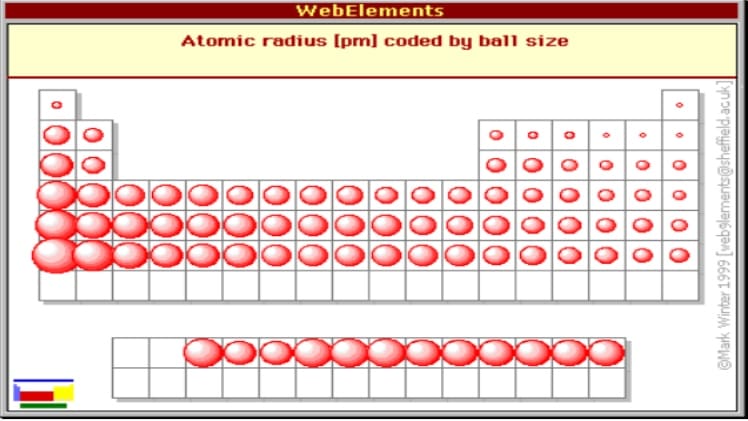
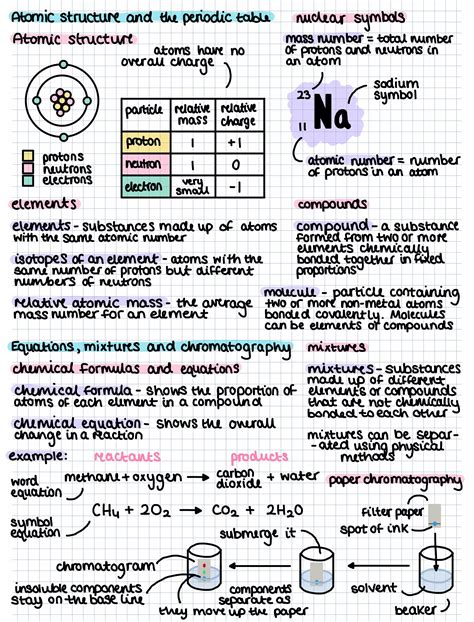
The atomic radius is a fundamental concept in chemistry, referring to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron in its atomic orbit. Understanding the trends in atomic radius is crucial for predicting the chemical properties of elements. One of the key trends observed in the periodic table is the decrease in atomic radius across periods. This trend is influenced by the increase in the number of protons in the nucleus, which leads to a stronger nuclear attraction, pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus.
To comprehend this phenomenon, it's essential to delve into the factors that contribute to the decrease in atomic radius across periods. The primary factor is the increase in the effective nuclear charge, which is the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a multi-electron atom. As we move from left to right across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, resulting in a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. This increased attraction causes the electrons to be drawn closer to the nucleus, leading to a decrease in the atomic radius.
Key Points
- The atomic radius decreases across periods due to the increase in effective nuclear charge.
- The number of protons in the nucleus increases from left to right across a period, leading to a stronger nuclear attraction.
- The increased nuclear attraction causes the electrons to be drawn closer to the nucleus, resulting in a decrease in atomic radius.
- The decrease in atomic radius across periods is a key factor in determining the chemical properties of elements.
- Understanding the trends in atomic radius is essential for predicting the reactivity and other chemical properties of elements.
Factors Influencing Atomic Radius
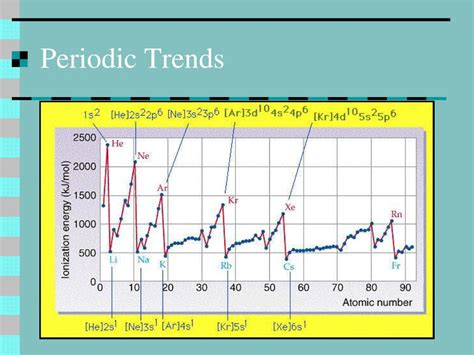
Besides the increase in effective nuclear charge, other factors also influence the atomic radius. The shielding effect, which refers to the reduction in the effective nuclear charge due to the presence of inner electrons, plays a significant role. As the number of inner electrons increases, the shielding effect becomes more pronounced, reducing the effective nuclear charge and resulting in an increase in atomic radius. However, the increase in the number of protons in the nucleus across a period dominates the shielding effect, leading to an overall decrease in atomic radius.
Effect of Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of an element also affects its atomic radius. The arrangement of electrons in different orbitals and energy levels influences the overall size of the atom. For instance, the presence of electrons in the d-orbitals can lead to a slight increase in atomic radius due to the increased shielding effect. However, this effect is relatively small compared to the decrease in atomic radius caused by the increase in effective nuclear charge.
| Period | Atomic Radius (pm) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 30-50 |
| 2 | 50-100 |
| 3 | 100-150 |
| 4 | 150-200 |
| 5 | 200-250 |
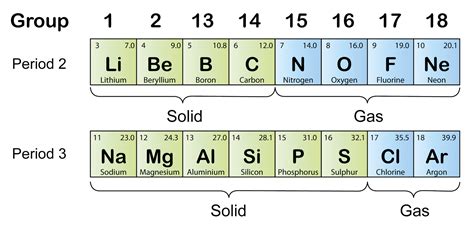
Implications of Decreasing Atomic Radius
The decrease in atomic radius across periods has significant implications for the chemical properties of elements. As the atomic radius decreases, the electrons are held more tightly to the nucleus, resulting in a higher ionization energy. This means that elements with smaller atomic radii tend to be less reactive, as it requires more energy to remove an electron from the atom. Additionally, the decrease in atomic radius affects the electronegativity of elements, with smaller atoms having a higher electronegativity due to the increased attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
Chemical Reactivity and Atomic Radius
The relationship between chemical reactivity and atomic radius is complex, with multiple factors influencing the reactivity of an element. However, the decrease in atomic radius across periods provides a general trend, with smaller atoms tend to be less reactive. This trend is particularly evident in the alkali metals, where the increase in atomic radius from lithium to francium results in a decrease in ionization energy and an increase in reactivity.
What is the primary factor contributing to the decrease in atomic radius across periods?
+The primary factor contributing to the decrease in atomic radius across periods is the increase in effective nuclear charge, which results from the increase in the number of protons in the nucleus.
How does the shielding effect influence the atomic radius?
+The shielding effect reduces the effective nuclear charge by the presence of inner electrons, resulting in an increase in atomic radius. However, this effect is dominated by the increase in the number of protons in the nucleus across a period, leading to an overall decrease in atomic radius.
What is the relationship between atomic radius and chemical reactivity?
+The decrease in atomic radius across periods results in a higher ionization energy and a lower reactivity, as the electrons are held more tightly to the nucleus. However, the relationship between atomic radius and chemical reactivity is complex, with multiple factors influencing the reactivity of an element.
In conclusion, the decrease in atomic radius across periods is a fundamental trend in the periodic table, influenced by the increase in effective nuclear charge and the shielding effect. Understanding this trend is essential for predicting the chemical properties of elements and designing new compounds and materials with specific properties. By analyzing the factors that contribute to the decrease in atomic radius, chemists can gain a deeper understanding of the complex relationships between atomic structure and chemical reactivity.