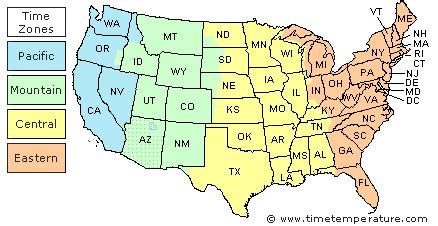
Pennsylvania, known as the Keystone State, is located in the northeastern United States and observes the Eastern Time Zone (ET). The Eastern Time Zone is one of the six time zones in the United States and is identified by the UTC-5 offset. This means that during standard time, Pennsylvania is five hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The state's location in the Eastern Time Zone has significant implications for its economy, culture, and daily life, as it is strategically positioned to facilitate trade and communication with other major cities and states along the East Coast.
Key Points
- Pennsylvania is located in the Eastern Time Zone (ET), which is UTC-5.
- The state observes daylight saving time (DST), with clocks springing forward one hour in March and falling back one hour in November.
- Pennsylvania's time zone has economic and cultural implications, including facilitating trade and communication with other East Coast states.
- The state's location in the Eastern Time Zone also affects its daily life, with businesses and residents adapting to the time zone's schedule.
- Pennsylvania's time zone is closely tied to its history and geography, with the state's position in the northeastern United States influencing its time zone designation.
Understanding Time Zones in Pennsylvania

Pennsylvania’s time zone is an essential aspect of its daily life and operations. The Eastern Time Zone is the most populous time zone in the United States, with numerous major cities, including New York City, Boston, and Washington, D.C., located within it. This time zone is also home to many significant economic and cultural centers, making it a critical component of the country’s overall economy and cultural landscape. The time zone’s impact on Pennsylvania’s economy and culture is multifaceted, with the state’s businesses, schools, and residents all adapting to the time zone’s schedule.
Daylight Saving Time in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, like most states in the United States, observes daylight saving time (DST). DST is the practice of temporarily advancing clocks during the summer months by one hour so that people can make the most of the sunlight during their waking hours. In Pennsylvania, clocks spring forward one hour in March, typically on the second Sunday, and fall back one hour in November, usually on the first Sunday. This practice is designed to reduce energy consumption, promote outdoor activities, and improve overall productivity. However, the effectiveness of DST has been debated, with some arguing that it has little impact on energy consumption and can disrupt sleep patterns and other aspects of daily life.
| Time Zone | UTC Offset | Daylight Saving Time |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Time Zone (ET) | -5 | Observed, with clocks springing forward one hour in March and falling back one hour in November |

Implications of Pennsylvania’s Time Zone

Pennsylvania’s time zone has numerous implications for its economy, culture, and daily life. The state’s location in the Eastern Time Zone facilitates trade and communication with other major cities and states along the East Coast, making it an attractive location for businesses and industries. Additionally, the time zone’s impact on daily life is significant, with residents and businesses adapting to the time zone’s schedule. This includes adjusting work schedules, school hours, and other daily activities to accommodate the time zone’s rhythm. Furthermore, the time zone’s influence on the state’s culture is evident in its vibrant cities, rich history, and diverse population, all of which are shaped by the state’s unique position in the Eastern Time Zone.
Economic Implications
The economic implications of Pennsylvania’s time zone are substantial. The state’s location in the Eastern Time Zone allows it to participate in the global economy, with many international businesses and financial institutions operating in the state. The time zone also facilitates trade with other states and countries, making it an essential component of the state’s economy. Moreover, the time zone’s impact on the state’s workforce is significant, with many employees working non-traditional hours to accommodate the demands of the global economy. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, in 2020, the median hourly wage for all occupations in Pennsylvania was $23.45, with the state’s economy driven by major industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
| Industry | Median Hourly Wage |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | $34.19 |
| Finance | $43.21 |
| Manufacturing | $28.45 |
What is the current time in Pennsylvania?
+The current time in Pennsylvania is Eastern Time (ET), which is UTC-5. However, during daylight saving time, the state observes Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), which is UTC-4.
Does Pennsylvania observe daylight saving time?
+Yes, Pennsylvania observes daylight saving time (DST). The state springs forward one hour in March and falls back one hour in November.
What are the implications of Pennsylvania's time zone on its economy?
+Pennsylvania's time zone has significant implications for its economy, including facilitating trade and communication with other major cities and states along the East Coast. The state's location in the Eastern Time Zone also attracts businesses and industries, making it an essential component of the state's economy.
In conclusion, Pennsylvania’s time zone is a critical aspect of its daily life and operations. The state’s location in the Eastern Time Zone has significant implications for its economy, culture, and daily life, making it essential to understand the complexities of time zone designations and their impact on the state. By recognizing the importance of Pennsylvania’s time zone, residents, businesses, and visitors can better navigate the state’s unique rhythm and make the most of their time in the Keystone State.