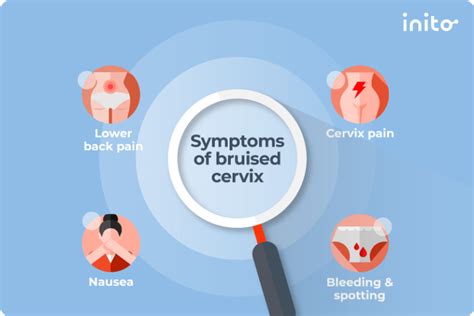
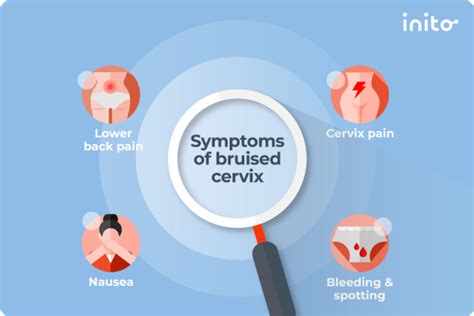
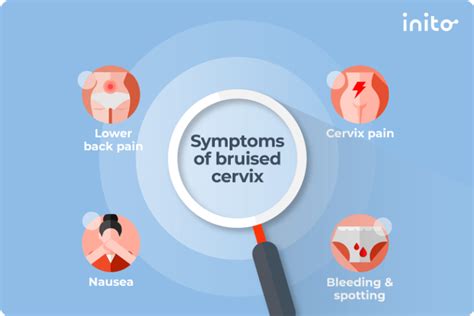
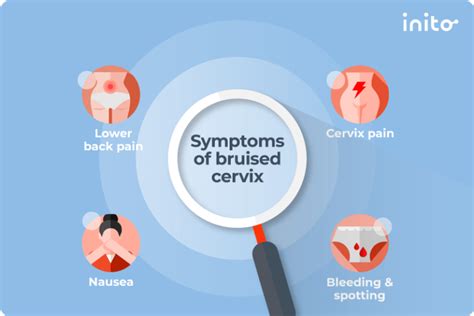
A bruised cervix, also known as a cervical contusion, can occur due to various reasons such as sexual intercourse, childbirth, or medical procedures. The cervix is a sensitive and vital part of the female reproductive system, and any injury to this area can cause discomfort and concern. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of a bruised cervix to seek proper medical attention and prevent potential complications.
The symptoms of a bruised cervix can vary in severity and may include mild to severe pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or vagina. Women may experience pain during or after sexual intercourse, which can be a sign of a bruised cervix. Other symptoms may include spotting or light bleeding, which can be caused by the bruising or injury to the cervical tissue. In some cases, women may also experience discomfort or pain during urination or bowel movements.
Key Points
- A bruised cervix can occur due to various reasons, including sexual intercourse, childbirth, or medical procedures.
- Symptoms may include mild to severe pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or vagina.
- Pain during or after sexual intercourse can be a sign of a bruised cervix.
- Spotting or light bleeding may occur due to the bruising or injury to the cervical tissue.
- Discomfort or pain during urination or bowel movements can also be a symptom of a bruised cervix.
Causes and Risk Factors
A bruised cervix can occur due to various causes, including sexual intercourse, childbirth, or medical procedures. Sexual intercourse can cause bruising or injury to the cervix, especially if it is vigorous or if the woman is not adequately lubricated. Childbirth can also cause bruising or injury to the cervix, particularly if the delivery is difficult or if there are any complications. Medical procedures, such as a cervical biopsy or colposcopy, can also cause bruising or injury to the cervix.
There are also several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of a bruised cervix. These include a history of cervical trauma, cervical surgery, or cervical cancer. Women who have a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or other pelvic infections may also be at increased risk of a bruised cervix. Additionally, women who engage in vigorous or rough sexual activity may be more likely to experience a bruised cervix.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing a bruised cervix can be challenging, as the symptoms may be similar to those of other conditions, such as a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, to check for any signs of bruising or injury to the cervix. They may also take a medical history to determine the cause of the symptoms.
Treatment for a bruised cervix typically involves managing the symptoms and allowing the cervix to heal. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain and discomfort. Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen may also help to reduce pain and discomfort. In some cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection or promote healing.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain | Mild to severe pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or vagina |
| Bleeding | Spotting or light bleeding due to bruising or injury to the cervical tissue |
| Discomfort | Discomfort or pain during urination or bowel movements |
Prevention and Self-Care
Preventing a bruised cervix involves taking steps to reduce the risk of injury or bruising to the cervix. Practicing safe sex, such as using lubricants and avoiding vigorous or rough activity, can help to reduce the risk of a bruised cervix. Getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help to identify any potential issues early on.
Self-care is also essential for promoting healing and reducing symptoms. Getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and avoiding strenuous activity can help to promote healing and reduce discomfort. Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen may also help to reduce pain and discomfort.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
If left untreated, a bruised cervix can lead to complications, such as infection or scarring. In rare cases, a bruised cervix can also increase the risk of cervical cancer. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time to prevent potential complications.
In some cases, a bruised cervix can also have long-term effects, such as chronic pain or discomfort. Women who experience a bruised cervix may also be at increased risk of future cervical trauma or injury. Practicing safe sex and getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help to reduce the risk of future complications.
What are the symptoms of a bruised cervix?
+The symptoms of a bruised cervix can include mild to severe pain in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or vagina, spotting or light bleeding, and discomfort or pain during urination or bowel movements.
How is a bruised cervix diagnosed?
+A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, to check for any signs of bruising or injury to the cervix. They may also take a medical history to determine the cause of the symptoms.
What is the treatment for a bruised cervix?
+Treatment for a bruised cervix typically involves managing the symptoms and allowing the cervix to heal. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain and discomfort. Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen may also help to reduce pain and discomfort.
Meta description: Learn about the symptoms, causes, and treatment of a bruised cervix, and how to prevent and manage this condition. Get expert advice and insights on promoting healing and reducing discomfort. (149 characters)