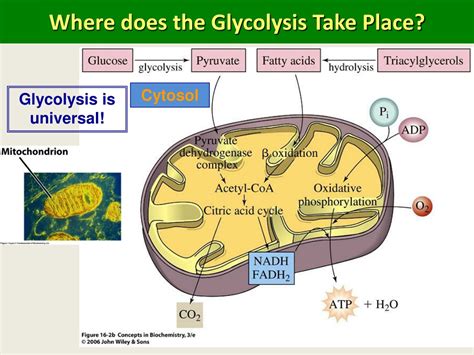
Glycolysis is a crucial metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, where it plays a central role in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. This complex process involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, resulting in the conversion of one glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH in the process. As the first step in cellular respiration, glycolysis is essential for the production of energy in the form of ATP, which is then used to power various cellular functions. The fact that glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm allows for the efficient regulation of this pathway, as it can be readily influenced by the cell's energy needs and the availability of glucose.
The cytoplasmic location of glycolysis also enables the cell to respond quickly to changes in energy demand, as the enzymes involved in this pathway are present in the cytosol and can be readily activated or inhibited as needed. Furthermore, the proximity of glycolysis to other metabolic pathways, such as the pentose phosphate pathway and the citric acid cycle, allows for the efficient exchange of intermediates and the coordination of cellular metabolism. With a deeper understanding of the mechanisms and regulation of glycolysis, researchers can gain valuable insights into the complex processes that underlie cellular energy production and the development of various diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders.
Key Points
- Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, where it breaks down glucose to produce energy.
- This pathway involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, resulting in the conversion of one glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules.
- Glycolysis generates a small amount of ATP and NADH, which are then used to power various cellular functions.
- The cytoplasmic location of glycolysis allows for the efficient regulation of this pathway, enabling the cell to respond quickly to changes in energy demand.
- Understanding the mechanisms and regulation of glycolysis can provide valuable insights into cellular energy production and the development of various diseases.
Glycolytic Pathway Overview

The glycolytic pathway can be divided into two main stages: the energy investment phase and the energy generation phase. The energy investment phase involves the conversion of glucose into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, which requires the investment of two ATP molecules. The energy generation phase, on the other hand, involves the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into pyruvate, generating four ATP molecules and two NADH molecules in the process. The net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules makes glycolysis a crucial energy-producing pathway in cells.
Enzymes Involved in Glycolysis
The glycolytic pathway involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, each of which is mediated by a specific enzyme. These enzymes include hexokinase, phosphoglucose isomerase, aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase, and pyruvate kinase, among others. Each of these enzymes plays a critical role in the regulation of glycolysis, and their activity can be influenced by various factors, including the availability of substrates, the energy needs of the cell, and the presence of regulatory molecules.
| Enzyme | Reaction | Substrates | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hexokinase | Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP | Glucose, ATP | Glucose-6-phosphate, ADP |
| Phosphoglucose Isomerase | Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate | Glucose-6-phosphate | Fructose-6-phosphate |
| Aldolase | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + Dihydroxyacetone phosphate | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, Dihydroxyacetone phosphate |
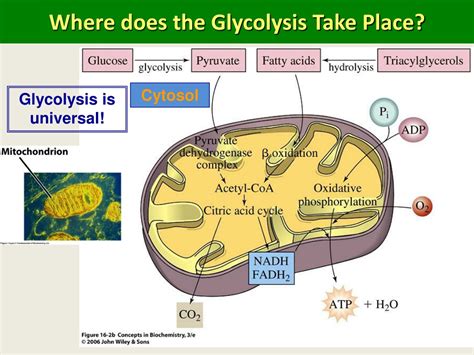
Regulation of Glycolysis

The regulation of glycolysis is a critical process that ensures the efficient production of energy in cells. This regulation involves the coordinated action of multiple enzymes and regulatory molecules, including ATP, ADP, and NADH. The activity of these enzymes can be influenced by various factors, including the availability of substrates, the energy needs of the cell, and the presence of regulatory molecules. For example, the enzyme pyruvate kinase is inhibited by high levels of ATP, which indicates that the cell has sufficient energy and does not require additional glucose breakdown.
Feedback Inhibition
Feedback inhibition is a critical mechanism that regulates the activity of enzymes involved in glycolysis. This process involves the inhibition of enzyme activity by the accumulation of downstream products, which prevents the overproduction of energy and maintains the balance of cellular metabolism. For example, the accumulation of ATP inhibits the activity of phosphofructokinase, which is a key enzyme in the glycolytic pathway. This inhibition prevents the overproduction of ATP and maintains the balance of cellular energy production.
In conclusion, glycolysis is a critical metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, where it plays a central role in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. The regulation of glycolysis is a complex process that involves the coordinated action of multiple enzymes and regulatory molecules, ensuring the efficient production of energy in cells. Understanding the mechanisms that underlie the regulation of glycolysis can provide valuable insights into the development of various diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders.
What is the main function of glycolysis in cells?
+The main function of glycolysis is to break down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP, which is then used to power various cellular functions.
Where does glycolysis take place in cells?
+Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of cells, where it can be readily influenced by the cell’s energy needs and the availability of glucose.
What are the key enzymes involved in glycolysis?
+The key enzymes involved in glycolysis include hexokinase, phosphoglucose isomerase, aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase, and pyruvate kinase, among others.