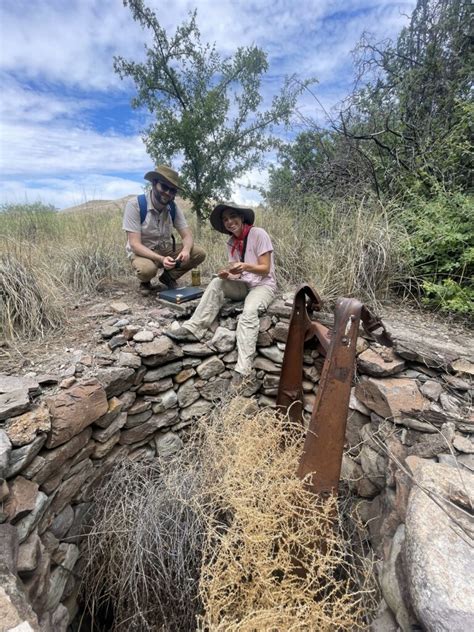
Arizona, with its rich cultural heritage and diverse landscapes, is a paradise for archaeology enthusiasts. The state is home to numerous archaeological sites, each offering a unique glimpse into the lives of ancient civilizations. From the intricate pottery of the Ancestral Puebloans to the mysterious rock art of the Hohokam, Arizona's archaeological treasures are a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of its prehistoric inhabitants. In this article, we will delve into the world of Arizona archaeology, exploring five essential tips for those seeking to uncover the secrets of the past.
Key Points
- Understanding the cultural context of Arizona's prehistoric civilizations
- Identifying and respecting protected archaeological sites
- Recognizing the importance of preserving archaeological artifacts
- Utilizing online resources and archaeological databases
- Collaborating with professional archaeologists and local communities
Understanding Arizona’s Prehistoric Cultures
Before embarking on an archaeological adventure in Arizona, it is essential to understand the cultural context of the state’s prehistoric civilizations. The Ancestral Puebloans, Hohokam, and Mogollon are just a few of the many cultures that have left their mark on the region. Each of these cultures developed unique technologies, artistic traditions, and spiritual practices, which are reflected in the archaeological record. By gaining a deeper understanding of these cultures, archaeology enthusiasts can better appreciate the significance of the sites they visit and the artifacts they encounter.
Protected Archaeological Sites
Arizona is home to numerous protected archaeological sites, which are safeguarded by federal and state laws. These sites are protected to preserve the integrity of the archaeological record and to ensure that future generations can learn from and appreciate the cultural heritage of the region. When visiting protected sites, it is crucial to respect the rules and regulations in place, which may include restrictions on photography, camping, or collecting artifacts. Remember, it is essential to leave artifacts in their original context, as removing them can damage the site and compromise the integrity of the archaeological record.
| Cultural Group | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|
| Ancestral Puebloans | Multi-story dwellings, intricate pottery, and sophisticated irrigation systems |
| Hohokam | Extensive canal systems, shell jewelry, and ritual ball courts |
| Mogollon | Distinctive pottery styles, pit houses, and early evidence of maize cultivation |

Preserving Archaeological Artifacts

Archaeological artifacts are a window into the past, providing valuable insights into the lives of prehistoric cultures. However, these artifacts are fragile and require careful handling to ensure their preservation. When encountering artifacts, it is essential to avoid touching or handling them, as the oils from human skin can damage the artifact’s surface. Instead, observe and photograph the artifact, taking note of its context and any surrounding features. By preserving artifacts in their original context, we can ensure that future generations can learn from and appreciate the cultural heritage of Arizona.
Online Resources and Archaeological Databases
The internet has revolutionized the field of archaeology, providing access to a wealth of information and resources. Online databases, such as the Arizona State Museum’s Arizona Archaeological Site Database, offer a wealth of information on archaeological sites, including site descriptions, photographs, and artifact collections. Additionally, online resources, such as the National Park Service’s Archaeology Program, provide valuable information on archaeological preservation, cultural resource management, and community engagement.
Collaborating with Professional Archaeologists and Local Communities
Finally, collaborating with professional archaeologists and local communities is essential for a comprehensive understanding of Arizona’s archaeological heritage. By working together, archaeology enthusiasts can gain a deeper appreciation for the cultural context of the sites they visit and the artifacts they encounter. Additionally, collaboration can help ensure that archaeological sites are protected and preserved for future generations, while also promoting a greater understanding and appreciation of Arizona’s rich cultural heritage.
What are some essential skills for Arizona archaeology enthusiasts?
+Essential skills for Arizona archaeology enthusiasts include a strong understanding of the cultural context of prehistoric civilizations, the ability to identify and respect protected archaeological sites, and knowledge of artifact preservation techniques.
How can I get involved in Arizona archaeology projects?
+Getting involved in Arizona archaeology projects can be as simple as volunteering for a local archaeological society or participating in a community-based excavation. Additionally, many universities and museums offer archaeological field schools and internships, which provide hands-on experience and training in archaeological techniques.
What are some of the most significant archaeological discoveries in Arizona?
+Some of the most significant archaeological discoveries in Arizona include the discovery of the Hohokam canal system, the excavation of the Ancestral Puebloan cliff dwellings at Montezuma Castle, and the uncovering of the Mogollon pit houses at the Gila Cliff Dwellings.
In conclusion, Arizona archaeology is a rich and fascinating field, offering a unique glimpse into the lives of prehistoric cultures. By following these five essential tips, archaeology enthusiasts can deepen their understanding of the state’s cultural heritage, while also contributing to the preservation and protection of Arizona’s archaeological treasures. Whether you are a seasoned archaeologist or just starting to explore the world of Arizona archaeology, remember to always respect the cultural context of the sites you visit and the artifacts you encounter, and to collaborate with professional archaeologists and local communities to ensure the long-term preservation of these valuable cultural resources.