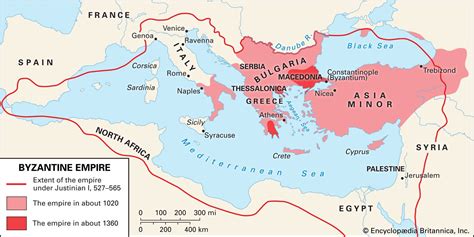
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was a vast and influential state that existed from the 4th to the 15th century. Its capital, Constantinople, was a major center of trade, culture, and learning, and the empire played a significant role in shaping the course of European history. However, the Byzantine Empire eventually fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453, marking the end of a centuries-long era of Byzantine dominance. Here are five key facts about the fall of the Byzantine Empire:
Key Points
- The Byzantine Empire faced numerous challenges, including internal conflicts, external pressures, and economic decline, which ultimately contributed to its downfall.
- The Black Death, which ravaged Europe in the 14th century, had a devastating impact on the Byzantine Empire, weakening its population and economy.
- The Ottoman Turks, led by Mehmed II, launched a successful siege of Constantinople in 1453, breaching the city's defenses and capturing the capital.
- The fall of the Byzantine Empire had significant cultural and historical implications, leading to a period of Ottoman dominance in the region and influencing the development of European art, architecture, and literature.
- The legacy of the Byzantine Empire continues to be felt today, with its rich cultural heritage and historical significance remaining an important part of modern society.
The Decline of the Byzantine Empire
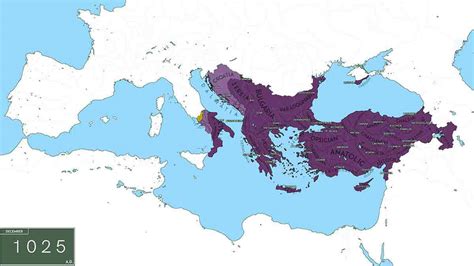
The Byzantine Empire’s decline was a gradual process that occurred over several centuries. The empire faced numerous challenges, including internal conflicts, external pressures, and economic decline. One of the major factors contributing to the empire’s decline was the constant struggle for power and influence among its ruling elite. This led to a series of civil wars and power struggles, which weakened the empire and made it more vulnerable to external threats.
External Pressures and the Rise of the Ottoman Turks
The Byzantine Empire also faced significant external pressures, particularly from the rising Ottoman Turkish Empire. The Ottomans had been expanding their territories in the region for centuries and had become a major power by the 14th century. They launched a series of attacks on the Byzantine Empire, capturing key cities and territories and eventually laying siege to Constantinople. The Ottomans’ military tactics and technology, including the use of cannons and other siege engines, gave them a significant advantage over the Byzantines.
| Event | Date | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Black Death | 1346-1353 | Devastating impact on Byzantine population and economy |
| Ottoman siege of Constantinople | 1453 | Fall of Constantinople and end of the Byzantine Empire |
| Byzantine-Ottoman War | 1326-1453 | Gradual decline of the Byzantine Empire and expansion of the Ottoman Empire |
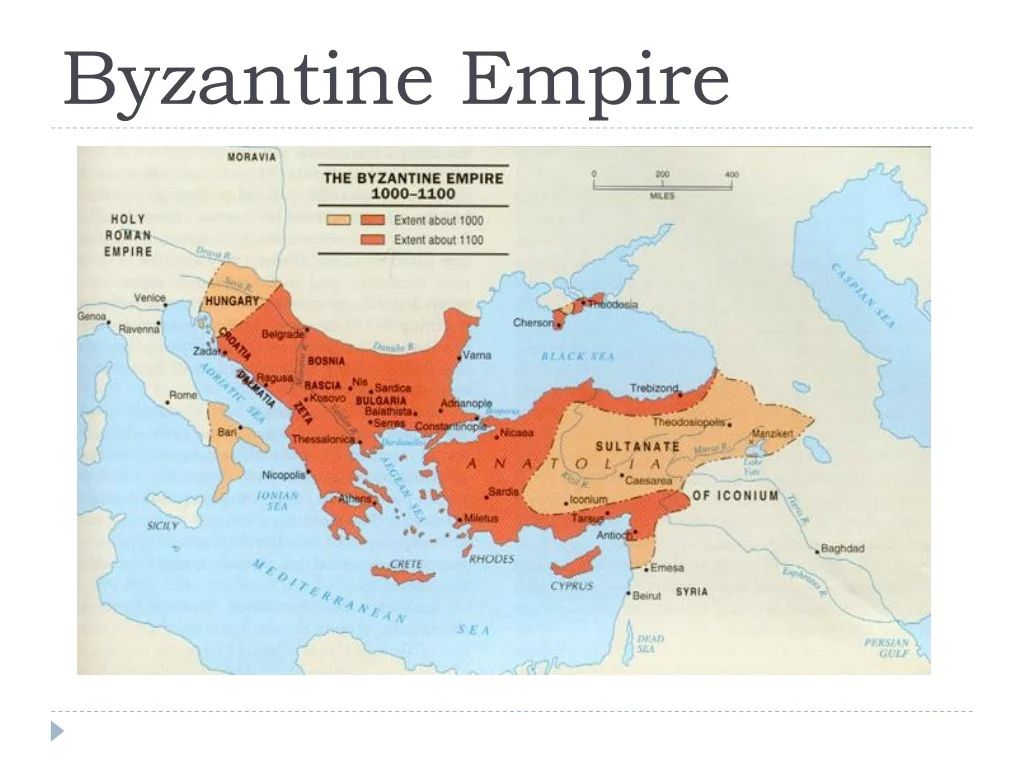
The Fall of Constantinople

The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the end of the Byzantine Empire. The city was besieged by the Ottoman Turks, led by Mehmed II, who used advanced military tactics and technology to breach the city’s defenses. The Byzantines, led by Emperor Constantine XI, fought valiantly, but they were ultimately unable to withstand the Ottoman onslaught. The city fell on May 29, 1453, and the Byzantine Empire came to an end.
Cultural and Historical Implications
The fall of the Byzantine Empire had significant cultural and historical implications. The Ottoman Turks went on to dominate the region, influencing the development of European art, architecture, and literature. The Byzantine legacy can still be seen in the many churches, monasteries, and other buildings that remain from the empire’s heyday. The empire’s cultural achievements, including its stunning mosaics, intricate manuscripts, and beautiful icons, continue to inspire and influence artists and scholars today.
What were the main factors that contributed to the fall of the Byzantine Empire?
+The main factors that contributed to the fall of the Byzantine Empire included internal conflicts, external pressures, and economic decline. The empire faced numerous challenges, including the constant struggle for power and influence among its ruling elite, the rise of the Ottoman Turks, and the devastating impact of the Black Death.
What was the significance of the fall of Constantinople in 1453?
+The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the end of the Byzantine Empire and had significant cultural and historical implications. The city’s capture by the Ottoman Turks led to a period of Ottoman dominance in the region and influenced the development of European art, architecture, and literature.
What is the legacy of the Byzantine Empire today?
+The legacy of the Byzantine Empire can still be seen today in its stunning cultural achievements, including its mosaics, manuscripts, and icons. The empire’s historical significance remains an important part of modern society, and its influence can be seen in many areas, including art, architecture, and literature.