In recent years, Tesla has emerged not just as a frontrunner in electric vehicle (EV) innovation, but as a truly global manufacturing powerhouse. From its beginnings as a niche manufacturer primarily based in California, the company's expansion strategy has transformed it into a multinational entity with production facilities spanning multiple continents. Understanding the geographic distribution of Tesla's manufacturing footprint reveals critical insights into its supply chain dynamics, regulatory environment considerations, and strategic ambitions aimed at capturing the rapidly expanding EV market. This comprehensive overview explores the various locations where Tesla's vehicles and components are produced, highlighting the operational scale, regional advantages, and future expansion plans within the context of a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
Key Points
- Tesla's manufacturing network includes facilities across North America, Asia, and Europe, reflecting a strategic approach to global market penetration.
- Primary production hubs—such as Fremont, Shanghai, and Berlin—serve as essential nodes in Tesla’s operational architecture, enabling cost efficiencies and regional customization.
- Emerging facilities and planned giga factories signify Tesla's ambition to scale production capacity and minimize supply chain dependencies.
- Manufacturing localization not only reduces tariffs and logistical costs but also aligns Tesla with regional regulatory standards.
- The geographic diversification of production supports Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy by ensuring supply resilience and market adaptability.
Foundational Overview of Tesla’s Manufacturing Footprint
At its core, Tesla’s manufacturing footprint exemplifies modern strategic industrial planning, leveraging location advantages, technological innovation, and regulatory compliance to optimize output. The inception of Tesla’s production operations in California exemplifies a typical startup approach—focused on proximity to innovation hubs and skilled labor pools. However, as Tesla’s product lines expanded and global demand surged, the company adopted a geographically diversified approach to manufacturing. This shift enabled Tesla to address regional market needs more effectively, reduce costs, and mitigate the risks associated with supply chain disruptions—a tactic particularly relevant amid the complexities of international trade and fluctuating geopolitical climates.
Investments in regional manufacturing facilities also stem from a desire to conform to local policies encouraging EV adoption, such as government incentives and emission reduction mandates. These factors combined have prompted Tesla to establish manufacturing bases that support regional compliance while maintaining its hallmark high volume, high efficiency production standards. Currently, the company operates several key facilities around the world, with others in various stages of development, demonstrating a sustained commitment toward expanding its manufacturing competence on a global scale.
Tesla’s Major Manufacturing Sites: A Global Breakdown
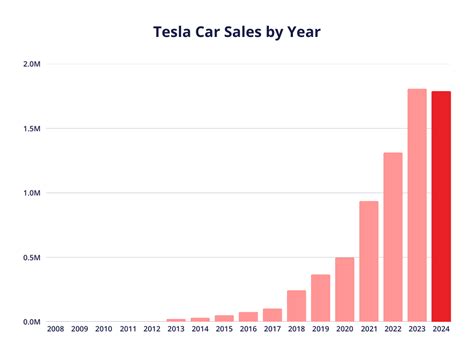
As of 2023, Tesla’s operational manufacturing footprint includes three principal factories—each serving as pillars for regional production—as well as upcoming giga factories in strategic locations. Here’s an in-depth look at each:
The Fremont Factory, California
The Fremont Factory, situated in the San Francisco Bay Area, is Tesla’s original manufacturing site and a symbol of its startup origins. Covering over 5.3 million square feet, this facility produces the Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y for the North American market. It exemplifies high-tenth manufacturing precision and integrates advanced automation to achieve exceptional efficiency levels. Despite being nestled in a region with high operational costs, Fremont remains critical for Tesla’s North American assembly, R&D activities, and as a testing ground for innovative manufacturing techniques.
Gigafactory Shanghai, China
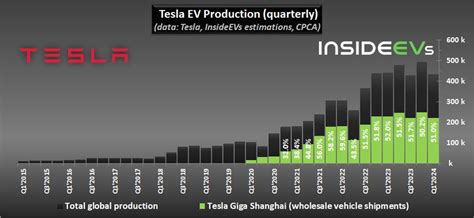
In 2019, Tesla inaugurated its first gigafactory outside North America—located in Shanghai’s Lingang Free Trade Zone. This site, officially known as Gigafactory 3, marks a pivotal step in Tesla’s localization strategy for Asia. With an initial capacity of 250,000 vehicles annually, it rapidly scaled to produce over 700,000 cars in 2022, with plans to double capacity further. The Shanghai plant’s strategic proximity to China’s vast EV market and supply chain ecosystem has enabled Tesla to reduce tariffs, lower costs, and customize vehicles for regional preferences. Additionally, China’s favorable policies towards EVs and renewable energy align with Tesla’s global mission, making Shanghai a crucial hub in its international expansion.
