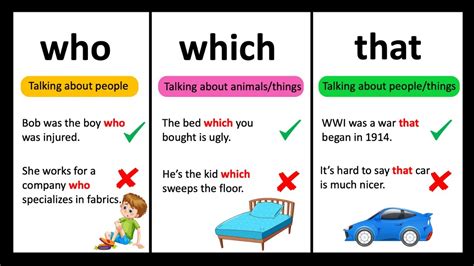
When it comes to the English language, few grammatical elements can be as confusing as the words "which" and "that." Both are used to introduce dependent clauses, but they serve different purposes and are used in different contexts. Understanding the difference between "which" and "that" is crucial for clear and effective communication. In this article, we will delve into the distinctions between these two words, providing you with 5 tips to help you use them correctly.
Understanding the Basics

The primary distinction between “which” and “that” lies in the type of clause they introduce. “That” is used to introduce a restrictive clause, which is essential to the meaning of the sentence. On the other hand, “which” introduces a non-restrictive clause, which provides additional information that is not essential to the sentence’s meaning. To illustrate this difference, consider the following examples:
A sentence using "that" might look like this: "The book that is on the table is mine." Here, "that is on the table" is a restrictive clause because it specifies which book is being referred to. Without this clause, the sentence would be unclear.
In contrast, a sentence using "which" could be: "The book, which is on the table, is mine." The clause "which is on the table" is non-restrictive because it provides additional information about the book, but the sentence would still be clear without it.
Tips for Using “Which” and “That” Correctly
Here are five tips to help you decide whether to use “which” or “that” in your writing:
- Identify the Clause Type: Determine whether the clause is restrictive or non-restrictive. If it's restrictive, use "that." If it's non-restrictive, use "which."
- Punctuation Matters: Non-restrictive clauses introduced by "which" are usually set off by commas. Restrictive clauses introduced by "that" are not.
- Essential vs. Non-Essential Information: Ask yourself if the information in the clause is essential to the meaning of the sentence. If it is, use "that." If not, use "which."
- Relative Pronoun Role: Consider the role of the relative pronoun in the sentence. "That" is more commonly used when referring to things, while "which" can refer to both things and ideas.
- Read Aloud: Sometimes, reading your sentence aloud can help you decide. If the clause sounds like an aside or additional information, it's likely a non-restrictive clause that should be introduced by "which."
| Word | Clause Type | Punctuation |
|---|---|---|
| That | Restrictive | No commas |
| Which | Non-Restrictive | Commas |

Key Points
- Use "that" for restrictive clauses and "which" for non-restrictive clauses.
- Punctuation can help differentiate between restrictive and non-restrictive clauses.
- Determine if the clause provides essential or non-essential information to decide between "that" and "which."
- The role of the relative pronoun and the subject of the clause can influence the choice between "that" and "which."
- Reading your sentences aloud can provide insight into whether a clause is restrictive or non-restrictive.
Practical Applications and Common Mistakes

In practical terms, the distinction between “which” and “that” can be subtle, and even native speakers may sometimes use them incorrectly. A common mistake is using “which” in place of “that” in restrictive clauses, which can lead to ambiguity. For example, saying “The car which I bought is red” instead of “The car that I bought is red” can make the sentence less clear, as it implies the clause “which I bought” is non-essential.
Moreover, understanding the nuances of "which" and "that" can enhance your writing style, making it more precise and engaging. It shows attention to detail and a command of the language, which are essential for effective communication in both personal and professional contexts.
Looking Ahead: The Evolution of Language
Language is constantly evolving, with usage and grammatical rules changing over time. While the distinction between “which” and “that” remains a cornerstone of English grammar, it’s interesting to consider how language learning tools and writing assistants might influence their usage in the future. As AI technology advances, it may play a larger role in guiding writers towards correct usage, potentially reducing errors and improving clarity in communication.
What is the main difference between "which" and "that" in English grammar?
+The main difference is that "that" introduces a restrictive clause (essential to the sentence's meaning), while "which" introduces a non-restrictive clause (provides additional, non-essential information).
How can punctuation help in deciding between "which" and "that"?
+Punctuation can help because non-restrictive clauses (introduced by "which") are typically set off by commas, whereas restrictive clauses (introduced by "that") are not.
What role does reading aloud play in determining the correct usage of "which" and "that"?
+Reading aloud can help you decide whether a clause sounds like an essential part of the sentence (use "that") or an aside (use "which").
In conclusion, mastering the difference between “which” and “that” is a significant step towards improving your command of the English language. By understanding and applying the tips outlined above, you can enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your communication, whether in writing or speech. Remember, the key to using “which” and “that” correctly lies in identifying the type of clause you are introducing and being mindful of punctuation and the role of the relative pronoun.