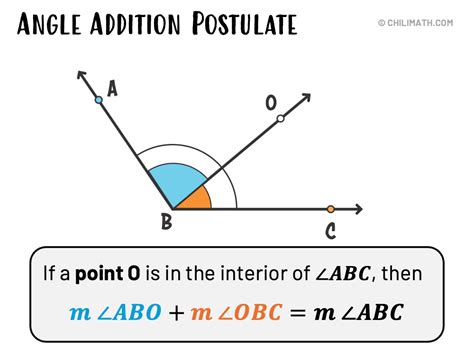
The Angle Addition Postulate is a fundamental concept in geometry, stating that the measure of an angle is equal to the sum of the measures of its parts. This postulate is crucial in various geometric proofs and theorems, allowing us to calculate and analyze angles in different configurations. In this article, we will explore five ways the Angle Addition Postulate is applied in geometry, demonstrating its significance and versatility.
Introduction to the Angle Addition Postulate
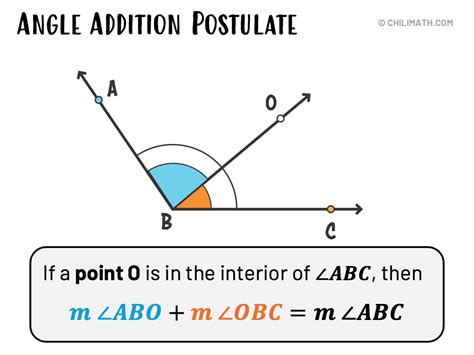
The Angle Addition Postulate can be formally stated as: if D is a point in the interior of angle ABC, then the measure of angle ABC is equal to the sum of the measures of angles ABD and CBD. This concept is essential for understanding and working with angles in various geometric shapes and theorems. By applying the Angle Addition Postulate, we can derive numerous important results in geometry.
Key Points
- The Angle Addition Postulate allows us to calculate the measure of an angle by summing the measures of its parts.
- This postulate is fundamental in geometric proofs, especially in the context of angle relationships and theorems.
- Understanding the Angle Addition Postulate is crucial for working with angles in triangles, polygons, and other geometric shapes.
- The postulate has numerous applications in real-world problems, including architecture, engineering, and design.
- Mastering the Angle Addition Postulate enhances problem-solving skills and deepens understanding of geometric concepts.
Applications of the Angle Addition Postulate
The Angle Addition Postulate has far-reaching implications in geometry, facilitating the proof of various theorems and lemmas. For instance, it is used in the proof of the Angle Sum Property of Triangles, which states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. This property, in turn, has numerous applications in trigonometry, geometry, and other areas of mathematics.
Calculating Angles in Triangles
In the context of triangles, the Angle Addition Postulate is instrumental in determining the measures of angles. By applying this postulate, we can find the measure of the third angle of a triangle if the measures of the other two angles are known. For example, if we have a triangle ABC with angle measures m∠A = 60° and m∠B = 70°, we can use the Angle Addition Postulate to find the measure of angle C.
| Angle | Measure |
|---|---|
| A | 60° |
| B | 70° |
| C | 50° |

Given that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°, we can calculate the measure of angle C as follows: m∠C = 180° - (m∠A + m∠B) = 180° - (60° + 70°) = 50°. This calculation demonstrates the practical application of the Angle Addition Postulate in solving geometric problems.
Real-World Applications of the Angle Addition Postulate
Beyond its theoretical significance in geometry, the Angle Addition Postulate has numerous real-world applications. Architects, engineers, and designers often rely on geometric principles, including the Angle Addition Postulate, to create structures, models, and designs that meet specific requirements and constraints. For instance, in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure, precise calculations of angles and shapes are critical for ensuring stability, safety, and aesthetic appeal.
Design and Architecture
In design and architecture, the Angle Addition Postulate is used to create balanced and functional spaces. By applying geometric principles, designers can determine the optimal angles and shapes for various elements, such as doors, windows, and staircases, to achieve both functional and aesthetic goals. For example, the design of a staircase involves careful calculation of angles to ensure safety and comfort. The Angle Addition Postulate is essential in these calculations, enabling designers to create stairs that are both functional and visually appealing.
In conclusion, the Angle Addition Postulate is a foundational concept in geometry, with far-reaching implications for various geometric theorems and real-world applications. By mastering this postulate, individuals can deepen their understanding of geometric principles and enhance their problem-solving skills, ultimately contributing to advancements in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
What is the Angle Addition Postulate, and why is it important in geometry?
+The Angle Addition Postulate states that the measure of an angle is equal to the sum of the measures of its parts. It is crucial for understanding and working with angles in various geometric shapes and theorems, facilitating the proof of numerous important results in geometry.
How is the Angle Addition Postulate applied in real-world problems?
+The Angle Addition Postulate is applied in various real-world problems, including architecture, engineering, and design. It is used to calculate angles and shapes in constructions, ensuring stability, safety, and aesthetic appeal. Additionally, it is instrumental in the design of functional and balanced spaces, such as staircases, doors, and windows.
What are the implications of the Angle Addition Postulate for geometric reasoning and problem-solving skills?
+The Angle Addition Postulate enhances geometric reasoning and problem-solving skills by providing a fundamental concept for understanding and working with angles. By mastering this postulate, individuals can deepen their understanding of geometric principles and develop more effective strategies for solving geometric problems.