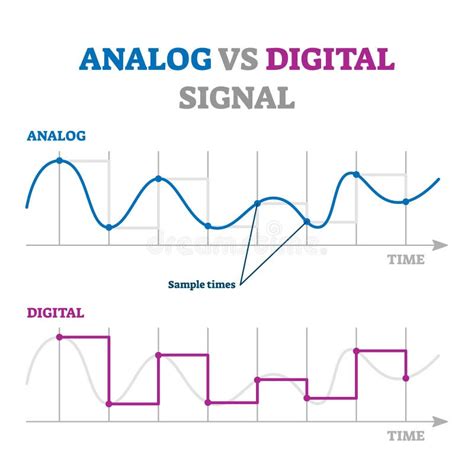
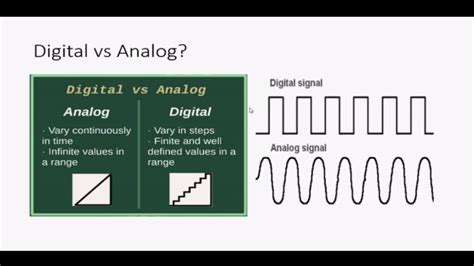
The realm of signal processing is a fundamental aspect of various fields, including telecommunications, audio engineering, and medical imaging. At the heart of signal processing lies the distinction between analog and digital signals. Understanding the differences between these two types of signals is crucial for designing, implementing, and optimizing systems that rely on signal transmission and processing. In this article, we will delve into the world of analog and digital signals, exploring their definitions, characteristics, advantages, and applications.
Introduction to Analog Signals
Analog signals are continuous signals that represent physical measurements, such as sound, light, or temperature. These signals are characterized by their continuous range of values, which can be thought of as a smooth, unbroken curve. Analog signals are often represented as a function of time, with the signal’s amplitude varying continuously over time. Examples of analog signals include audio signals from a microphone, video signals from a camera, and biomedical signals from an electrocardiogram (ECG). The continuous nature of analog signals allows for a high degree of precision, making them suitable for applications where subtle variations in the signal are critical.
Analog Signal Characteristics
Analog signals have several key characteristics that distinguish them from digital signals. These characteristics include: - Continuous amplitude: Analog signals can take on any value within a given range, allowing for a high degree of precision. - Continuous time: Analog signals are defined at all points in time, resulting in a smooth, continuous waveform. - Noise sensitivity: Analog signals are prone to noise and interference, which can degrade the signal’s quality and accuracy. - Bandwidth limitations: Analog signals are limited by their bandwidth, which can restrict the amount of information that can be transmitted.
| Signal Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Analog | Continuous amplitude, continuous time, noise sensitive, bandwidth limited |
| Digital | Discrete amplitude, discrete time, noise resistant, high bandwidth |

Introduction to Digital Signals

Digital signals, on the other hand, are discrete signals that represent information as a series of binary digits (0s and 1s). These signals are characterized by their discrete range of values, which can be thought of as a series of distinct, separate points. Digital signals are often represented as a function of time, with the signal’s amplitude taking on only specific, discrete values at specific points in time. Examples of digital signals include computer data, digital audio, and digital images. The discrete nature of digital signals provides a high degree of noise resistance and flexibility, making them suitable for applications where data needs to be transmitted, stored, and processed efficiently.
Digital Signal Characteristics
Digital signals have several key characteristics that distinguish them from analog signals. These characteristics include: - Discrete amplitude: Digital signals can only take on specific, discrete values, reducing the impact of noise and interference. - Discrete time: Digital signals are defined only at specific points in time, resulting in a series of distinct, separate samples. - Noise resistance: Digital signals are more resistant to noise and interference, making them suitable for applications where data integrity is critical. - High bandwidth: Digital signals can be transmitted at high speeds, allowing for a large amount of information to be transmitted in a short amount of time.
Key Points
- Analog signals are continuous, while digital signals are discrete.
- Analog signals are prone to noise and interference, while digital signals are more resistant.
- Digital signals can be transmitted at high speeds, while analog signals are limited by their bandwidth.
- The choice between analog and digital signals depends on the specific application and requirements.
- Analog signals are often preferred in applications where high precision and continuous measurement are necessary.
Comparison of Analog and Digital Signals
When comparing analog and digital signals, it is essential to consider the trade-offs between precision, noise resistance, and bandwidth. Analog signals offer high precision and continuous measurement, making them suitable for applications where subtle variations in the signal are critical. However, analog signals are prone to noise and interference, which can degrade the signal’s quality and accuracy. Digital signals, on the other hand, offer high noise resistance and flexibility, making them suitable for applications where data needs to be transmitted, stored, and processed efficiently. However, digital signals can be limited by their discrete nature, which can result in a loss of precision.
Applications of Analog and Digital Signals
Analog and digital signals have a wide range of applications in various fields. Analog signals are commonly used in: - Audio engineering: Analog signals are used to represent sound waves, allowing for high-quality audio reproduction. - Medical imaging: Analog signals are used to represent medical images, such as X-rays and MRI scans. - Telecommunications: Analog signals are used to transmit voice and data over telephone lines. Digital signals, on the other hand, are commonly used in: - Computer systems: Digital signals are used to represent data and instructions, allowing for efficient processing and storage. - Digital audio: Digital signals are used to represent audio data, allowing for high-quality audio reproduction and editing. - Digital imaging: Digital signals are used to represent images, allowing for efficient storage and processing.
What is the main difference between analog and digital signals?
+The main difference between analog and digital signals is that analog signals are continuous, while digital signals are discrete.
What are the advantages of analog signals?
+Analog signals offer high precision and continuous measurement, making them suitable for applications where subtle variations in the signal are critical.
What are the advantages of digital signals?
+Digital signals offer high noise resistance and flexibility, making them suitable for applications where data needs to be transmitted, stored, and processed efficiently.
In conclusion, analog and digital signals have distinct characteristics, advantages, and applications. Understanding the differences between these two types of signals is crucial for designing, implementing, and optimizing systems that rely on signal transmission and processing. By considering the trade-offs between precision, noise resistance, and bandwidth, engineers and technicians can choose the most suitable signal type for their specific application, ensuring efficient and effective signal processing and transmission.