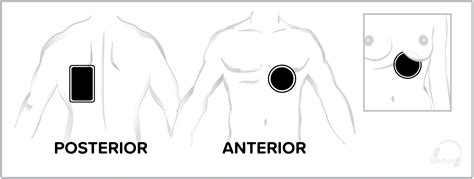
The anteroposterior placement of Automated External Defibrillator (AED) pads is a critical aspect of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and emergency medical response. The American Heart Association (AHA) and other reputable medical organizations have established guidelines for the proper placement of AED pads to ensure effective defibrillation and minimize complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of anteroposterior placement, the recommended techniques, and the evidence-based rationale behind this approach.
Key Points
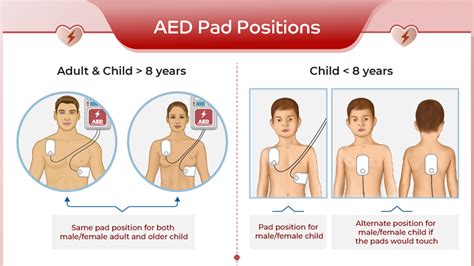
- The anteroposterior placement of AED pads is recommended for adults and children over 8 years old or weighing more than 25 kg (55 lbs).
- This placement allows for optimal distribution of the electrical current and minimizes the risk of complications.
- The AHA guidelines emphasize the importance of following the manufacturer's instructions for AED pad placement.
- Proper training and practice are essential for ensuring correct AED pad placement and effective defibrillation.
- Anteroposterior placement may not be suitable for all patients, such as those with pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs).
Recommended Placement Techniques
The anteroposterior placement of AED pads involves placing one pad on the anterior (front) chest and the other on the posterior (back) chest. This placement allows for optimal distribution of the electrical current and minimizes the risk of complications. The AHA recommends the following placement techniques:
- Place one pad on the upper right side of the chest, approximately 2.5 cm (1 inch) to the right of the sternum and 2.5 cm (1 inch) below the clavicle.
- Place the second pad on the upper left side of the back, approximately 2.5 cm (1 inch) to the left of the spine and 2.5 cm (1 inch) below the scapula.
Importance of Following Manufacturer’s Instructions
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for AED pad placement, as different devices may have varying pad placement recommendations. The AHA emphasizes the importance of reading and following the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure proper placement and effective defibrillation.
| AED Pad Placement | Recommended Location |
|---|---|
| Anterior Pad | Upper right side of the chest, 2.5 cm (1 inch) to the right of the sternum and 2.5 cm (1 inch) below the clavicle |
| Posterior Pad | Upper left side of the back, 2.5 cm (1 inch) to the left of the spine and 2.5 cm (1 inch) below the scapula |

Evidence-Based Rationale

The anteroposterior placement of AED pads is supported by evidence-based research. Studies have shown that this placement allows for optimal distribution of the electrical current and minimizes the risk of complications, such as myocardial damage or burns. A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that anteroposterior placement resulted in a higher success rate of defibrillation compared to other placement techniques.
Limitations and Considerations
While the anteroposterior placement of AED pads is recommended for most adults and children, there may be certain situations where alternative placement techniques are necessary. For example, patients with pacemakers or ICDs may require special consideration, as the electrical current from the AED may interfere with the functioning of these devices. In such cases, it is essential to consult with a medical professional or follow established guidelines for AED pad placement.
What is the recommended placement of AED pads for children under 8 years old or weighing less than 25 kg (55 lbs)?
+For children under 8 years old or weighing less than 25 kg (55 lbs), the AHA recommends using pediatric AED pads or manually adjusting the adult pads to ensure proper placement. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult with a medical professional if unsure.
Can I use AED pads on a patient with a pacemaker or ICD?
+While AED pads can be used on patients with pacemakers or ICDs, it is essential to exercise caution and follow established guidelines. The electrical current from the AED may interfere with the functioning of these devices, and alternative placement techniques may be necessary. Consult with a medical professional or follow established guidelines for AED pad placement in such cases.
How often should I practice AED pad placement to ensure proficiency?
+It is recommended to practice AED pad placement regularly, ideally during CPR training sessions or as part of ongoing education and training. The AHA suggests practicing AED pad placement at least once a year to maintain proficiency and build confidence.
In conclusion, the anteroposterior placement of AED pads is a critical aspect of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency medical response. By following the recommended placement techniques and guidelines, healthcare professionals and lay responders can ensure effective defibrillation and minimize complications. Proper training and practice are essential for building confidence and proficiency in AED pad placement, and it is crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest evidence-based research and guidelines to provide optimal care for patients in need.