The concept of zero as an integer is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, and its properties have far-reaching implications in various fields, including arithmetic, algebra, and calculus. In this article, we will explore five ways in which zero is indeed an integer, highlighting its significance and the reasoning behind its classification as such.
Definition and Classification of Integers
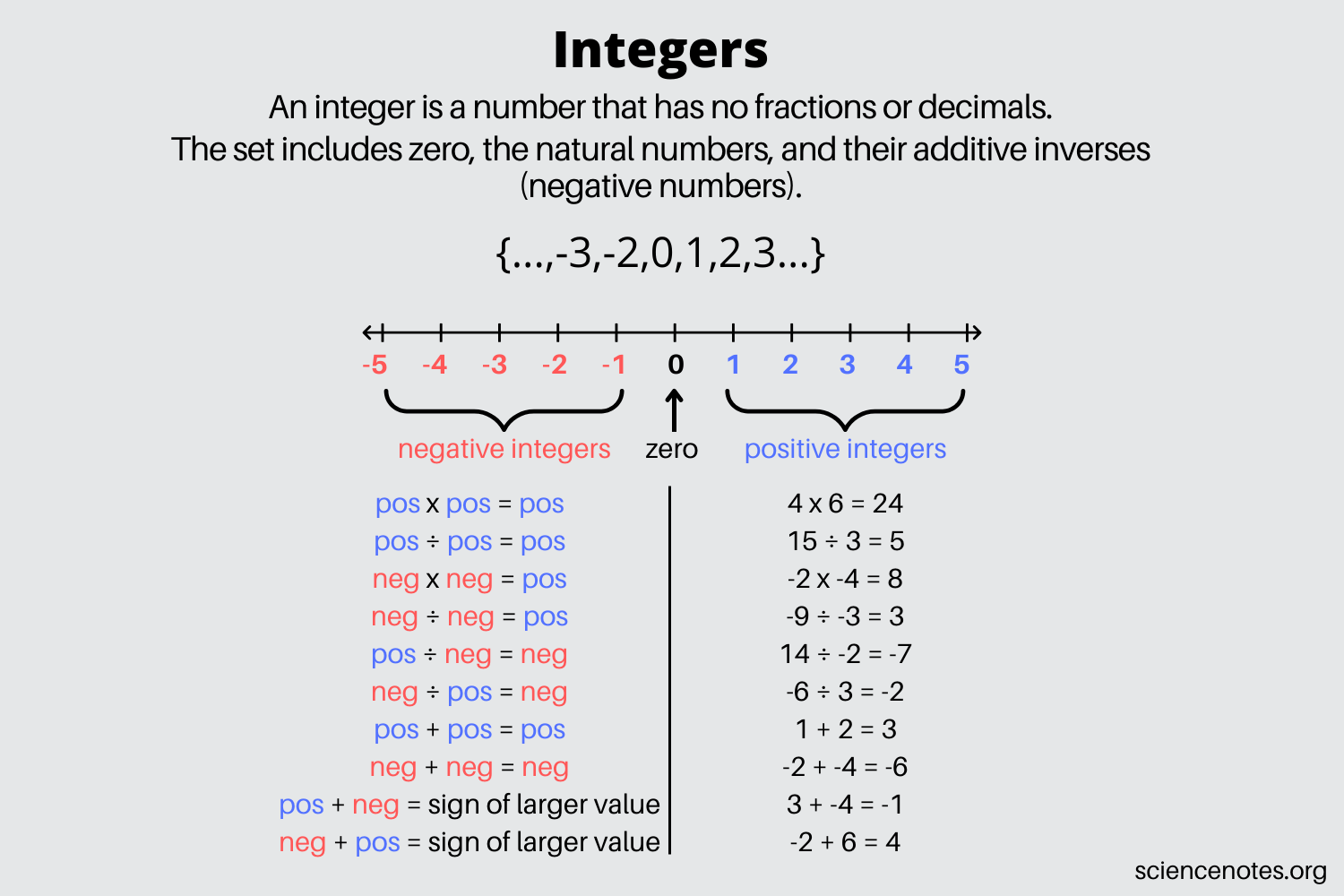
To understand why zero is considered an integer, it’s essential to first define what integers are. Integers are whole numbers, either positive, negative, or zero, without a fractional part. They can be represented on the number line, with zero serving as the reference point that separates the positive and negative integers. The set of integers is often denoted as {…, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,…}, clearly including zero as a member.
Mathematical Operations and Zero
One of the key reasons zero is classified as an integer is its behavior in mathematical operations. When performing addition or subtraction with zero, the result is the number itself, which aligns with the properties of integers. For example, 5 + 0 = 5 and 5 - 0 = 5. Similarly, in multiplication, any number multiplied by zero results in zero, which is also an integer. This consistency in arithmetic operations supports the inclusion of zero among the integers.
| Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | 5 + 0 | 5 |
| Subtraction | 5 - 0 | 5 |
| Multiplication | 5 * 0 | 0 |

Number Line Representation

The number line is a visual representation of numbers, where integers are marked at equal intervals. Zero occupies the central position, equidistant from positive and negative infinity, serving as the origin from which all other numbers are measured. This graphical representation reinforces the notion that zero is an integral part of the integer set, bridging the positive and negative integers.
Algebraic Properties
In algebra, zero exhibits properties that are consistent with those of integers. For instance, zero is the additive identity, meaning that when added to any integer, the result is the integer itself. This property is crucial in solving equations and manipulating algebraic expressions, further solidifying zero’s position as an integer.
Key Points
- Zero is defined as an integer due to its whole number nature and lack of a fractional part.
- Its behavior in addition, subtraction, and multiplication aligns with the properties of integers.
- Zero serves as the origin on the number line, marking the transition between positive and negative integers.
- Algebraically, zero functions as the additive identity, a property essential for solving equations and manipulating expressions.
- The inclusion of zero in the set of integers ensures consistency and completeness in mathematical operations and theories.
Consistency in Mathematical Theories
The classification of zero as an integer is also supported by its role in various mathematical theories and models. In calculus, for example, understanding limits and derivatives often involves considering functions as they approach zero. The continuity and differentiability of functions at zero are critical aspects of these studies, highlighting the integral nature of zero in advanced mathematical analyses.
Historical and Evolutionary Context
Historically, the concept of zero evolved over time, with its introduction and acceptance varying across different cultures. Initially met with skepticism, zero eventually became a cornerstone of mathematics, facilitating the development of more complex and precise mathematical systems. Its recognition as an integer reflects a deep understanding of its fundamental role in arithmetic and beyond.
In conclusion, the notion that zero is an integer is supported by its definition, its behavior in mathematical operations, its representation on the number line, its algebraic properties, and its consistency in mathematical theories. These aspects collectively demonstrate the integral nature of zero, underscoring its importance in the structure of mathematics.
Why is zero considered an integer in mathematics?
+Zero is considered an integer because it is a whole number without a fractional part, it behaves consistently in mathematical operations, and it serves as the origin on the number line, marking the transition between positive and negative integers.
How does zero function in algebraic expressions and equations?
+Zero acts as the additive identity in algebra, meaning that when added to any number, the result is the number itself. This property is essential for solving equations and manipulating algebraic expressions.
What is the significance of zero in the development of calculus and advanced mathematical theories?
+Zero plays a critical role in calculus, particularly in the study of limits and derivatives. Understanding how functions behave as they approach zero is fundamental to these analyses, highlighting the importance of zero in advanced mathematical studies.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover why zero is classified as an integer, exploring its role in mathematics, from basic operations to advanced theories, and understand its significance in the structure of numbers.”