Giga Berlin and Brandenburg, Germany
Launched in 2022, Giga Berlin (or Giga Brandenburg) is Tesla’s first European manufacturing plant, strategically located near the German capital. Spanning approximately 740 hectares, its complex manufacturing infrastructure is designed to enable regional assembly, battery manufacturing, and supply chain integration. Giga Berlin aims to produce the Model Y primarily for the European market, which has seen rapid EV adoption owing to stringent emissions targets and support policies. The plant underscores Tesla’s long-term commitment to market diversification and regional manufacturing autonomy in Europe, supporting the EU’s sustainability initiatives.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Fremont Factory Location | San Francisco Bay Area, California; over 5.3 million sq. ft. of manufacturing space |
| Shanghai Gigafactory Annual Production | Over 700,000 vehicles in 2022; capacity expanding to approximately 1 million per year |
| Giga Berlin Capacity | Targeting 500,000 vehicles annually; focused on Model Y and battery pack production |

Emerging and Future Giga Factories: Extending Global Reach
Beyond its current operational facilities, Tesla is actively developing new giga factories, which are critical for scaling production and securing its competitive edge. Notably, the upcoming giga factory in Texas, often referred to as Giga Texas, represents a significant leap forward. Covering more than 4,000 acres, it aims to produce not only the Model Y but also the highly anticipated Cybertruck, alongside battery manufacturing capacity capable of supporting multiple models and vehicle segments.
Meanwhile, the planned Giga Mexico project is poised to serve Latin America and North America, bridging the geographical gap and fostering regional supply chain development. Tesla’s approach to establishing these giga factories involves a combination of strategic location selection, regional economic incentives, and an emphasis on supply chain resilience via local sourcing. These developments hint at a future where Tesla's manufacturing network becomes even more resilient, flexible, and capable of meeting surging global demand, particularly as EV adoption accelerates worldwide.
Supply Chain and Localization Benefits
Manufacturing localization brings tangible advantages. By reducing dependence on long supply chains that often involve multi-national logistics networks, Tesla enhances its operational resilience against geopolitical risks and global disruptions. For example, the proximity of Giga Shanghai to local suppliers has shortened lead times, facilitating just-in-time manufacturing practices. Similarly, Giga Berlin’s integration with European suppliers enables adherence to EU certification standards and reduces tariffs.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Resilience | Localization reduces lead times by up to 30%, minimizes logistical disruptions, and supports rapid innovation cycles |
| Regulatory Compliance | Regional manufacturing helps Tesla meet specific safety, emissions, and quality standards, expediting vehicle certification processes |
Implications for Market Strategy and Industry Leadership
Tesla’s global manufacturing setup not only supports its capacity to scale but also influences its strategic positioning within the EV industry. Geographic diversification acts as a hedge against political and trade uncertainties, while also facilitating tailored marketing and aftersales services. Moreover, this approach has spurred competitors to reconsider their own manufacturing and supply chain configurations, pushing the entire EV sector toward greater regionalization.
From a competitive perspective, Tesla’s capacity to build giga factories in critical markets signals a long-term commitment to localization. This not only reduces operational risks but also strengthens its brand reputation as a committed local employer and technology innovator. As the market for EVs continues to grow—with projections estimating a compound annual growth rate of approximately 22% over the next five years—Tesla’s manufacturing agility will serve as a vital competitive advantage, enabling rapid scaling and adaptation to evolving consumer preferences and regulatory environments.
Where are Tesla’s main manufacturing plants located?
+Tesla’s primary manufacturing plants include the Fremont Factory in California, Gigafactory Shanghai in China, and Giga Berlin in Germany. Each site serves regional markets and reflects strategic regional investment.
What are Tesla’s future plans for manufacturing expansion?
+Upcoming giga factories in Texas (Giga Texas) and Mexico are set to expand production capacity, support new vehicle lines like the Cybertruck, and bolster supply chain resilience in North America and Latin America.
How does regional manufacturing benefit Tesla?
+Regional manufacturing minimizes logistical costs, improves supply chain resilience, helps meet local standards quicker, and accelerates market responsiveness.
What challenges does Tesla face with its global manufacturing approach?
+Challenges include managing complex supply chains, complying with diverse regulatory environments, potential geopolitical risks, and the high costs of establishing and maintaining multiple giga factories.



