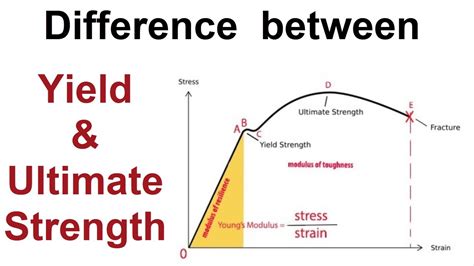
Yield stress, a critical parameter in the rheology of complex fluids, has significant implications for various industrial processes and applications. Understanding and managing yield stress is essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of systems involving non-Newtonian fluids. In this article, we will delve into the concept of yield stress, its measurement, and provide actionable tips for working with yield stress in different contexts.
Key Points
- Understanding the definition and significance of yield stress in non-Newtonian fluids
- Accurate measurement techniques for determining yield stress
- Strategies for managing yield stress in industrial applications
- Considerations for yield stress in material selection and design
- Best practices for optimizing system performance in the presence of yield stress
Understanding Yield Stress
Yield stress refers to the minimum stress that must be applied to a fluid to initiate flow. Below this stress, the fluid behaves like a solid, exhibiting elastic deformation without flowing. Yield stress is a characteristic property of non-Newtonian fluids, which include a wide range of materials such as polymers, suspensions, emulsions, and gels. The yield stress of a fluid can be influenced by various factors, including its composition, concentration, temperature, and shear history.
Measurement of Yield Stress
The measurement of yield stress is crucial for understanding the rheological behavior of non-Newtonian fluids. Several techniques are available for determining yield stress, including rotational rheometry, tube flow experiments, and indentation tests. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of technique depends on the specific application and the properties of the fluid being studied. For example, rotational rheometry is widely used for measuring the yield stress of fluids in a controlled and precise manner, while tube flow experiments can provide insights into the flow behavior of fluids in more complex geometries.
| Measurement Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Rotational Rheometry | A technique using a rotational rheometer to measure the torque and deformation of a fluid under controlled shear conditions |
| Tube Flow Experiments | Experiments involving the flow of a fluid through a tube to study its flow behavior and determine yield stress |
| Indentation Tests | A method involving the indentation of a fluid surface to measure its resistance to deformation and yield stress |
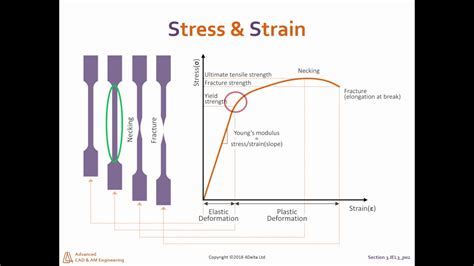
Managing Yield Stress in Industrial Applications

Yield stress plays a critical role in various industrial processes, including pipeline flow, mixing, and coating. In these applications, understanding and managing yield stress is essential for optimizing performance, reducing energy consumption, and preventing equipment damage. Strategies for managing yield stress include the use of additives or surfactants to modify the fluid’s rheological properties, optimizing process conditions such as temperature and pressure, and designing equipment with geometries that minimize yield stress effects.
Considerations for Material Selection and Design
When selecting materials or designing systems involving non-Newtonian fluids, it’s crucial to consider the yield stress of the fluid. Materials with high yield stress may require specialized handling and processing equipment, while systems designed to operate with fluids having low yield stress may need to incorporate features that prevent sedimentation or phase separation. A thorough understanding of the yield stress and its implications for material selection and design can help mitigate potential issues and ensure the successful operation of industrial processes.
In conclusion, yield stress is a fundamental property of non-Newtonian fluids that has significant implications for various industrial applications. By understanding the concept of yield stress, measuring it accurately, and managing its effects in different contexts, industries can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and improve product quality. As research and development continue to advance our understanding of complex fluids, the importance of yield stress in industrial applications is likely to grow, making it an essential consideration for engineers, researchers, and professionals working in this field.
What is the significance of yield stress in non-Newtonian fluids?
+Yield stress is significant because it determines the minimum stress required to initiate flow in a non-Newtonian fluid, influencing its behavior in various industrial processes and applications.
How is yield stress measured in practice?
+Yield stress is measured using techniques such as rotational rheometry, tube flow experiments, and indentation tests, each with its advantages and limitations depending on the specific application and fluid properties.
What strategies can be used to manage yield stress in industrial applications?
+Strategies for managing yield stress include using additives or surfactants, optimizing process conditions, and designing equipment with geometries that minimize yield stress effects, aiming to optimize performance, reduce energy consumption, and prevent equipment damage.