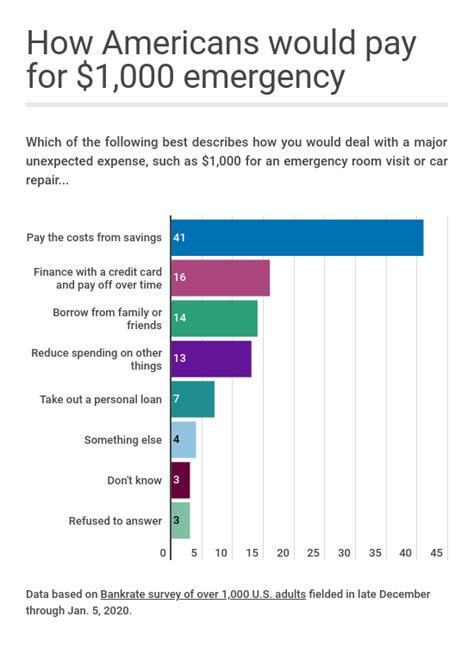
When it comes to understanding and working with data, two fundamental concepts that are often encountered are the average and the weighted average. While these terms are frequently used in various fields, including finance, economics, and statistics, they are not always well understood, even by professionals. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, applications, and differences between the average and the weighted average, providing a comprehensive overview of these essential statistical measures.
Understanding the Average
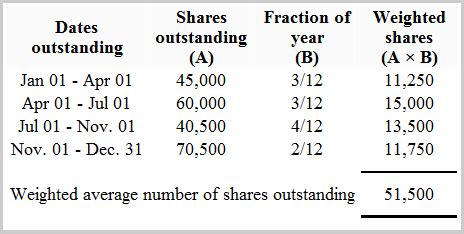
The average, also known as the mean, is a statistical measure that calculates the central tendency of a dataset. It is computed by summing up all the values in the dataset and then dividing by the number of values. The formula for calculating the average is straightforward: Average = (Sum of all values) / (Number of values). For instance, if we have a dataset of exam scores: 80, 70, 90, 85, the average score would be (80 + 70 + 90 + 85) / 4 = 325 / 4 = 81.25. The average provides a general idea of the data’s central tendency, making it easier to compare different datasets or to understand the performance of a group.
Calculating the Average: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the average involves a simple, two-step process. First, add up all the numbers in your dataset. This will give you the total sum of your data. Second, divide this sum by the number of items in your dataset. This will yield the average. It’s essential to ensure that all values are included in the sum and that the number of values is correctly counted to avoid errors in calculation.
| Dataset Values | Sum of Values | Number of Values | Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80, 70, 90, 85 | 325 | 4 | 81.25 |
Understanding the Weighted Average
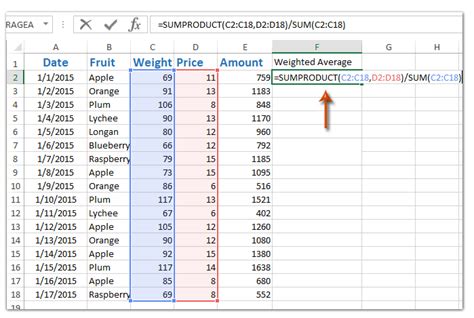
A weighted average, on the other hand, is a measure of central tendency that takes into account the relative importance or weight of each value in the dataset. Unlike the average, which gives equal weight to each value, the weighted average assigns different weights to different values based on their significance or frequency. The formula for the weighted average is: Weighted Average = (Sum of each value multiplied by its weight) / (Sum of all weights). For example, if we have two investments, one with a return of 10% and a weight of 60% (because it constitutes 60% of the total portfolio), and another with a return of 20% and a weight of 40%, the weighted average return would be (0.10 * 0.60 + 0.20 * 0.40) / (0.60 + 0.40) = (0.06 + 0.08) / 1 = 0.14 or 14%.
Calculating the Weighted Average: A Practical Approach
Calculating the weighted average involves a slightly more complex process than the average. First, multiply each value by its corresponding weight. Then, sum up these products. Afterward, sum up all the weights. Finally, divide the sum of the products by the sum of the weights to obtain the weighted average. This method ensures that the calculation reflects the proportional importance of each value in the dataset.
| Value | Weight | Product |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | 60% | 6% |
| 20% | 40% | 8% |
| 14% |
Key Points
- The average gives equal weight to all values in a dataset, providing a general measure of central tendency.
- The weighted average takes into account the relative importance of each value, making it more representative of datasets with varying significance or frequency.
- Calculating the average involves summing all values and dividing by the number of values, while the weighted average requires multiplying each value by its weight, summing these products, and then dividing by the sum of the weights.
- Both measures are crucial in statistics and data analysis, with the choice between them depending on the nature of the data and the purpose of the analysis.
- Understanding and correctly applying these measures can significantly impact the interpretation and decision-making based on data analysis.
Comparing Average and Weighted Average: Applications and Implications
The choice between using the average and the weighted average depends on the context and the characteristics of the data. The average is useful for datasets where all values have equal importance or when the dataset is small and evenly distributed. However, in scenarios where the data points have different levels of significance or when dealing with large datasets with outliers, the weighted average provides a more accurate representation of the central tendency. For instance, in finance, the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is used to calculate the average cost of capital, considering the proportion of debt and equity in a company’s capital structure.
Real-World Applications: A Deeper Dive
In real-world applications, both the average and the weighted average have their places. For example, in education, the average score of a class might be used to assess overall performance, while in investment analysis, the weighted average return of a portfolio, considering the weights of different assets, provides a more nuanced view of performance. Understanding when to apply each measure is crucial for accurate analysis and informed decision-making.
What is the primary difference between the average and the weighted average?
+The primary difference lies in how each value in the dataset is treated. The average gives equal weight to all values, while the weighted average assigns different weights based on the significance or frequency of each value.
When should I use the weighted average instead of the average?
+Use the weighted average when the values in your dataset have different levels of importance or frequency. This ensures that your calculation reflects the true nature of your data, providing a more accurate representation of central tendency.
Can the weighted average be used in all types of data analysis?
+No, the weighted average is most appropriately used when there is a clear rationale for assigning different weights to different values. In datasets where all values are of equal importance, the average is sufficient and more straightforward to calculate.
Meta Description: Understand the difference between average and weighted average, including their calculations, applications, and implications in data analysis, with a comprehensive guide and examples.