The concept of derivatives of inverse functions is a fundamental aspect of calculus, allowing us to analyze and understand the behavior of functions and their inverses. In this article, we will delve into the world of inverse functions, exploring their properties, and deriving formulas for their derivatives. We will also examine the applications of these derivatives in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
Key Points
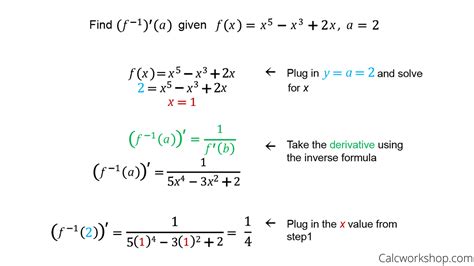
- The derivative of an inverse function can be found using the formula f^(-1)'(x) = 1 / f'(f^(-1)(x)), which is derived from the chain rule and the definition of an inverse function.
- The inverse function theorem states that if a function f is continuously differentiable and has a non-zero derivative at a point a, then the inverse function f^(-1) is also continuously differentiable at the point f(a).
- Derivatives of inverse functions have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and economics, including optimization problems, curve fitting, and modeling population growth.
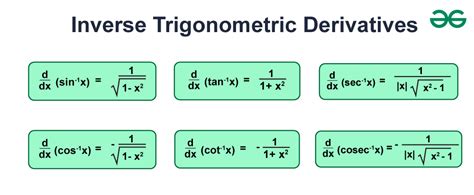
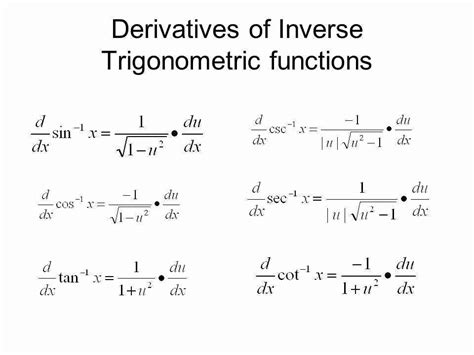
- The derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, such as arcsin(x) and arctan(x), can be found using the formulas d(arcsin(x))/dx = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) and d(arctan(x))/dx = 1 / (1 + x^2).
- Derivatives of inverse functions can be used to model and analyze complex systems, such as electrical circuits, mechanical systems, and population dynamics.
Introduction to Inverse Functions
An inverse function is a function that undoes the action of another function. In other words, if we have a function f(x) that maps an input x to an output y, then the inverse function f^(-1)(y) maps the output y back to the original input x. The concept of inverse functions is crucial in calculus, as it allows us to analyze and understand the behavior of functions and their inverses.
Properties of Inverse Functions
Inverse functions have several important properties that make them useful in calculus. One of the most significant properties is that the derivative of an inverse function is the reciprocal of the derivative of the original function. This property can be expressed mathematically as f^(-1)‘(x) = 1 / f’(f^(-1)(x)). This formula is derived from the chain rule and the definition of an inverse function.
| Function | Derivative | Inverse Function | Derivative of Inverse |
|---|---|---|---|
| f(x) = x^2 | f'(x) = 2x | f^(-1)(x) = sqrt(x) | f^(-1)'(x) = 1 / (2 * sqrt(x)) |
| f(x) = e^x | f'(x) = e^x | f^(-1)(x) = ln(x) | f^(-1)'(x) = 1 / x |
| f(x) = sin(x) | f'(x) = cos(x) | f^(-1)(x) = arcsin(x) | f^(-1)'(x) = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) |
Derivatives of Inverse Functions
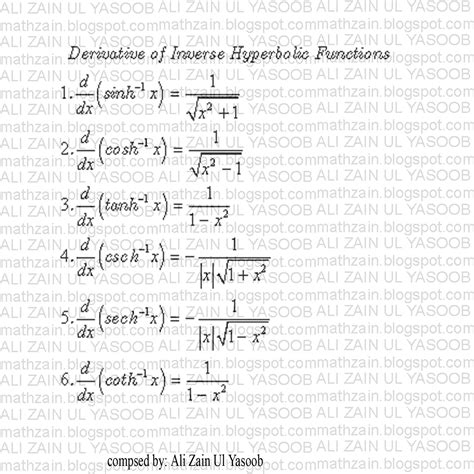
The derivative of an inverse function can be found using the formula f^(-1)‘(x) = 1 / f’(f^(-1)(x)). This formula is derived from the chain rule and the definition of an inverse function. To find the derivative of an inverse function, we first need to find the derivative of the original function. Then, we can use the formula to find the derivative of the inverse function.
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
The derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, such as arcsin(x) and arctan(x), can be found using the formulas d(arcsin(x))/dx = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) and d(arctan(x))/dx = 1 / (1 + x^2). These formulas are derived from the definition of the inverse trigonometric functions and the chain rule.
Applications of Derivatives of Inverse Functions
Derivatives of inverse functions have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and economics. One of the most significant applications is in optimization problems, where we need to find the maximum or minimum of a function. By using the derivatives of inverse functions, we can find the optimal solution to the problem. Another application is in curve fitting, where we need to find the best fit of a curve to a set of data points. By using the derivatives of inverse functions, we can find the best fit of the curve and use it to model and analyze complex systems.
Modeling Population Growth
Derivatives of inverse functions can be used to model and analyze population growth. By using the logistic growth model, we can find the derivative of the population growth function and use it to analyze the behavior of the population. The logistic growth model is given by the equation dP/dt = r * P * (1 - P/K), where P is the population size, r is the growth rate, and K is the carrying capacity. By using the derivatives of inverse functions, we can find the optimal solution to the problem and use it to model and analyze complex systems.
What is the formula for the derivative of an inverse function?
+The formula for the derivative of an inverse function is f^(-1)‘(x) = 1 / f’(f^(-1)(x)).
What are the applications of derivatives of inverse functions?
+Derivatives of inverse functions have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and economics, including optimization problems, curve fitting, and modeling population growth.
How do you find the derivative of an inverse trigonometric function?
+The derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, such as arcsin(x) and arctan(x), can be found using the formulas d(arcsin(x))/dx = 1 / sqrt(1 - x^2) and d(arctan(x))/dx = 1 / (1 + x^2).