The medical imaging landscape has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans emerging as two of the most widely used diagnostic tools. Both MRI and CT scans provide detailed images of the internal structures of the body, but they differ significantly in terms of their underlying technology, applications, and advantages. In this article, we will delve into the world of MRI and CT scans, exploring their principles, differences, and applications, to help you understand which one is best suited for your specific medical needs.
Key Points
- MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of internal structures, whereas CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images.
- MRI is particularly useful for imaging soft tissues, such as organs and tendons, while CT scans are better suited for imaging bones, lungs, and blood vessels.
- MRI is generally considered safer than CT scans, as it does not involve radiation, but it can be more time-consuming and expensive.
- CT scans are faster and more widely available than MRI, but they may not provide the same level of detail for certain types of tissues.
- The choice between MRI and CT scan ultimately depends on the specific medical condition being diagnosed and the individual patient's needs.
Understanding MRI and CT Scans

MRI and CT scans are both medical imaging modalities that use different technologies to produce detailed images of the internal structures of the body. MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate images, whereas CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images. The choice between MRI and CT scan depends on various factors, including the type of tissue being imaged, the medical condition being diagnosed, and the individual patient’s needs.
How MRI Works
MRI uses a strong magnetic field to align the hydrogen atoms in the body, and then uses radio waves to disturb these atoms, causing them to emit signals. These signals are then used to create detailed images of the internal structures of the body. MRI is particularly useful for imaging soft tissues, such as organs and tendons, as it can provide high-resolution images of these structures.
How CT Scans Work
CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body. The X-rays are directed at the body from different angles, and the resulting images are used to create a detailed picture of the internal structures. CT scans are particularly useful for imaging bones, lungs, and blood vessels, as they can provide high-resolution images of these structures.
| Imaging Modality | MRI | CT Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Magnetic fields and radio waves | X-rays |
| Applications | Soft tissues, organs, tendons | Bones, lungs, blood vessels |
| Radiation | No radiation | Ionizing radiation |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Generally less expensive |
| Availability | Less widely available | More widely available |

Comparing MRI and CT Scans
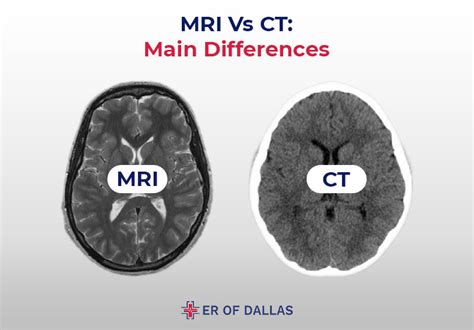
Both MRI and CT scans have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on various factors, including the type of tissue being imaged, the medical condition being diagnosed, and the individual patient’s needs. MRI is generally considered safer than CT scans, as it does not involve radiation, but it can be more time-consuming and expensive. CT scans, on the other hand, are faster and more widely available, but they may not provide the same level of detail for certain types of tissues.
Advantages of MRI
MRI has several advantages over CT scans, including its ability to provide high-resolution images of soft tissues, such as organs and tendons. MRI is also generally considered safer than CT scans, as it does not involve radiation. Additionally, MRI can provide detailed images of the brain, spine, and joints, making it a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of medical conditions.
Advantages of CT Scans
CT scans have several advantages over MRI, including their speed and availability. CT scans are generally faster than MRI, making them a better choice for emergency situations or for imaging bones and lungs. CT scans are also more widely available than MRI, making them a more accessible option for patients in remote or underserved areas.
Applications of MRI and CT Scans
Both MRI and CT scans have a wide range of applications in medical imaging, including diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. MRI is particularly useful for imaging soft tissues, such as organs and tendons, while CT scans are better suited for imaging bones, lungs, and blood vessels.
Diagnostic Applications
MRI and CT scans are both used to diagnose a wide range of medical conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. MRI is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, while CT scans are better suited for diagnosing conditions such as lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and bone fractures.
Monitoring Applications
MRI and CT scans are also used to monitor the progression of various medical conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. MRI is particularly useful for monitoring the progression of conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, while CT scans are better suited for monitoring the progression of conditions such as lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and bone fractures.
What is the difference between MRI and CT scan?
+MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of internal structures, whereas CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images.
Which is safer, MRI or CT scan?
+MRI is generally considered safer than CT scans, as it does not involve radiation.
What are the advantages of MRI over CT scans?
+MRI provides high-resolution images of soft tissues, such as organs and tendons, and is generally considered safer than CT scans.
What are the advantages of CT scans over MRI?
+CT scans are faster and more widely available than MRI, making them a better choice for emergency situations or for imaging bones and lungs.
Which imaging modality is best suited for my medical condition?
+The choice between MRI and CT scan depends on various factors, including the type of tissue being imaged, the medical condition being diagnosed, and the individual patient's needs. It is essential to consult with a medical professional to determine which imaging modality is best suited for your specific medical condition.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the differences between MRI and CT scans, including their technology, applications, and advantages. Learn which imaging modality is best suited for your medical condition and make informed decisions about your healthcare.” (149 characters)