The concept of Lucifer, the fallen angel, has been a subject of fascination and debate among scholars, theologians, and the general public for centuries. The name Lucifer, which translates to "light-bearer" in Latin, is often associated with the morning star or the planet Venus, and its origins can be traced back to ancient Roman and Greek mythologies. However, the character of Lucifer as a fallen angel is primarily rooted in Christian theology, particularly in the Bible and subsequent interpretations by early Church Fathers.
The Biblical Account of Lucifer
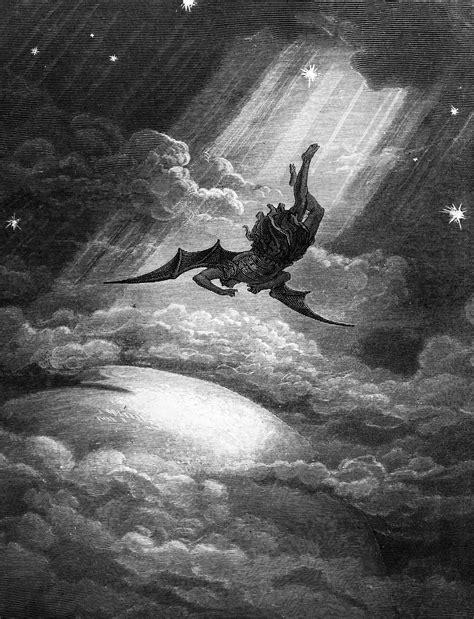

In the Bible, the character of Lucifer is not explicitly mentioned, but rather inferred through various passages, particularly in the books of Isaiah and Ezekiel. The most commonly cited reference to Lucifer is found in Isaiah 14:12, which states, “How you have fallen from heaven, O morning star, son of the dawn! You have been cast down to the earth, you who once laid low the nations!” This passage is often interpreted as a reference to a fallen angel, later identified as Lucifer, who rebelled against God and was cast out of heaven.
Early Christian Interpretations
The early Christian Church Fathers, such as Origen and Jerome, further developed the concept of Lucifer as a fallen angel, drawing from biblical passages and apocryphal texts. According to these interpretations, Lucifer was once a beautiful and powerful angel, created by God to serve as a guardian and protector of humanity. However, Lucifer’s pride and ambition led him to rebel against God, and he was subsequently cast out of heaven, along with a third of the angelic host, who became known as demons.
| Characteristics of Lucifer | Description |
|---|---|
| Pride and Ambition | Lucifer's primary motivations for rebelling against God |
| Beauty and Power | Lucifer's original attributes as a created being |
| Fall from Heaven | Lucifer's punishment for rebelling against God |
| Demonic Nature | Lucifer's subsequent role as a leader of demons |

Lucifer in Literature and Art

The character of Lucifer has been extensively explored in literature and art throughout history, from John Milton’s epic poem “Paradise Lost” to modern works such as Philip Pullman’s “His Dark Materials” series. These depictions often portray Lucifer as a complex, multifaceted character, embodying both positive and negative traits, and raising questions about the nature of good and evil, free will, and the human condition.
Psychological and Philosophical Implications
The story of Lucifer also has significant psychological and philosophical implications, as it touches on themes such as identity, morality, and the human condition. The character of Lucifer can be seen as a symbol of the shadow self, representing the repressed or hidden aspects of human personality. Additionally, the concept of Lucifer as a fallen angel raises questions about the nature of free will, the consequences of rebellion, and the complexities of moral decision-making.
Key Points
- The concept of Lucifer as a fallen angel is rooted in Christian theology, particularly in the Bible and early Church Fathers' interpretations.
- Lucifer's character is often associated with pride, ambition, and rebellion against authority.
- The story of Lucifer has been extensively explored in literature and art, raising questions about the nature of good and evil, free will, and the human condition.
- The character of Lucifer can be seen as a symbol of the shadow self, representing the repressed or hidden aspects of human personality.
- The concept of Lucifer as a fallen angel has significant psychological and philosophical implications, touching on themes such as identity, morality, and the human condition.
In conclusion, the character of Lucifer, the fallen angel, is a complex and multifaceted figure, embodying both positive and negative traits, and raising questions about the nature of good and evil, free will, and the human condition. Through its exploration in literature, art, and theology, the story of Lucifer continues to fascinate and inspire, offering insights into the human condition and the complexities of moral decision-making.
What is the origin of the name Lucifer?
+The name Lucifer is derived from the Latin word “lucem ferre,” meaning “light-bearer,” and is often associated with the morning star or the planet Venus.
What is the biblical account of Lucifer’s fall from heaven?
+The biblical account of Lucifer’s fall from heaven is found in Isaiah 14:12, which states, “How you have fallen from heaven, O morning star, son of the dawn! You have been cast down to the earth, you who once laid low the nations!”
What are the psychological and philosophical implications of the story of Lucifer?
+The story of Lucifer has significant psychological and philosophical implications, touching on themes such as identity, morality, and the human condition. The character of Lucifer can be seen as a symbol of the shadow self, representing the repressed or hidden aspects of human personality.