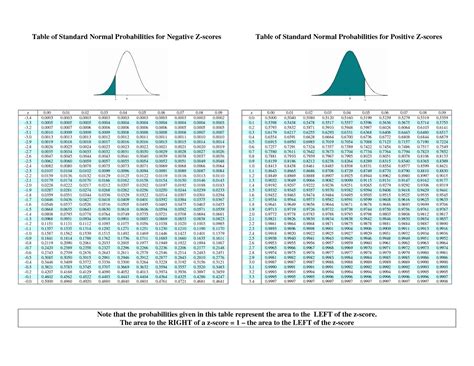
The Z scores table, also known as the standard normal distribution table or Z table, is a statistical tool used to find the probability that a value is less than or equal to a given Z score in a standard normal distribution. This distribution is a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. The Z scores table is essential in hypothesis testing and confidence intervals, allowing researchers to determine the significance of their results.
Understanding Z Scores
A Z score indicates how many standard deviations an element is from the mean. A Z score of 0 means the value is equal to the mean, while a positive Z score indicates the value is above the mean, and a negative Z score indicates the value is below the mean. The Z score is calculated using the formula: Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.
Z Scores Table Structure
The Z scores table is typically structured with Z scores ranging from -3.09 to 3.09, although the exact range can vary depending on the table. Each Z score corresponds to a probability, which represents the area under the standard normal curve to the left of the Z score. This probability is crucial for making inferences about populations based on sample data.
| Z Score | Probability |
|---|---|
| -3.09 | 0.001 |
| -2.58 | 0.005 |
| -2.33 | 0.01 |
| -1.96 | 0.025 |
| -1.64 | 0.05 |
| 0 | 0.5 |
| 1.64 | 0.95 |
| 1.96 | 0.975 |
| 2.33 | 0.99 |
| 2.58 | 0.995 |
| 3.09 | 0.999 |
Applying Z Scores in Research
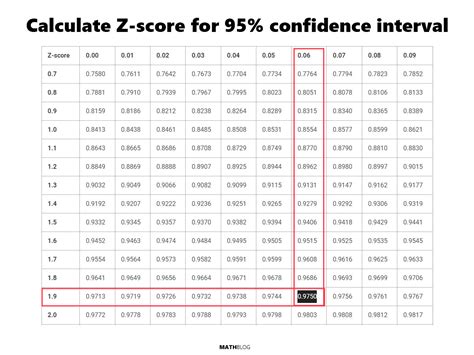
Z scores have numerous applications in research, including hypothesis testing and the construction of confidence intervals. For instance, in hypothesis testing, a Z score can be used to determine if the difference between a sample mean and a known population mean is statistically significant. The null hypothesis typically states that there is no difference, and the alternative hypothesis states there is a difference.
Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which a population parameter is likely to lie. The width of the interval depends on the confidence level (e.g., 95%), the sample size, and the standard deviation of the sample. A Z score can be used to find the critical value for constructing a confidence interval, especially when the sample size is large.
Key Points
- The Z scores table is a critical tool in statistical analysis for finding probabilities associated with Z scores.
- Z scores measure how many standard deviations an element is from the mean.
- The table is used in hypothesis testing to determine statistical significance.
- Confidence intervals can be constructed using Z scores to estimate population parameters.
- Understanding the Z scores table requires knowledge of the standard normal distribution and how to interpret probabilities.
In conclusion, the Z scores table is a fundamental resource in statistical analysis, providing a way to calculate probabilities and make inferences about populations based on sample data. Its applications in hypothesis testing and confidence intervals make it an indispensable tool for researchers across various disciplines.
What is the primary use of the Z scores table in statistical analysis?
+The primary use of the Z scores table is to find the probability that a value is less than or equal to a given Z score in a standard normal distribution, which is crucial for hypothesis testing and constructing confidence intervals.
How do you calculate a Z score?
+A Z score is calculated using the formula: Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.
What does a positive Z score indicate?
+A positive Z score indicates that the value is above the mean, while a negative Z score indicates that the value is below the mean.