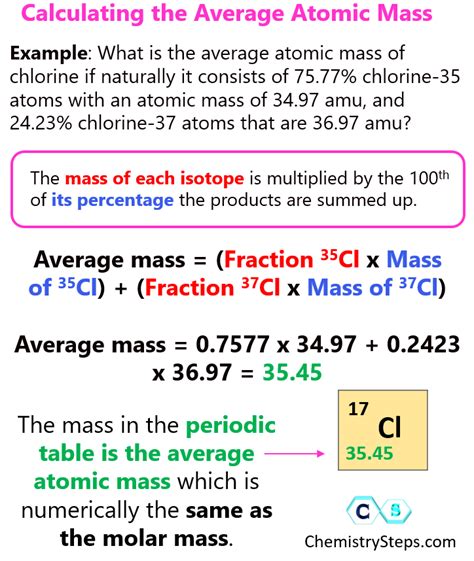
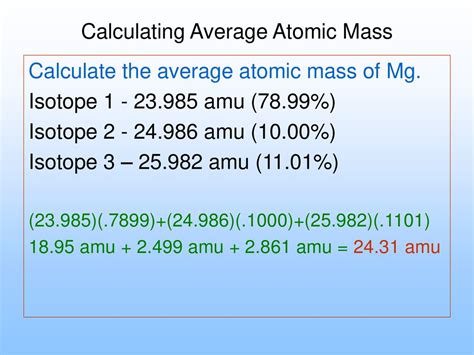
The concept of average atomic mass is crucial in chemistry, as it helps in understanding the properties and behavior of elements. The average atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes. To calculate the average atomic mass, we use the formula: Average Atomic Mass = (Mass of Isotope 1 x Abundance of Isotope 1) + (Mass of Isotope 2 x Abundance of Isotope 2) +... + (Mass of Isotope n x Abundance of Isotope n). This formula is essential in determining the average atomic mass of an element, which is then used in various chemical calculations and applications.
Key Points
- The average atomic mass is the weighted average of the masses of an element's naturally occurring isotopes.
- The formula for calculating average atomic mass involves multiplying the mass of each isotope by its abundance and summing these products.
- Isotopic abundance is usually expressed as a percentage or a decimal fraction of the total abundance of the element.
- Accurate calculation of average atomic mass is critical for chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and understanding elemental properties.
- Changes in isotopic abundance due to natural variations or artificial enrichment can affect the average atomic mass of an element.
Understanding Isotopes and Their Abundance
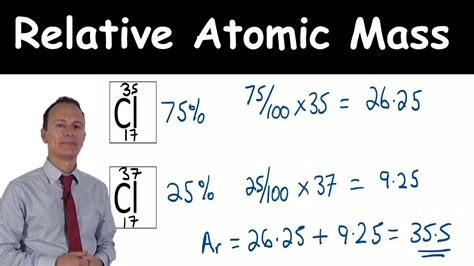
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, leading to variations in mass. The abundance of an isotope refers to its percentage or fraction of the total amount of the element found in nature. The most common isotopes and their abundances are usually determined through mass spectrometry. For example, chlorine has two main isotopes: chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, with abundances of approximately 75.78% and 24.22%, respectively.
Calculating Average Atomic Mass
To illustrate the calculation, let’s consider chlorine. The average atomic mass of chlorine can be calculated as follows: Average Atomic Mass = (35.00 x 0.7578) + (36.97 x 0.2422). Performing the calculation yields: Average Atomic Mass = 26.4961 + 8.9533 = 35.4494, which is typically rounded to 35.45. This value is the average atomic mass of chlorine that you would find on the periodic table.
| Isotope | Mass (u) | Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorine-35 | 34.9689 | 75.78 |
| Chlorine-37 | 36.9659 | 24.22 |
Applications of Average Atomic Mass
The average atomic mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry, with applications in stoichiometry, the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It is used to calculate the number of moles of a substance, which is critical in determining the amounts of reactants needed and products formed in a chemical reaction. Additionally, the average atomic mass is essential in understanding the physical and chemical properties of elements and compounds, such as density and melting point.
Stoichiometry and Chemical Reactions
In stoichiometry, the average atomic mass is used to convert between the mass of a substance and the number of moles. The mole is a unit of amount of substance that contains as many particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon-12. This relationship is expressed through the molar mass, which for elements is the average atomic mass expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). For compounds, the molar mass is the sum of the average atomic masses of the constituent atoms.
For instance, to find the mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) that contains 1 mole of chlorine, you would use the average atomic masses of sodium (22.99 g/mol) and chlorine (35.45 g/mol) to calculate the molar mass of NaCl, which is 58.44 g/mol. This calculation is essential in preparing solutions and reactants for chemical experiments.
What is the significance of average atomic mass in chemistry?
+The average atomic mass is significant because it allows chemists to calculate the amounts of substances involved in chemical reactions, understand the properties of elements and compounds, and determine the composition of substances.
How does the abundance of isotopes affect the average atomic mass?
+The abundance of isotopes directly affects the average atomic mass, as the formula for calculating it involves multiplying the mass of each isotope by its abundance. Changes in isotopic abundance can result in variations in the average atomic mass of an element.
What is the difference between atomic mass and average atomic mass?
+Atomic mass refers to the mass of a single atom of an element, while average atomic mass is the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element. The average atomic mass takes into account the different masses and abundances of isotopes, providing a more representative value for the element.
In conclusion, the average atomic mass formula is a fundamental tool in chemistry, allowing for the calculation of the weighted average of the masses of an element’s naturally occurring isotopes. Understanding and applying this concept are essential for accurate chemical calculations, stoichiometry, and comprehension of elemental properties. As research and applications in chemistry continue to evolve, the importance of average atomic mass in both theoretical and practical aspects of the field remains unabated.