The origins of music are a complex and multifaceted topic, with various theories and hypotheses attempting to explain how and when music first emerged in human culture. While it is impossible to pinpoint an exact time and place for the birth of music, historians and musicologists have made several discoveries that shed light on the early development of music. One of the most widely accepted theories is that music originated from the sounds of nature, such as birdsong and waterfalls, which humans mimicked and adapted to create their own musical expressions. This theory is supported by the fact that many ancient cultures believed that music had mystical and spiritual powers, and that it was a gift from the gods.
Another theory suggests that music originated from the rhythms and sounds of everyday life, such as the beating of hearts, the rustling of leaves, and the rhythms of speech and language. This theory is supported by the fact that many traditional music styles, such as African and Native American music, feature complex polyrhythms and percussive elements that reflect the natural rhythms of the environment. Additionally, the use of musical instruments, such as drums and rattles, in ancient cultures suggests that music was closely tied to the sounds and rhythms of everyday life.
Key Points
- The origins of music are complex and multifaceted, with various theories attempting to explain its emergence in human culture.
- Music may have originated from the sounds of nature, such as birdsong and waterfalls, which humans mimicked and adapted to create their own musical expressions.
- Music may have also originated from the rhythms and sounds of everyday life, such as the beating of hearts and the rustling of leaves.
- The use of musical instruments, such as drums and rattles, in ancient cultures suggests that music was closely tied to the sounds and rhythms of everyday life.
- Music has been an integral part of human culture for thousands of years, with evidence of musical activity dating back to ancient civilizations in Egypt, Greece, and Mesopotamia.
Early Music History

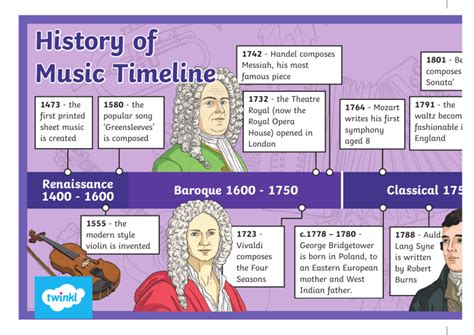
The earliest evidence of music dates back to ancient civilizations in Egypt, Greece, and Mesopotamia, where music was an integral part of religious and cultural rituals. In these cultures, music was often used to accompany dance, storytelling, and other forms of expression, and was considered an essential part of community life. The ancient Greeks, for example, believed that music had the power to heal the sick, bring people together, and even influence the gods. They developed a sophisticated system of music theory, which included the use of scales, modes, and harmonies, and which laid the foundation for Western classical music.
Ancient Music Instruments
The earliest music instruments were likely made from natural materials, such as wood, bone, and stone, and were used to create a variety of sounds and rhythms. The lyre, for example, was a popular instrument in ancient Greece, and was often depicted in art and literature as a symbol of music and poetry. The lyre was a stringed instrument, played by plucking the strings with a plectrum, and was used to accompany singing and dancing. Other ancient instruments, such as the flute and the harp, were also used in a variety of cultural and social contexts, and were often played in combination with singing and dancing.
| Instrument | Description |
|---|---|
| Lyre | A stringed instrument played by plucking the strings with a plectrum |
| Flute | A woodwind instrument played by blowing air through a reed or embouchure |
| Harp | A stringed instrument played by plucking the strings with the fingers |

Music in Different Cultures

Music has been an integral part of human culture for thousands of years, and has been expressed in a wide variety of forms and styles across different cultures and societies. In Africa, for example, music is often used in traditional rituals and ceremonies, and is characterized by complex polyrhythms and percussive elements. In Asia, music has been influenced by a variety of cultural and historical factors, including Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam, and features a wide range of instruments and styles, from the sitar and tabla of India to the shamisen and koto of Japan.
Music and Cultural Identity
Music has long been recognized as an important aspect of cultural identity, and has played a significant role in shaping and expressing the values, beliefs, and traditions of different cultures and societies. In many cultures, music is used to pass down stories, legends, and historical events from one generation to the next, and is often used in traditional rituals and ceremonies to mark important life events, such as births, weddings, and funerals. Music has also been used as a form of social commentary and protest, and has played a significant role in shaping social and political movements throughout history.
For example, in the United States, music has been used to express the experiences and struggles of African Americans, from the spirituals and blues of the rural South to the jazz and hip-hop of urban cities. Similarly, in Latin America, music has been used to express the cultural and social identity of different countries and regions, from the salsa and merengue of Cuba and the Dominican Republic to the tango and bossa nova of Argentina and Brazil.
What is the significance of music in human culture?
+Music has been an integral part of human culture for thousands of years, and has played a significant role in shaping and expressing the values, beliefs, and traditions of different cultures and societies.
How has music evolved over time?
+Music has evolved over time through a variety of cultural, historical, and technological factors, from the development of new instruments and styles to the influence of different cultures and societies.
What is the role of music in shaping cultural identity?
+Music has long been recognized as an important aspect of cultural identity, and has played a significant role in shaping and expressing the values, beliefs, and traditions of different cultures and societies.
In conclusion, the origins of music are complex and multifaceted, and reflect the diversity and creativity of human culture. From the sounds of nature to the rhythms of everyday life, music has been an integral part of human expression and identity for thousands of years, and continues to play a vital role in shaping and expressing the values, beliefs, and traditions of different cultures and societies. Whether through the development of new instruments and styles, the influence of different cultures and societies, or the expression of social and political movements, music remains a powerful and universal language that continues to inspire and unite people around the world.