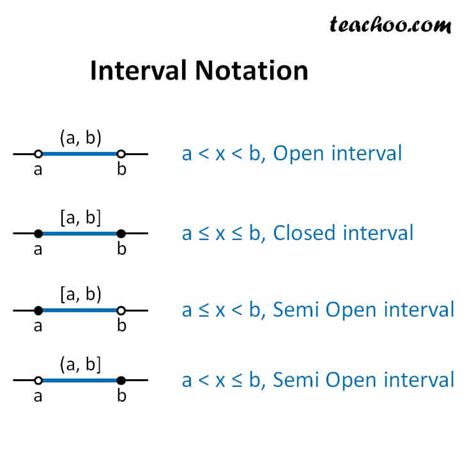
Interval notation is a crucial concept in mathematics, particularly in calculus, algebra, and real analysis. It provides a concise way to represent intervals on the real number line, which is essential for solving equations, inequalities, and analyzing functions. In this article, we will explore five ways interval notation is used, its applications, and provide examples to illustrate its importance.
Introduction to Interval Notation
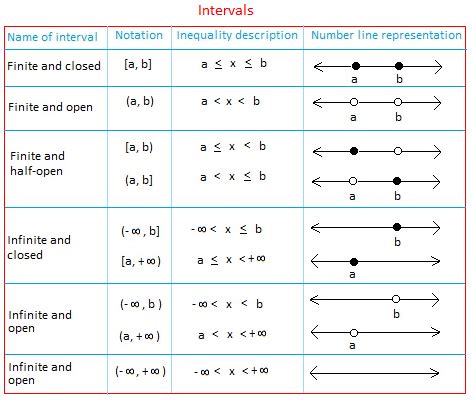
Interval notation is a mathematical notation used to represent a set of real numbers between two endpoints. It consists of a pair of numbers, often represented in square brackets or parentheses, to indicate whether the endpoints are included or excluded. The five main types of intervals are: closed, open, half-open, half-closed, and infinite intervals. Understanding interval notation is vital for solving problems in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields.
Key Points
- Interval notation represents sets of real numbers between two endpoints.
- There are five main types of intervals: closed, open, half-open, half-closed, and infinite intervals.
- Interval notation is crucial for solving equations, inequalities, and analyzing functions.
- Applications of interval notation include calculus, algebra, real analysis, physics, and engineering.
- Understanding interval notation is essential for problem-solving in various mathematical and scientific contexts.
1. Solving Inequalities with Interval Notation
One of the primary applications of interval notation is solving inequalities. When solving linear inequalities, the solution set can be represented using interval notation. For example, the inequality x > 2 can be represented as (2, \infty), indicating that x is greater than 2. Similarly, the inequality x \leq 5 can be represented as (-\infty, 5], indicating that x is less than or equal to 5.
Examples of Solving Inequalities
Consider the inequality x^2 - 4x + 3 > 0. Factoring the quadratic equation yields (x - 3)(x - 1) > 0. The solution to this inequality is x < 1 or x > 3, which can be represented in interval notation as (-\infty, 1) \cup (3, \infty).
| Interval Notation | Example Inequality |
|---|---|
| (2, 5) | $2 < x < 5$ |
| [3, 7] | $3 \leq x \leq 7$ |
| (-∞, 2) | $x < 2$ |
| (5, ∞) | $x > 5$ |

2. Analyzing Functions with Interval Notation
Interval notation is also used to analyze functions, particularly in calculus. When studying the behavior of a function, interval notation can be used to represent the domain and range of the function. For example, the function f(x) = \frac{1}{x} has a domain of (-\infty, 0) \cup (0, \infty), indicating that the function is undefined at x = 0.
Examples of Analyzing Functions
Consider the function f(x) = \sqrt{x}. The domain of this function is [0, \infty), indicating that the function is only defined for non-negative values of x. The range of the function is also [0, \infty), indicating that the output of the function is always non-negative.
3. Calculus Applications with Interval Notation
Interval notation has numerous applications in calculus, particularly in the study of limits, derivatives, and integrals. When evaluating limits, interval notation can be used to represent the interval of convergence. For example, the series \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{1}{n^2} converges on the interval [1, \infty).
Examples of Calculus Applications
Consider the function f(x) = \frac{x^2 - 4}{x - 2}. The limit of this function as x approaches 2 can be evaluated using interval notation. The function can be simplified to f(x) = x + 2, which has a limit of 4 as x approaches 2. This can be represented in interval notation as \lim_{x \to 2} f(x) = 4.
4. Real Analysis Applications with Interval Notation

Interval notation is also essential in real analysis, particularly in the study of real numbers and their properties. When working with real numbers, interval notation can be used to represent the set of real numbers between two endpoints. For example, the set of real numbers between 2 and 5, including 2 and 5, can be represented as [2, 5].
Examples of Real Analysis Applications
Consider the set of real numbers S = \{x \in \mathbb{R} : 2 < x < 5\}. This set can be represented in interval notation as (2, 5), indicating that x is greater than 2 and less than 5.
5. Physics and Engineering Applications with Interval Notation
Interval notation has numerous applications in physics and engineering, particularly in the study of motion, forces, and energies. When modeling physical systems, interval notation can be used to represent the domain and range of physical quantities. For example, the distance traveled by an object can be represented in interval notation as [0, \infty), indicating that the distance is always non-negative.
Examples of Physics and Engineering Applications
Consider the motion of an object under the influence of gravity. The height of the object can be represented in interval notation as [0, h], where h is the maximum height reached by the object. The velocity of the object can also be represented in interval notation as [-v, v], where v is the maximum velocity reached by the object.
What is interval notation?
+Interval notation is a mathematical notation used to represent a set of real numbers between two endpoints.
What are the five main types of intervals?
+The five main types of intervals are: closed, open, half-open, half-closed, and infinite intervals.
What are some applications of interval notation?
+Applications of interval notation include calculus, algebra, real analysis, physics, and engineering.
How is interval notation used in solving inequalities?
+Interval notation is used to represent the solution set of an inequality, indicating the range of values that satisfy the inequality.
What is the importance of understanding interval notation?
+Understanding interval notation is essential for problem-solving in various mathematical and scientific contexts, including calculus, algebra, real analysis, physics, and engineering.
Meta description suggestion (140-155 characters): Learn about interval notation, its applications, and examples in mathematics, physics, and engineering.