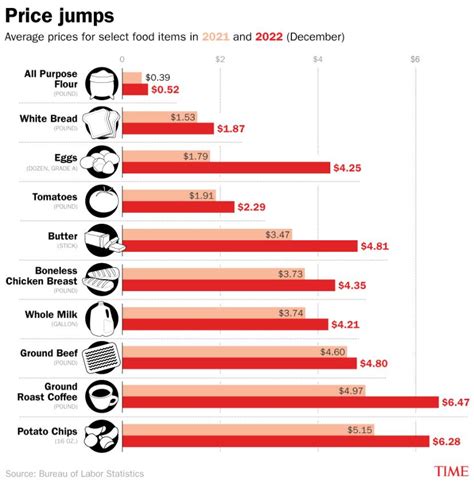
The issue of high prices has been a persistent concern for consumers across various industries and markets. Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to these elevated costs is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact. In this context, it's crucial to examine the multifaceted reasons behind high prices, including supply chain disruptions, inflation, consumer demand, production costs, and regulatory factors. By delving into these factors, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex interplay that drives pricing trends.
Key Points
- Supply chain disruptions significantly impact pricing due to increased costs and reduced efficiency.
- Inflationary pressures, driven by monetary policies and economic growth, contribute to rising prices.
- Consumer demand, particularly for luxury or unique products, can drive up prices due to the principle of scarcity.
- Production costs, including labor, materials, and technology, are a fundamental determinant of pricing strategies.
- Regulatory factors, such as taxes and trade policies, influence prices by affecting production and import costs.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Impact on Prices
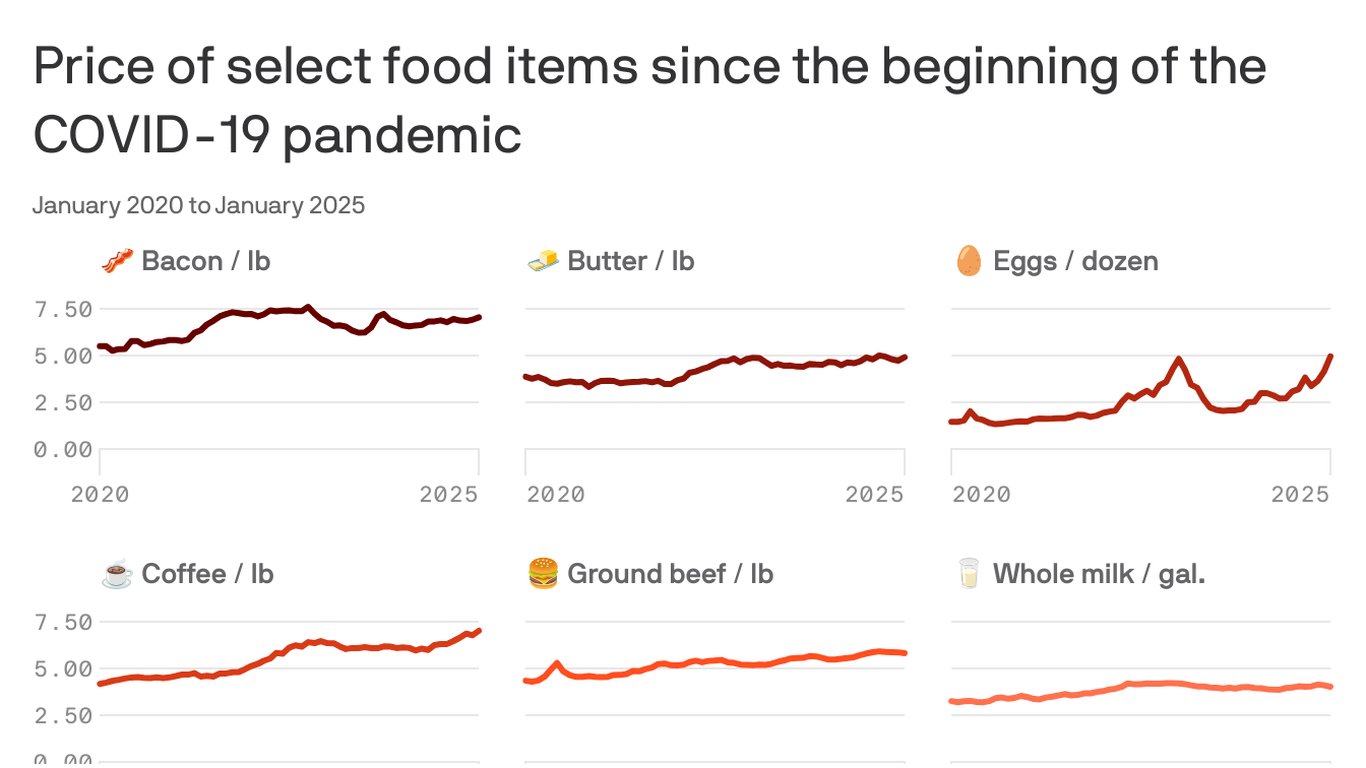
Supply chain disruptions have become increasingly common due to factors like natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and the COVID-19 pandemic. These disruptions can lead to delays, increased transportation costs, and scarcity of certain goods, all of which contribute to higher prices. For instance, the semiconductor shortage that began in 2020 significantly affected the automotive and electronics industries, leading to production halts and increased costs for consumers. Understanding the vulnerability of global supply chains is crucial for anticipating and mitigating the effects of such disruptions on pricing.
