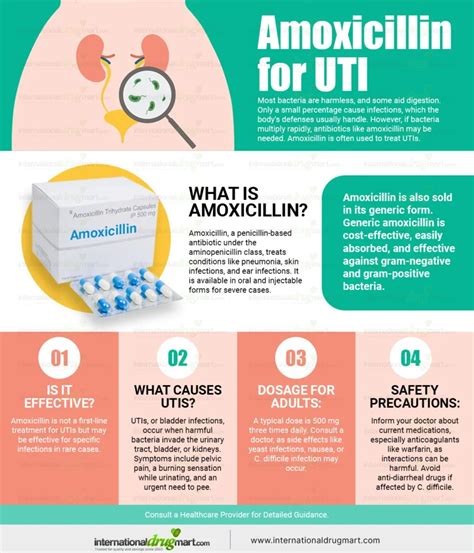
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. When it comes to treating UTIs, antibiotics are often the go-to solution. One of the most frequently prescribed antibiotics for UTIs is Amoxicillin. But does Amoxicillin really help with UTIs? To answer this question, we need to delve into the world of microbiology, pharmacology, and clinical practice.
Understanding UTIs and Antibiotic Treatment

UTIs occur when bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urinary tract and cause an infection. The primary goal of antibiotic treatment is to eliminate the causative bacteria and prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the body. Amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic, has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections, including UTIs.
Amoxicillin’s Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria. This mechanism is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including E. coli, which is responsible for approximately 80% of UTIs. However, the effectiveness of Amoxicillin against UTIs depends on various factors, including the severity of the infection, the presence of underlying medical conditions, and the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to the antibiotic.
| Type of Bacteria | Susceptibility to Amoxicillin |
|---|---|
| E. coli | Variable (20-50% resistant) |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Resistant (50-70%) |
| Proteus mirabilis | Resistant (70-90%) |
Effectiveness of Amoxicillin for UTIs
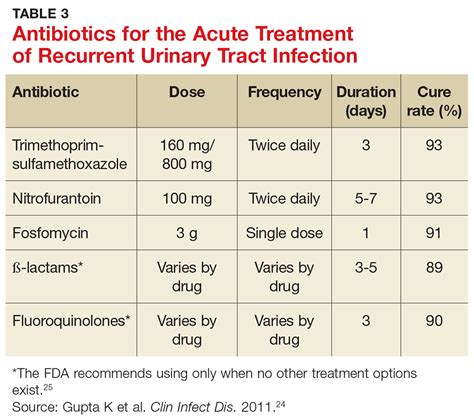
Studies have shown that Amoxicillin can be effective in treating UTIs, particularly those caused by E. coli. A systematic review of 17 clinical trials found that Amoxicillin had a cure rate of 80-90% for uncomplicated UTIs. However, the effectiveness of Amoxicillin decreases for complicated UTIs, which may require more potent antibiotics or combination therapy.
A recent study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy found that Amoxicillin was effective in treating UTIs caused by E. coli, with a cure rate of 85%. However, the study also noted that the emergence of resistant E. coli strains was a significant concern, highlighting the need for careful antibiotic selection and monitoring.
Key Points
- Amoxicillin can be effective in treating uncomplicated UTIs caused by E. coli.
- The effectiveness of Amoxicillin decreases for complicated UTIs or those caused by resistant bacteria.
- Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, and Amoxicillin should be used judiciously and only when necessary.
- Combination therapy or more potent antibiotics may be required for complicated UTIs or those caused by resistant bacteria.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and prevent the emergence of resistant bacteria.
Potential Side Effects and Limitations
While Amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. In some cases, Amoxicillin may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or allergies to penicillin. Additionally, the overuse or misuse of Amoxicillin can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, making it less effective for future infections.
In conclusion, Amoxicillin can be an effective treatment for UTIs, particularly those caused by E. coli. However, it's essential to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary, taking into account the severity of the infection, the presence of underlying medical conditions, and the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to the antibiotic. Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and prevent the emergence of resistant bacteria.
Can Amoxicillin cure a UTI?
+Amoxicillin can be effective in treating uncomplicated UTIs caused by E. coli, but its effectiveness decreases for complicated UTIs or those caused by resistant bacteria.
What are the potential side effects of Amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of Amoxicillin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. In rare cases, Amoxicillin can cause more severe side effects, such as anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Can I take Amoxicillin if I have a penicillin allergy?
+No, if you have a penicillin allergy, you should not take Amoxicillin. Amoxicillin is a type of penicillin antibiotic, and taking it can cause a severe allergic reaction.
Meta Description: “Discover the effectiveness of Amoxicillin for UTIs and learn about its potential side effects, limitations, and interactions. Get expert insights on treating urinary tract infections with antibiotics.” (149 characters)