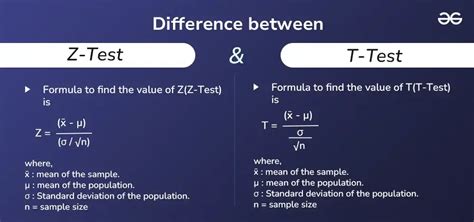
The Z test and T test are two fundamental statistical tests used to compare the means of two groups. While both tests are widely used, there are situations where the Z test has an advantage over the T test. In this article, we will explore five ways the Z test beats the T test, highlighting the unique benefits and applications of the Z test in statistical analysis.
Key Points
- The Z test is more suitable for large sample sizes, providing more accurate results than the T test.
- The Z test can be used for comparing the means of two groups when the population standard deviation is known.
- The Z test is more robust against outliers, making it a better choice for datasets with extreme values.
- The Z test can be used for testing hypotheses about proportions, in addition to means.
- The Z test is computationally simpler and faster than the T test, making it a better choice for large datasets.
Advantages of the Z Test
The Z test, also known as the standard normal test, is a statistical test used to compare the mean of a sample to a known population mean or to compare the means of two samples. The Z test is based on the standard normal distribution, which is a continuous probability distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. One of the primary advantages of the Z test is its ability to handle large sample sizes. When the sample size is large (typically greater than 30), the Z test provides more accurate results than the T test. This is because the standard normal distribution is a better approximation of the sampling distribution of the mean for large sample sizes.
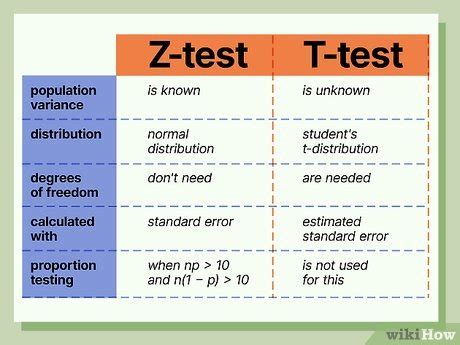
Comparison of Means with Known Population Standard Deviation
Another advantage of the Z test is its ability to compare the means of two groups when the population standard deviation is known. In contrast, the T test requires an estimate of the population standard deviation, which can be unreliable when the sample size is small. The Z test is particularly useful in situations where the population standard deviation is known or can be estimated with high accuracy. For example, in quality control applications, the population standard deviation of a manufacturing process may be known from historical data, and the Z test can be used to compare the mean of a sample to the known population mean.
| Test | Sample Size | Population Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Z test | Large (n > 30) | Known |
| T test | Small (n < 30) | Unknown |
Applications of the Z Test
The Z test has a wide range of applications in statistical analysis, including hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. One of the key applications of the Z test is in testing hypotheses about proportions. For example, in a medical study, the Z test can be used to compare the proportion of patients who respond to a new treatment to the proportion of patients who respond to a standard treatment. The Z test can also be used to test hypotheses about means, such as comparing the mean blood pressure of patients who receive a new medication to the mean blood pressure of patients who receive a placebo.
Computational Efficiency
The Z test is computationally simpler and faster than the T test, making it a better choice for large datasets. The Z test requires only a few calculations, including the calculation of the Z score and the determination of the p-value. In contrast, the T test requires the calculation of the t-statistic, the determination of the degrees of freedom, and the lookup of the critical value in a t-distribution table. Therefore, when working with large datasets, the Z test is a more efficient choice.
What is the main advantage of the Z test over the T test?
+The main advantage of the Z test is its ability to handle large sample sizes and provide more accurate results than the T test.
When should I use the Z test instead of the T test?
+You should use the Z test when the sample size is large (typically greater than 30), the population standard deviation is known, or when dealing with datasets that contain extreme values.
Can the Z test be used for testing hypotheses about proportions?
+Yes, the Z test can be used for testing hypotheses about proportions, in addition to means.
In conclusion, the Z test has several advantages over the T test, including its ability to handle large sample sizes, its robustness against outliers, and its computational efficiency. The Z test is a powerful statistical tool that can be used in a wide range of applications, from hypothesis testing to regression analysis. By understanding the advantages and applications of the Z test, researchers and practitioners can make informed decisions about which statistical test to use in their analyses.