The Role of Inflation in Price Increases
Inflation, characterized by a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time, is another key factor driving high prices. Central banks and governments use monetary and fiscal policies to manage inflation rates, aiming for a delicate balance that promotes economic growth without overheating the economy. However, when inflation exceeds targeted levels, it can erode the purchasing power of consumers, leading to higher prices for goods and services. The relationship between inflation and prices is complex, influenced by factors such as economic activity, wage growth, and global commodity prices.
| Category | Impact on Prices |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased costs due to delays and scarcity |
| Inflation | Reduction in purchasing power, leading to higher prices |
| Consumer Demand | Higher prices for in-demand products due to scarcity |
| Production Costs | Direct impact on pricing due to labor, material, and technology costs |
| Regulatory Factors | Influence on production and import costs through taxes and trade policies |

Consumer Demand and the Pricing of Goods and Services
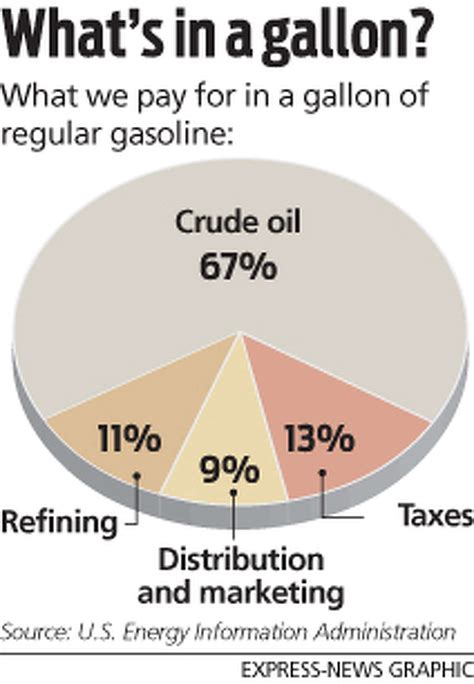
Consumer demand plays a significant role in determining prices, particularly for products that are in high demand or have limited supply. The principle of scarcity suggests that when demand exceeds supply, businesses can increase prices, and consumers are often willing to pay these higher prices to acquire the desired goods or services. This phenomenon is observed in markets for luxury goods, unique experiences, and during holiday seasons when certain products are in high demand. Understanding consumer behavior and demand patterns is essential for businesses to develop effective pricing strategies that balance revenue goals with consumer affordability.
Production Costs as a Determinant of Pricing
Production costs, encompassing labor, materials, technology, and other expenses, are a fundamental factor in pricing decisions. Businesses aim to cover these costs while also generating a profit, which means that increases in production costs can lead to higher prices for consumers. For instance, rises in minimum wage rates or increases in the cost of raw materials can necessitate price adjustments to maintain profit margins. The impact of production costs on pricing is direct and significant, making it a critical consideration for businesses and policymakers alike.
Regulatory Factors Influencing Prices
Regulatory factors, including taxes, subsidies, and trade policies, also play a crucial role in shaping prices. Taxes imposed on goods and services increase their cost, which is then passed on to consumers. Similarly, subsidies can reduce prices by offsetting production costs. Trade policies, such as tariffs and quotas, can affect the price of imported goods, influencing consumer prices and business profitability. Understanding these regulatory factors is essential for predicting price movements and developing strategies to mitigate their impact on consumers and businesses.
What are the primary causes of high prices?
+The primary causes of high prices include supply chain disruptions, inflation, consumer demand, production costs, and regulatory factors. Each of these factors can contribute to higher prices through different mechanisms, such as increased costs, scarcity, or policy-driven changes.
How do supply chain disruptions affect prices?
+Supply chain disruptions can lead to higher prices by causing delays, increasing transportation costs, and creating scarcity of certain goods. These disruptions can be due to various factors, including natural disasters, geopolitical issues, and pandemics, and their impact on prices can be significant and long-lasting.
What role does consumer demand play in pricing?
+Consumer demand is a critical factor in pricing, as high demand for a product can drive up its price, especially if supply is limited. Businesses often adjust their pricing strategies based on consumer demand, aiming to capitalize on willingness to pay while ensuring affordability and competitiveness.
How do regulatory factors influence prices?
+Regulatory factors, such as taxes, subsidies, and trade policies, can significantly influence prices. Taxes increase costs, subsidies reduce them, and trade policies can affect the price of imported goods. Understanding these regulatory factors is crucial for predicting price movements and developing pricing strategies.
What can be done to mitigate the impact of high prices on consumers?
+To mitigate the impact of high prices on consumers, businesses and policymakers can implement strategies such as improving supply chain resilience, promoting competitive markets, and adjusting regulatory policies. Additionally, consumers can make informed purchasing decisions, seek alternatives, and support policies that aim to reduce prices and increase affordability.
In conclusion, the reasons behind high prices are complex and multifaceted, involving supply chain disruptions, inflation, consumer demand, production costs, and regulatory factors. Understanding these factors and their interplay is essential for developing effective strategies to manage and mitigate the impact of high prices on consumers and businesses. By addressing these underlying causes and promoting a balanced approach to pricing, we can work towards creating more affordable and sustainable markets that benefit all stakeholders.