of understanding the composition and interactions of lipid monomers in biological systems.
What are the primary components of lipid monomers?
+The primary components of lipid monomers are glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphoric acid.
What is the role of fatty acid composition in lipid monomers?
+The fatty acid composition of lipid monomers is a critical determinant of their functional properties and interactions within biological systems.
What are the biological functions of lipid monomers?
+Lipid monomers play critical roles in various biological processes, including energy storage, membrane structure, and cellular signaling.
In conclusion, the composition of lipid monomers is a critical determinant of their functional properties and interactions within biological systems. Understanding the types and proportions of lipid monomers, as well as their interactions with other biomolecules, is essential for elucidating their roles in maintaining cellular integrity, regulating metabolic pathways, and influencing disease pathogenesis. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the complex relationships between lipid monomers and biological processes, and to explore the potential therapeutic applications of lipid monomer manipulation in various diseases.