Respiration is a vital process that occurs in various forms and locations throughout the natural world. While human respiration is well understood, respiration also takes place in other organisms and environments. The process of respiration involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy, which is then used to power the various functions of an organism. In this article, we will explore five places where respiration occurs, highlighting the diversity and complexity of this essential biological process.
Key Points
- Human lungs are the primary site of respiration in humans, where oxygen is inhaled and carbon dioxide is exhaled.
- Plant roots respire, releasing carbon dioxide and absorbing oxygen from the surrounding soil.
- Microorganisms such as bacteria and archaea respire in various environments, including soil, water, and the human gut.
- Fungal mycelium respire, breaking down organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide and other compounds.
- Corals respire, exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the surrounding water through a process known as diffusion.
Human Lungs
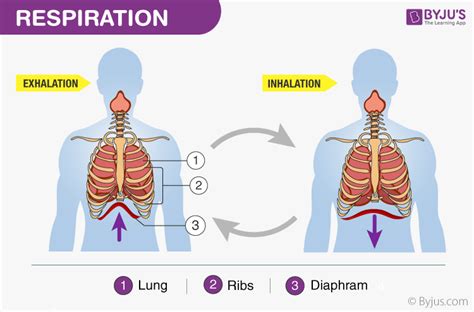
Human lungs are the primary site of respiration in humans. The process of respiration in the lungs involves the inhalation of oxygen and the exhalation of carbon dioxide. This exchange of gases occurs through the alveoli, small air sacs located at the end of the bronchioles. The alveoli are surrounded by a network of capillaries, which allow for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the lungs. The oxygen is then transported to the body’s tissues, where it is used to produce energy through the process of cellular respiration.
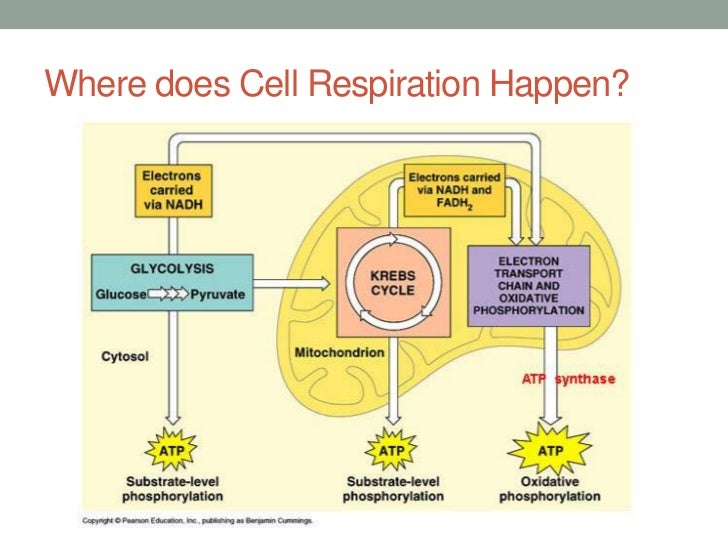
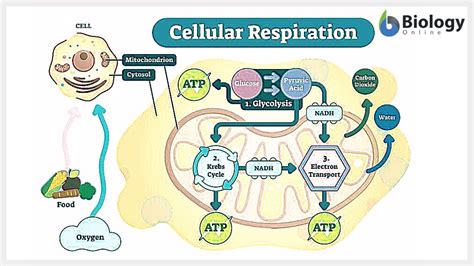
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy from the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules. This process occurs in the mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell. During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy is then used to power the various functions of the cell, including muscle contraction, nerve impulses, and biosynthesis.
Plant Roots
Plant roots respire, releasing carbon dioxide and absorbing oxygen from the surrounding soil. This process is essential for plant growth and development, as it provides the energy necessary for root growth and maintenance. Plant roots respire through a process known as aerobic respiration, which involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy. This energy is then used to power the various functions of the plant, including root growth, stem elongation, and leaf expansion.
Soil Microorganisms
Soil microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, respire in the soil, breaking down organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide and other compounds. These microorganisms play a crucial role in the decomposition process, as they break down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds that can be used by plants and other organisms. Soil microorganisms also contribute to the formation of soil structure and fertility, making it possible for plants to grow and thrive.
Fungal Mycelium
Fungal mycelium respire, breaking down organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide and other compounds. Fungal mycelium is a network of fine, branching filaments that absorb nutrients from the surrounding environment. This process of absorption and breakdown of organic matter is essential for fungal growth and development, as it provides the energy necessary for mycelium expansion and maintenance. Fungal mycelium also plays a crucial role in the decomposition process, as it breaks down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds that can be used by other organisms.
Corals
Corals respire, exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the surrounding water through a process known as diffusion. Corals are small, sessile animals that are attached to a substrate, such as a rock or reef. They have a symbiotic relationship with algae, which provide them with nutrients through photosynthesis. Corals respire through a process known as aerobic respiration, which involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy. This energy is then used to power the various functions of the coral, including growth, maintenance, and reproduction.
| Organism | Respiration Process |
|---|---|
| Humans | Aerobic respiration, involving the breakdown of glucose to produce energy |
| Plant Roots | Aerobic respiration, involving the breakdown of glucose to produce energy |
| Soil Microorganisms | Aerobic and anaerobic respiration, involving the breakdown of organic matter to produce energy |
| Fungal Mycelium | Aerobic respiration, involving the breakdown of organic matter to produce energy |
| Corals | Aerobic respiration, involving the breakdown of glucose to produce energy |
What is the primary function of respiration in humans?
+The primary function of respiration in humans is to provide energy for the body's tissues through the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules.
How do plant roots respire?
+Plant roots respire through a process known as aerobic respiration, which involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy.
What role do soil microorganisms play in the decomposition process?
+Soil microorganisms play a crucial role in the decomposition process, as they break down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds that can be used by plants and other organisms.
How do corals respire?
+Corals respire through a process known as diffusion, exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the surrounding water.
What is the importance of respiration in fungi?
+Respiration is essential for fungal growth and development, as it provides the energy necessary for mycelium expansion and maintenance.
Meta Description: Discover the diverse ways in which respiration occurs in different organisms and environments, from human lungs to plant roots to fungal mycelium. Learn about the importance of respiration in various ecosystems and the complex interactions between living things and their environments. (149 characters)