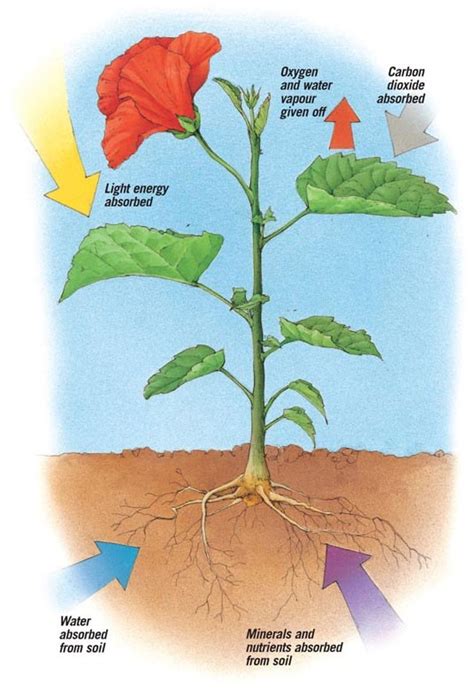
Leaves are often regarded as the primary organs of plants responsible for producing food through the process of photosynthesis. This complex biochemical process involves the conversion of light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose, a type of sugar. The equation for photosynthesis can be simplified as: 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen). This process not only sustains the plant itself but also indirectly supports nearly all life forms on Earth by producing oxygen as a byproduct.
The structure of leaves is highly specialized to maximize the efficiency of photosynthesis. They are typically flat and contain a high concentration of chlorophyll, the green pigment that absorbs light energy. The arrangement of veins on the leaf's surface ensures that water and minerals are evenly distributed, while the stomata (small pores) facilitate the exchange of gases, including the intake of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen and water vapor. This intricate system allows leaves to play a critical role in the global carbon cycle and the Earth's climate system.
Key Points
- Leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
- The primary product of photosynthesis is glucose, which serves as a source of energy for the plant.
- Oxygen is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis, supporting aerobic life forms.
- The structure of leaves, including their flat shape and high chlorophyll content, is optimized for photosynthesis.
- Leaves play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle and Earth's climate through their regulation of gas exchange.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll, found in the chloroplasts of leaf cells, is essential for the absorption of light energy. There are several types of chlorophyll, but chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are the most common in higher plants. These pigments absorb light in the blue and red parts of the visible spectrum but reflect green light, which is why they appear green to our eyes. The energy from absorbed light is then transferred to other molecules, initiating a series of chemical reactions that ultimately produce glucose and oxygen.
Efficiency of Photosynthesis
The efficiency of photosynthesis can vary depending on several factors, including light intensity, temperature, water availability, and the concentration of carbon dioxide. Under optimal conditions, the maximum efficiency of photosynthesis is around 3-6% of the incoming solar radiation, though this can be significantly lower in less favorable conditions. Despite this relatively low efficiency, photosynthesis is the foundation of most food chains and the primary means by which energy enters ecosystems.
| Factor | Optimal Condition | Effect on Photosynthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Light Intensity | Full sun to partial shade | Increases rate of photosynthesis up to a point, then can cause photoinhibition |
| Temperature | 20-30°C (68-86°F) | Optimizes enzyme activity and metabolic rates |
| Water Availability | Adequate moisture | Essential for maintaining turgor pressure and transporting nutrients |
| CO2 Concentration | 400-1000 ppm | Increases rate of photosynthesis, especially in C3 plants |

Technological and Ecological Implications

The study of leaves and photosynthesis has significant implications for both technology and ecology. In terms of technology, understanding how plants optimize their photosynthetic processes can inform the development of more efficient solar cells and other energy-harvesting technologies. Ecologically, the health and productivity of plant communities, which are heavily influenced by their ability to undergo photosynthesis, have profound effects on biodiversity, soil quality, and the global climate.
Sustainable Practices and Future Directions
Given the importance of photosynthesis, adopting sustainable practices that promote plant health and productivity is essential. This can include using farming techniques that minimize soil disturbance, optimizing water use, and reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Future research directions may focus on genetically engineering crops to enhance their photosynthetic efficiency, developing more accurate models of photosynthesis to predict plant responses to environmental changes, and exploring how photosynthetic organisms can be used in novel, bio-inspired technologies.
What is the primary function of leaves in plants?
+The primary function of leaves is to produce food for the plant through the process of photosynthesis, using energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
How does the structure of leaves contribute to photosynthesis?
+The flat shape of leaves maximizes their surface area exposed to sunlight, and their venation ensures efficient transport of water and minerals. Chlorophyll and other pigments in the leaf's cells absorb light energy, which is then used in photosynthesis.
What factors can limit the rate of photosynthesis?
+Limiting factors include insufficient light, extreme temperatures, lack of water, and low concentrations of carbon dioxide. These factors can reduce the efficiency of photosynthesis and, consequently, the growth and productivity of plants.
In conclusion, the role of leaves in producing food for plants through photosynthesis is not only vital for the survival of plants themselves but also underpins the entire food chain and contributes significantly to the Earth’s ecosystem balance. Understanding the intricacies of photosynthesis and how it is influenced by various factors is essential for addressing global challenges such as food security, climate change, and conservation of biodiversity.



