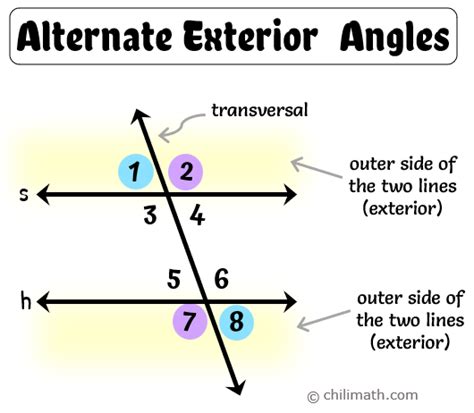
Alternate exterior angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, playing a crucial role in understanding the properties of lines and angles. When two lines intersect, they form four angles: two interior angles and two exterior angles. The alternate exterior angles are the angles that are outside the two lines and are on opposite sides of the transversal. These angles have unique properties that make them essential in various geometric applications. In this article, we will delve into the world of alternate exterior angles, exploring their characteristics, applications, and significance in geometry.
Key Points
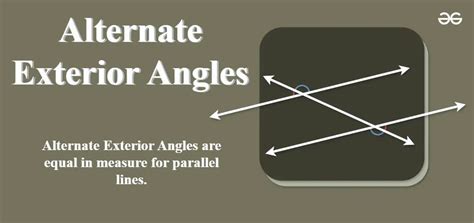
- Alternate exterior angles are equal when a transversal intersects two parallel lines.
- These angles are supplementary to the corresponding interior angles.
- Alternate exterior angles can be used to determine if two lines are parallel.
- The concept of alternate exterior angles is crucial in various geometric theorems and proofs.
- Understanding alternate exterior angles is essential for solving problems involving parallel lines and transversals.
Understanding Alternate Exterior Angles
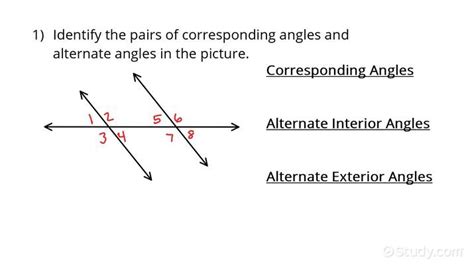
Alternate exterior angles are formed when a transversal intersects two lines. The transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines, and the angles formed by this intersection are the focus of our study. When the two lines are parallel, the alternate exterior angles are equal. This property is a direct consequence of the parallel lines’ definition, which states that parallel lines never intersect, and the corresponding angles are equal. The equality of alternate exterior angles is a fundamental concept in geometry, and it has numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design.
Properties of Alternate Exterior Angles
Alternate exterior angles have several properties that make them unique and useful in geometric applications. One of the most important properties is that they are equal when the two lines are parallel. This means that if we have two parallel lines intersected by a transversal, the alternate exterior angles will be equal. Another property of alternate exterior angles is that they are supplementary to the corresponding interior angles. This means that the sum of an alternate exterior angle and its corresponding interior angle is always 180 degrees. These properties make alternate exterior angles a powerful tool in geometric proofs and theorems.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Equality | Alternate exterior angles are equal when the two lines are parallel. |
| Supplementary | Alternate exterior angles are supplementary to the corresponding interior angles. |
| Transversal | A line that intersects two or more lines, forming alternate exterior angles. |
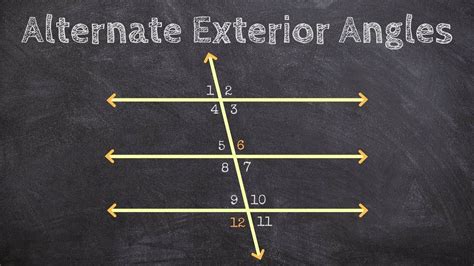
Applications of Alternate Exterior Angles
Alternate exterior angles have numerous applications in various fields, including geometry, architecture, engineering, and design. One of the most significant applications is in determining if two lines are parallel. By checking if the alternate exterior angles are equal, we can determine if the lines are parallel. This property is essential in various geometric theorems and proofs, including the parallel lines theorem and the transversal theorem. Additionally, alternate exterior angles are used in designing and constructing buildings, bridges, and other structures, where parallel lines and angles play a critical role.
Solving Problems with Alternate Exterior Angles
Solving problems involving alternate exterior angles requires a deep understanding of their properties and applications. One common problem is to determine if two lines are parallel based on the given angles. By using the properties of alternate exterior angles, we can solve this problem and determine if the lines are parallel. Another problem is to find the measure of an angle given the measure of its corresponding alternate exterior angle. By using the supplementary property of alternate exterior angles, we can solve this problem and find the measure of the angle.
What are alternate exterior angles?
+Alternate exterior angles are angles formed by a transversal intersecting two lines, where the angles are outside the two lines and on opposite sides of the transversal.
What is the property of alternate exterior angles when two lines are parallel?
+When two lines are parallel, the alternate exterior angles are equal.
How are alternate exterior angles used in geometric proofs and theorems?
+Alternate exterior angles are used in various geometric proofs and theorems, including the parallel lines theorem and the transversal theorem, to determine if two lines are parallel and to solve complex geometric problems.
In conclusion, alternate exterior angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, with unique properties and applications in various fields. By understanding the equality and supplementary properties of alternate exterior angles, we can determine if two lines are parallel and solve complex geometric problems. The concept of alternate exterior angles is crucial in various geometric theorems and proofs, and its applications extend to architecture, engineering, and design. As we continue to explore the world of geometry, the significance of alternate exterior angles will become increasingly apparent, and their importance in shaping our understanding of lines, angles, and shapes will be undeniable.